What Is A Calorimeter & What Are Its Limitations?

Chemists often need to know how much heat energy a particular reaction releases or absorbs. This measurement helps them understand more about why the reaction occurs and helps them make useful predictions. Calorimeters are instruments that measure the amount of heat released or absorbed by the contents during a reaction. It's easy to make a simple calorimeter, but the instruments used in labs are typically more precise.

TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read)
Calorimeters let you measure the amount of heat in a reaction. Their main limitations are losing heat to the environment and uneven heating.
The Functions of a Calorimeter
Basically, a calorimeter measures the change in temperature of the calorimeter and its contents. After the calorimeter calibration, the chemist will already have a number called the calorimeter constant, which shows how much the temperature of the calorimeter changes per amount of heat added. Using this information and the mass of the reactants, the chemist can determine how much heat gets released or absorbed. It's important that the calorimeter minimizes the rate of heat loss to the outside, since rapid heat loss to the surrounding air would skew the results.
Different Types of Calorimeters
It's easy to make a simple calorimeter yourself. You need two Styrofoam coffee cups, a thermometer or a lid. This coffee-cup calorimeter is surprisingly reliable and thus is a common feature of undergraduate chemistry labs. Physical chemistry laboratories have more sophisticated instruments such as "bomb calorimeters." In these devices, the reactants are in a sealed chamber called the bomb. After an electrical spark ignites them, the change in temperature helps determine the heat lost or gained.
Calibration of a Calorimeter
To calibrate a calorimeter, you can use a process that transfers a known amount of heat such as measuring the temperature of some hot and cold water. For example, you can mix cold and hot water in your coffee-cup calorimeter. Next, you measure the temperature over time and use linear regression to calculate the "final temperature" of the calorimeter and its contents. Subtracting the heat gained by the cold water from the heat lost by the hot water yields the heat gained by the calorimeter. Dividing this figure by the temperature change of the calorimeter gives its calorimeter constant, which you can use in other experiments.
Limitations of Calorimetry
No calorimeter is perfect because it can lose heat to its surroundings. Although bomb calorimeters in laboratories have insulation to minimize these loses, it's impossible to stop all heat loss. Moreover, the reactants in the calorimeter may not be well-mixed, which leads to uneven heating and another possible source of error in your measurements.
Aside from possible sources of error, another limitation involves the kinds of reactions you can study. For example, you may want to know how the decomposition of TNT releases heat. This kind of reaction would be impossible to study in a coffee-cup calorimeter and might not even be practical in a bomb calorimeter. Alternatively, a reaction may take place very slowly such as the oxidation of iron to form rust. This kind of reaction would be very difficult to study with a calorimeter.
- Calorimetry -Water equivalent Calorimetry
- Calorimetry
Cite This Article
Brennan, John. "What Is A Calorimeter & What Are Its Limitations?" sciencing.com , https://www.sciencing.com/calorimeter-its-limitations-8290898/. 27 April 2018.
Brennan, John. (2018, April 27). What Is A Calorimeter & What Are Its Limitations?. sciencing.com . Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/calorimeter-its-limitations-8290898/
Brennan, John. What Is A Calorimeter & What Are Its Limitations? last modified March 24, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/calorimeter-its-limitations-8290898/
Recommended
Sage-Advices
Collection of recommendatory guides
What are the possible sources of error in a calorimetry experiment?
Table of Contents
- 1 What are the possible sources of error in a calorimetry experiment?
- 2 What three factors affect the heat transfer that is necessary to change an object’s temperature?
- 3 What are sources of error in an experiment?
- 4 What factors affect calorimetry?
- 5 What are the limitations in using a coffee cup calorimeter?
- 6 Which is the most affecting factor of heat?
- 7 How to avoid sources of errors in physics?
- 8 How is the quantity of heat absorbed by the calorimeter determined?
Sources of error Likely sources of experimental error in this experiment include improper mixing, the placement of the thermometer bulb onto slowly dissolving solids, incorrect reading of the thermometer, not enough thermometer readings, and spillages.
What three factors affect the heat transfer that is necessary to change an object’s temperature?
Experiments show that the transferred heat depends on three factors—the change in temperature, the mass of the system, and the substance and phase of the substance.
What are the assumptions in performing coffee cup calorimetry calculations?
ASSUMPTIONS IN CALORIMETRY 1. no heat is transferred between the calorimeter and the outside environment. 2. any heat absorbed or released by the calorimeter materials is negligible.
What two factors affect specific heat?
This quantity is known as the specific heat capacity (or simply, the specific heat), which is the heat capacity per unit mass of a material . Experiments show that the transferred heat depends on three factors: (1) The change in temperature, (2) the mass of the system, and (3) the substance and phase of the substance .
What are sources of error in an experiment?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results. Instrumental error happens when the instruments being used are inaccurate, such as a balance that does not work (SF Fig.
What factors affect calorimetry?
They include:
- the volume of water used.
- the starting temperature of the water.
- the temperature increase.
- the distance of the flame from the calorimeter.
What three factors affect the heat transfer that is necessary to change an object’s temperature quizlet?
CQ: What three factors affect the heat transfer that is necessary to change an object’s temperature? Temperature change depends on (1) mass of the substance, (2) the make-up of the substance, and (3) the phase of the substance.
What three factors do you need to know in order to calculate the heat change?
Experiments show that the transferred heat depends on three factors: (1) The change in temperature, (2) the mass of the system, and (3) the substance and phase of the substance. The last two factors are encapsulated in the value of the specific heat.
What are the limitations in using a coffee cup calorimeter?
A coffee cup calorimeter is great for measuring heat flow in a chemical solution, but it can’t be used for reactions, which involve gases since they would escape from the cup. The coffee cup calorimeter can’t be used for high temperature reactions either, since these would melt the cup.
Which is the most affecting factor of heat?
Here are the factors that affect the rate of conduction:
- Temperature difference. The greater the difference in temperature between the two ends of the bar, the greater the rate of thermal energy transfer, so more heat is transferred.
- Cross-sectional area.
- Length (distance heat must travel).
Why are there errors in the enthalpy experiment?
When to include sources of errors in a lab report?
How to avoid sources of errors in physics?
How is the quantity of heat absorbed by the calorimeter determined.
Begin typing your search term above and press enter to search. Press ESC to cancel.
Privacy Overview

Calorimetry- Definition, Principle, Types, Application, and Limitations
Calorimetry is the science of measuring the heat exchange between a system and its surroundings to calculate the change in energy of the system. The word Calorimetry is derived from the Latin calor (“heat”) and Greek metron (“measure”), and so means “measuring heat.”
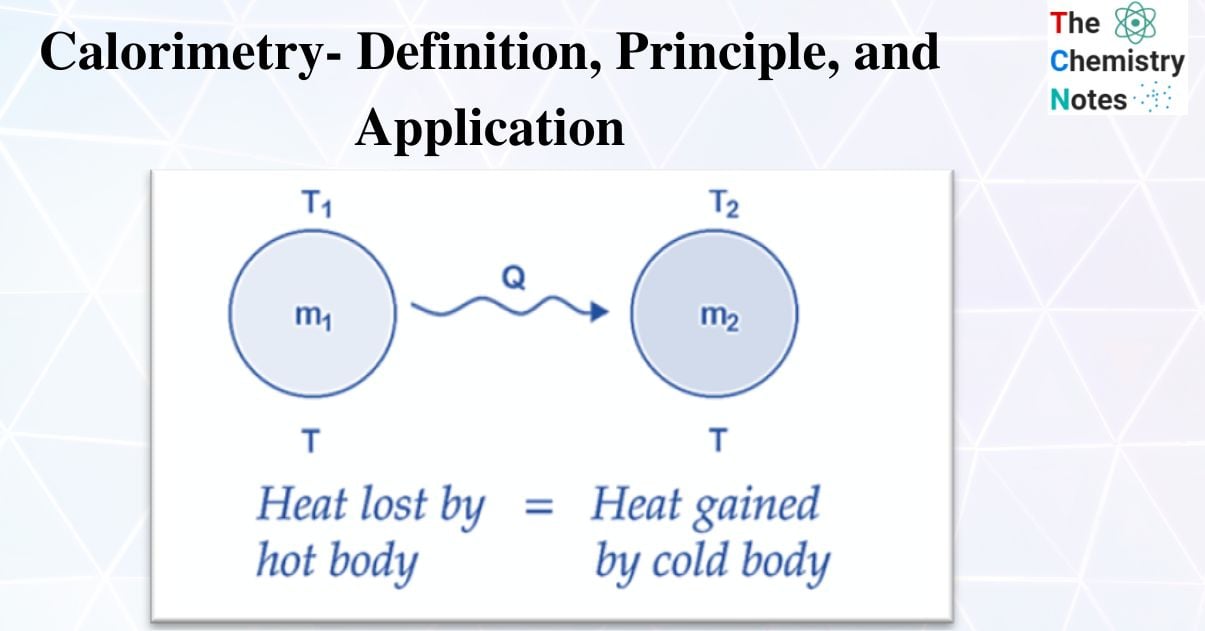
Table of Contents
Interesting Science Videos
What is Calorimetry?
Calorimetry is a branch of science concerned with measuring a body’s state in terms of thermal features to investigate its physical and chemical changes.
To determine the enthalpy, stability, heat capacity, and other thermochemical quantities, calorimetry is widely used. It is the technique of calculating how much heat is produced or absorbed while a chemical reaction occurs. It is possible to tell whether a reaction is exothermic (releases heat) or endothermic by knowing the change in heat (absorbs heat). Calorimetry also has a significant impact on daily living since it regulates human metabolic rates, which helps to keep things like body temperature stable.
A calorimeter is used to perform calorimetry.
Principle of Calorimetry
When a hot body and a cold body are combined, the heat lost by the hot body and the heat acquired by the cold body are equal.
Heat gain = Heat lost
i.e., the rule of conservation of thermal energy governs the principle of calorimetry.
Using the following formula, the heat transfer in a system is determined.
q = measure of heat transfer
m = mass of the body
c = specific heat of the body
Δt = change in the temperature
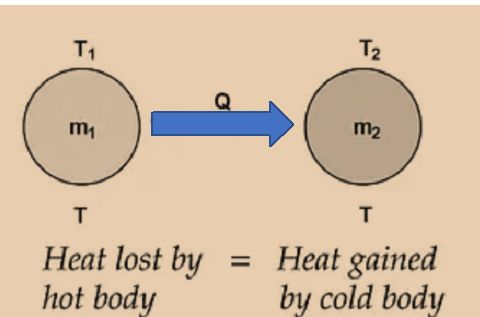
If two substances having masses m 1 and m 2 , specific heats c 1 and c 2 at temperatures T 1 and T 2 (T 1 >T 2 ) are mixed.
Hence, temperature of mixture at equilibrium is T mix .
m 1 c 1 (T 1 – T mix ) = m 2 c 2 (T mix – T 2 )
The exchange of heat occurs when two bodies with different surface temperatures come into thermal contact. At higher temperatures, the body emits heat, and at lower temperatures, the body receives heat. This back-and-forth will continue until they reach thermal equilibrium. Heat is released by the body at higher temperatures, whereas heat is absorbed by the body at lower temperatures. The concept of heat energy as a measurement of change in body temperature evolved much later, after a series of studies were carried out using calorimeters.
Assumptions in Calorimetry
- There is no heat transfer between the calorimeter and the surrounding environment.
- No heat is absorbed or released by the calorimeter materials.
- Pure water has the same density and specific heat capacity as a dilute aqueous solution.
Types of Calorimetry
Direct calorimetry: It detects the heat change of a chemical reaction by directly measuring the temperature change it creates.
Indirect Calorimetry: It is a way of evaluating an organism’s heat change by monitoring either its intake of oxygen or its production of carbon dioxide or nitrogen.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry: Differential scanning calorimetry is a technique for determining the amount of energy required to elevate the temperatures of a sample and a reference substance by the same amount. It is frequently used to determine the specific heat capacity of different proteins and other biological components, as well as to explore their reaction to heating.
These techniques are most applicable in biology for the study of heat transfer in organisms.
Applications of Calorimetry
Calorimetry, as a thermal analysis technique, has a broad range of applications that include not only studying the thermal characterisation (e.g. melting temperature, denaturation temperature, and enthalpy change) of small and large drug molecules, but also characterisation of fuel, metals, and oils.
- It is used to calculate the enthalpy changes that occur during a reaction.
- It is frequently used to investigate pharmacological and biological molecule thermal properties, such as denaturation temperature.
- This is also used to analyze polymers, allowing us to determine parameters such as crystallisation temperature.
- Generally used in food laboratories to determine the calorie content of foods.
- It is also used to determine the thermal characteristics of medicines, proteins, and other biological substances.
Calculating Enthalpy change using Calorimetry
By using a method calorimetry, we are able to determine the enthalpy change of various reactions.
A polystyrene cup can serve as a calorimeter.
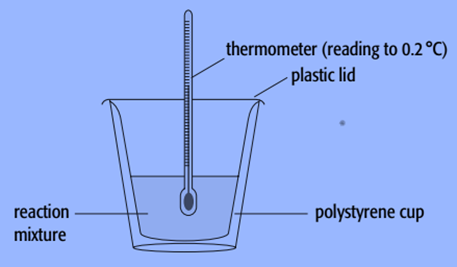
We employ known amounts of reactants and known volumes of liquids while doing experiments with calorimeters. As the reaction takes place, we also track the liquid’s temperature change in the calorimeter.
The energy is transferred as heat (the enthalpy change) is given by the relationship:
where: ΔH is the enthalpy change, in J m is the mass of water, in g c is the specific heat capacity, in J g –1 °C –1 ΔT is the temperature change, in °C
Steps to determine enthalpy of the reaction
- A polystyrene cup can be used as a calorimeter to determine the enthalpy change of a sodium hydroxide solution. To ensure that all of the solute dissolves, we employ known amounts of solvent and solute with an excess of the solvent.
- Weigh an empty polystyrene cup first.
- Fill the cup with 100cm 3 of water, then weigh the contents together.
- Use a thermometer to measure the water’s constant temperature, preferably to within 0.2 °C.
- Add a few sodium hydroxide pellets that have been dried-stored.
- Continue to stir the mixture while using a thermometer, and record the temperature at regular intervals, such as every 20 seconds.
- After the maximum temperature has been attained, continue to record the temperature for a further five minutes.
- Weigh the cup and everything inside it to determine how much sodium hydroxide dissolved.
Enthalpy change (J) of Sodium Hydroxide;
= – mass of water (g) × specific heat capacity (Jg –1 °C –1 )× temperature change (°C)
Calculating the Enthalpy Change of Combustion
By burning a known mass of material and utilizing the heat generated to raise the temperature of a known mass of water, we may determine the enthalpy change of combustion. A metal calorimeter and a spirit burner are the tools used for this.
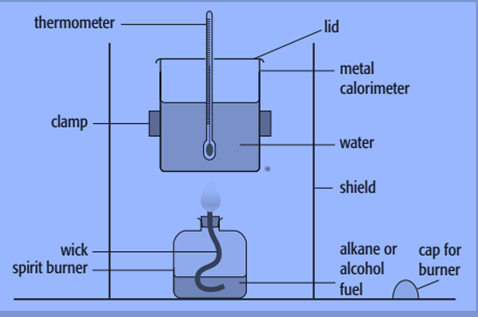
Steps to determine enthalpy of the combustion of propan-1-ol
- Weigh the propan-1-ol containing spirit burner. When the burner is not lit, the cap must be maintained to prevent fuel evaporation.
- Fill up the calorimeter with 100 cm 3 (100g) of water. This needs to be balanced out for improved accuracy.
- Stir the water and use a to take a temperature reading and the reading must be accurate to at least 0.1 °C.
- Position the spirit burner underneath the thermometer and light the wick after removing the cap. The size of the wick should have been modified in the past so that the wick’s substance doesn’t burn, and the flame barely reaches the calorimeter’s base.
- Continue agitating the water while using a thermometer until there is a 10 °C spike in temperature. Record this temperature.
- Remove the spirit burner, place the cap on it and reweigh it.
Using the relationship ΔH = –mcΔT (mass of water × specific heat capacity of water × temperature change)
Calculate the energy released by burning propan-1-ol.
Calorimetry can be quite difficult. This is because there are numerous variables at work during calorimetry, and it is hard to correctly monitor all of them.
- Energy may be transferred to or away from the environment, typically in the form of heat loss.
- We frequently presume that the used solution has the density and specific heat capacity of pure water, although this may not always be the case.
- The reaction might not be fully complete.
- The apparatus could be heated instead of the solution by some of the heat energy generated.
- Possible evaporation of some of the fuel
- Atkins, Peter and de Paula, Julio; Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences, United States, 2006.Katherine Hurley
- https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_Textbook_Maps/Supplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/Thermodynamics/Calorimetry
- https://www.studysmarter.us/explanations/chemistry/physical-chemistry/calorimetry/
- https://byjus.com/physics/principle-of-calorimetry/
- Bryan, G.H. (1907). Thermodynamics. An Introductory Treatise dealing mainly with First Principles and their Direct Applications , B.G. Tuebner, Leipzig.
- Crawford, F.H. (1963). Heat, Thermodynamics, and Statistical Physics , Rupert Hart-Davis, London, Harcourt, Brace, & World.
About Author
Jyoti Bashyal
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What are the limitations of calorimetry?
Well, honey, calorimetry may be great at measuring heat flow in a closed system, but it ain't no mind reader. It can't tell you about any chemical reactions happening outside of that system, so don't go expecting it to spill all the tea. Plus, it can be a bit finicky with certain types of reactions, so don't be surprised if it throws a hissy fit every now and then. Just remember, it's a tool, not a miracle worker.
Limitations of calorimetry include difficulty in determining the heat capacity of the sample accurately, the need for a well-insulated system to prevent heat loss, and limitations in the sensitivity and precision of the instruments used to measure heat flow. Additionally, the assumption of constant pressure conditions may not hold true in all situations.
The primary limit of calorimetry experiments is keeping the system closed. The heat energy that the experiment is trying to capture can easily be lost to the environment and then be immeasurable.
Most high grade calorimetry experiments employ advanced bomb calorimeters that ensure complete combustion of the sample. They also use a large amount of water as a heat sink with plenty of insulation to keep the energy from getting out. A stir rod keeps the temperature of the water homogeneous and ensures accurate results
Add your answer:
Chemistry calorimetry help?
Calorimetry measures the heat of chemical reactions and physical changes. The steps involved in solving calorimetry problems are as follows: The heat of the reaction is less than the amount of heat measured by the calometer. The heat gained by the calometer is the capacity of the calorimeter and temperature change of the sample undergoing the chemical and/or physical change. The combination of the two are calculated to heat reaction and given temperature change.
What is the unknown metal in the AP Chemistry Heat Effects and Calorimetry Lab?
that is supposed to be unknown until you figure it out.

What is meant by calorimetry?
Calorimetry is the science of measuring heat changes in a chemical or physical process. It involves using a calorimeter to measure the heat released or absorbed during a reaction to determine the energy change. This information is crucial for understanding the thermodynamic properties of substances and reactions.
What type of reaction is used in calorimetry?
Calorimetry typically involves measuring heat changes in a system during a chemical reaction, making it an example of an exothermic or endothermic reaction. These reactions release or absorb energy in the form of heat, which can be quantified to determine the heat capacity or enthalpy change of the reaction.
What is a hypothesis statement that can be used to explain that a calorimetry can be used to detect the amount o energy stored in the chemical bonds of foods?
A hypothesis statement could be: "Calorimetry can be used to detect the amount of energy stored in the chemical bonds of foods, as the heat produced during the combustion of food can be measured and equated to the energy content. By conducting calorimetric experiments and analyzing the heat released, we can determine the energy content of various foods and understand the relationship between the chemical bonds in the food and the energy it holds."
What is a calorimetry?
A calorimetry is a wide headband which covers the ears, suitable for wearing on cold days.
What is the relationship between heat and calorimetry?
Calorimetry is the scientific measurement of heat transfer during physical or chemical processes. It involves measuring the heat absorbed or released by a substance through temperature changes. Calorimetry is used to study the energetics of reactions and determine the specific heat capacity of substances.
What has the author J B Klumpp written?
J. B. Klumpp has written: 'Report of Committee on calorimetry' -- subject(s): Gas, Calorimetry
How does direct calorimetry and indirect calorimetry work?
Direct calorimetry measures energy expenditure by directly assessing heat production using a calorimeter. Indirect calorimetry estimates energy expenditure by measuring oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production, which are then used to calculate energy expenditure based on known respiratory exchange ratios and energy equivalents of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What did zuntz and hagemann develop?
Direct Calorimetry
What has the author Estal Dale West written?
Estal Dale West has written: 'Data analysis for isoperibol laser calorimetry' -- subject(s): Calorimetry, Lasers
Does calorimetry measure alcohol intake?
Calorimetry measures heat energy released or absorbed during a chemical reaction or process, not alcohol intake. Blood alcohol concentration (BAC) tests are typically used to measure alcohol intake.
What has the author Hugh L Callendar written?
Hugh L. Callendar has written: 'Continuous electrical calorimetry' -- subject(s): Calorimetry, Electric measurements, Temperature measurements
What is the difference between direct and indirect calorimetry?
Direct calorimetry measures heat production using a calorimeter, while indirect calorimetry estimates energy expenditure by measuring oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production. Direct calorimetry is more accurate but less practical, while indirect calorimetry is widely used in clinical and research settings.
Where can you find Priniciples of Calorimetry completed labs on the internet?
The words calorimeter calorimetry and calorie are all derived from the latin word calor.
Yes, calor is the Latin word for heat.Calorimeter and calorimetry are connected with measuring heat, and a calorie is a unit of (heat) energy.
On what principle does calorimetry depends?
Calorimetry depends on the principle of conservation of energy, which states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transferred or converted from one form to another. In calorimetry, heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction is measured to determine the change in energy of the system.
Top Categories


what is calorimetry limitations?
Expert verified solution.
The limitations of calorimetry include heat loss during combustion, assumptions about pressure dependence on volume and temperature, and non-ideal behavior of certain materials
Explanation
Calorimetry is a technique used to measure the amount of heat involved in chemical reactions or physical changes. However, it has several limitations that can affect the accuracy and reliability of the measurements
Heat Loss During Combustion One significant limitation is that during combustion reactions, some heat invariably escapes from the calorimeter. This heat loss can lead to an underestimation of the total heat produced. For instance, in reactions that release a small amount of heat, such as the rusting of iron, the heat that escapes can make it challenging to obtain accurate measurements. The formula for calculating the heat released can be expressed as:
$$q = m \cdot C \cdot \Delta T$$ q = m ⋅ C ⋅ Δ T
where $$q$$ q is the heat absorbed, $$m$$ m is the mass of the substance, $$C$$ C is the specific heat capacity, and $$\Delta T$$ Δ T is the change in temperature. If heat escapes, $$q$$ q will be lower than the actual heat produced
Assumptions of Classical Calorimetry Another limitation arises from the assumptions made in classical calorimetry. It is commonly assumed that the pressure of the calorimeter material is solely dependent on volume and temperature. However, this assumption fails during phase transitions (e.g., melting or boiling), where the relationship can change significantly
Non-ideal Behavior of Materials Certain materials do not adhere to the classical relationships expected in calorimetry. For example, some substances may exhibit non-ideal behavior under specific conditions, leading to discrepancies in the expected heat measurements
In: Chemistry
Part 1: Explain possible limitations of a calorimeter, and how you can overcome these limitations. Part...
Part 1: Explain possible limitations of a calorimeter, and how you can overcome these limitations.
Part 2: Design an experiment to calculate the energy contained in 5 grams of potato chips.
Expert Solution
The main limitation of a calorimeter is that it is not perfect, which means that it is not perfectly insulating.
As a result it will absorb some of the reaction heat and radiate it to the surroundings. Thus the assumption of no heat loss to the surroundings is generally not possible.
A basic experimental set up is as follows:
Take the potato chips and burn them( combustion). Place a beaker will a known quantity of water and a known initial temperature above the burning chips so that the energy of combustion from the chips goes directly into the beaker of water, which causes a rise in temperature.
This rise in temperature for the known quantity of water is used to get a fair estimate of the amount of energy stored in the chips.
Hope this helps !

Related Solutions
Discuss the limitations of break-even analysis in production and how to overcome these limitations., can you explain how to calculate with ti-84 calculator if possible thanks will rate 1) this..., how the company can overcome preventive cost, describe the financial challenges at each stage of the lifecycle. explain how entrepreneurs can overcome these..., can you explain this statement how "nurses are such a vital part of the workforce, and..., question 1: identify and explain three of the limitations that can affect the effectiveness of a..., based on the elasticity part 1 and part 2, can you provide an example of how..., how the company can overcome the internal failure cost, how can companies overcome withow can companies overcome with 4 social factors once people venture onlineh..., how can doctoral students overcome the challenges of becoming a scholar.
- Advanced Math
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science
- Electrical Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Operations Management
- Statistics and Probability
- 3) You are rolling a 12 sided die 8 times. a) What is the size for...
- explain the difference between quantitative and qualitative research strategies. Provide an example of a crime based...
- use postorder and inorder tree traversals to make preorder traversal. #!/usr/bin/env python3 # encoding: UTF-8 """Turning...
- 1. Write an if-else statement to describe an object. Print "Balloon" if isBalloon is true and...
- An investor is considering purchasing a Treasury bond with a 20 year maturity, an 8% coupon...
- Write a program that copies the contents of one file to a destination file. This program...
- how to conduct a marketing mix for 3d crest white strips
Wise-Answer
Find answers to all questions with us
What are sources of error in a calorimetry lab?
Table of Contents
- 1 What are sources of error in a calorimetry lab?
- 2 What are the possible sources of error in a bomb calorimetry experiment?
- 3 What are sources of error in a lab?
- 4 Why is calorimetry not accurate?
- 5 What are sources of error in an experiment?
- 6 How to do deionized water calorimetry in the lab?
- 7 How is the mass of water used in calorimetry?
The biggest source of error in calorimetry is usually unwanted heat loss to the surroundings. This can be reduced by insulating the sides of the calorimeter and adding a lid.
What are the limitations of calorimetry experiments?
Calorimeters let you measure the amount of heat in a reaction. Their main limitations are losing heat to the environment and uneven heating.
What are the possible sources of error in a bomb calorimetry experiment?
Sources of error include the percent error in water measurement and incomplete vaporization of the nichrome wire. The internal volume of the Parr-bomb was measured to be 341mL.
What materials can you use for the technique of calorimetry?
A simple calorimeter can be constructed from two polystyrene cups. A thermometer and stirrer extend through the cover into the reaction mixture. A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process.
What are sources of error in a lab?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results. Instrumental error happens when the instruments being used are inaccurate, such as a balance that does not work (SF Fig.
How do you do a calorimeter laboratory?
To use the calorimeter, the inner cup is half filled with a known mass of water, and the temperature is measured. The sample is added, the temperature is measured again, and the desired quantity (latent heat or specific heat) is calculated.
Why is calorimetry not accurate?
More reliable results can be obtained by repeating the experiment many times. The biggest source of error in calorimetry is usually unwanted heat loss to the surroundings.
How does calorimeter reduce heat loss?
Heat loss due to conduction is prevented by placing the calorimeter box in a well-lagged vessel using wool or cork material. Heat loss due to convection is prevented by placing a lid on the box. Heat loss due to radiation is minimized by polishing the box in order to smoothen it.
What are sources of error in an experiment?
How is temperature measured in a calorimetry experiment?
How to do deionized water calorimetry in the lab?
How to solve the sample problem in calorimetry?
How is the mass of water used in calorimetry?
Share this post
Privacy overview.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Dividing this figure by the temperature change of the calorimeter gives its calorimeter constant, which you can use in other experiments. Limitations of Calorimetry No calorimeter is perfect because it can lose heat to its surroundings.
Dividing this figure by the temperature change of the calorimeter gives its calorimeter constant, which can then be used in subsequent experiments. To calibrate a calorimeter, you use a process that transfers a known amount of heat -- measuring the temperature of some hot and cold water, for example, then mixing them in your coffee-cup calorimeter.
What are the limitations in using a coffee cup calorimeter? A coffee cup calorimeter is great for measuring heat flow in a chemical solution, but it can't be used for reactions, which involve gases since they would escape from the cup. The coffee cup calorimeter can't be used for high temperature reactions either, since these would melt the ...
Calorimetry is the science of measuring the heat exchange between a system and its surroundings to calculate the change in energy. ... Types, Application, and Limitations. December 14, 2022 December 14, 2022 by Jyoti Bashyal. ... We employ known amounts of reactants and known volumes of liquids while doing experiments with calorimeters. As the ...
The primary limit of calorimetry experiments is keeping the system closed. The heat energy that the experiment is trying to capture can easily be lost to the environment and then be immeasurable.
The limitations of calorimetry include heat loss during combustion, assumptions about pressure dependence on volume and temperature, and non-ideal behavior of certain materials. Explanation. Calorimetry is a technique used to measure the amount of heat involved in chemical reactions or physical changes. However, it has several limitations that ...
Errors in calorimetry experiments can occur due to a variety of factors, including: Inaccurate measurements of mass or temperature. Heat loss to the surroundings, which can be caused by imperfect insulation or incomplete mixing of reactants. Assumptions made about the system that are not entirely accurate.
Advantages of indirect whole body calorimetry Experiments using both whole body calorimetry and respirometry have demon- strated a correlation such that respirometry was soon thought to be as good as, and far more convenient than, whole body calorimetry. With indirect calorimetry, measurements are made of oxygen consumption, carbon dioxide ...
Part 1: Explain possible limitations of a calorimeter, and how you can overcome these limitations. Part 2: Design an experiment to calculate the energy contained in 5 grams of potato chips. Solutions. Expert Solution (1) The main limitation of a calorimeter is that it is not perfect, which means that it is not perfectly insulating. ...
What are the limitations of calorimetry experiments? Calorimeters let you measure the amount of heat in a reaction. Their main limitations are losing heat to the environment and uneven heating. ... In a typical calorimetry experiment, specific volumes of the reactants are dispensed into separate containers and the temperature of each is ...