- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Write My Assignment
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Research Paper Guide
Types Of Qualitative Research

8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
16 min read

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
A Catalog of 300+ Research Paper Topics
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Are you overwhelmed by the multitude of qualitative research methods available? It's no secret that choosing the right approach can leave you stuck at the starting line of your research.
Selecting an unsuitable method can lead to wasted time, resources, and potentially skewed results. But with so many options to consider, it's easy to feel lost in the complexities of qualitative research.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explain the types of qualitative research, their unique characteristics, advantages, and best use cases for each method.
Let's dive in!

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
- 1. What is Qualitative Research?
- 2. Types of Qualitative Research Methods
- 3. Types of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
What is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is a robust and flexible methodology used to explore and understand complex phenomena in-depth.
Unlike quantitative research , qualitative research dives into the rich and complex aspects of human experiences, behaviors, and perceptions.
At its core, this type of research question seeks to answer for:
- Why do people think or behave a certain way?
- What are the underlying motivations and meanings behind actions?
- How do individuals perceive and interpret the world around them?
This approach values context, diversity, and the unique perspectives of participants.
Rather than seeking generalizable findings applicable to a broad population, qualitative research aims for detailed insights, patterns, and themes that come from the people being studied.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research possesses the following characteristics:
- Subjective Perspective: Qualitative research explores subjective experiences, emphasizing the uniqueness of human behavior and opinions.
- In-Depth Exploration: It involves deep investigation, allowing a comprehensive understanding of specific phenomena.
- Open-Ended Questions: Qualitative research uses open-ended questions to encourage detailed, descriptive responses.
- Contextual Understanding: It emphasizes the importance of understanding the research context and setting.
- Rich Descriptions: Qualitative research produces rich, descriptive findings that contribute to a nuanced understanding of the topic.
Types of Qualitative Research Methods
Researchers collect data on the targeted population, place, or event by using different types of qualitative research analysis.
Each qualitative research method offers a distinct perspective, enabling researchers to reveal concealed meanings, patterns, and valuable insights.
Below are the most commonly used qualitative research types for writing a paper.
Ethnographic Research Method
Ethnography, a subfield of anthropology, provides a scientific approach to examining human societies and cultures. It ranks among the most widely employed qualitative research techniques.
In ethnographic field notes, researchers actively engage with the environment and live alongside the focus group.
This immersive interaction allows researchers to gain insights into the objectives, motivations, challenges, and distinctive cultural attributes of the individuals under study.
Key cultural characteristics that ethnography helps to illustrate encompass:
- Geographical Location
- Religious Practices
- Tribal Systems
- Shared Experiences
Unlike traditional survey and interview-based research methods, ethnographers don't rely on structured questioning.
Instead, they become observers within the community, emphasizing participant observation over an extended period. However, it may also be appropriate to complement observations with interviews of individuals who possess knowledge of the culture.
Ethnographic research can present challenges if the researcher is unfamiliar with the social norms and language of the group being studied.
Furthermore, interpretations made by outsiders may lead to misinterpretations or confusion. Therefore, thorough validation of data is essential before presenting findings.
Narrative Method
The narrative research design unfolds over an extended period to compile data, much like crafting a cohesive story. Similar to a narrative structure, it begins with a starting point and progresses through various life situations.
In this method, researchers engage in in-depth interviews and review relevant documents. They explore events that have had a significant impact on an individual's personality and life journey. Interviews may occur over weeks, months, or even years, depending on the depth and scope of the narrative being studied.
The outcome of narrative research is the presentation of a concise story that captures essential themes, conflicts, and challenges. It provides a holistic view of the individual's experiences, both positive and negative, which have shaped their unique narrative.
Phenomenological Method
The term "phenomenological" pertains to the study of phenomena, which can encompass events, situations, or experiences.
This method is ideal for examining a subject from multiple perspectives and contributing to existing knowledge, with a particular focus on subjective experiences.
Researchers employing the phenomenological method use various data collection techniques, including interviews, site visits, observations, surveys, and document reviews.
These methods help gather rich and diverse data about the phenomenon under investigation.
A central aspect of this technique is capturing how participants experience events or activities, delving into their subjective viewpoints. Ultimately, the research results in the creation of a thematic database that validates the findings and offers insights from the subject's perspective.
Grounded Theory Method
A grounded theory approach differs from a phenomenological study in that it seeks to explain, provide reasons for, or develop theories behind an event or phenomenon.
It serves as a means to construct new theories by systematically collecting and analyzing data related to a specific phenomenon.
Researchers employing the grounded theory method utilize a variety of data collection techniques, including observation, interviews, literature review , and the analysis of relevant documents.
The focus of content analysis is not individual behaviors but a specific phenomenon or incident.
This method typically involves various coding techniques and large sample sizes to identify themes and develop more comprehensive theories.
Case Study Research
The case study approach entails a comprehensive examination of a subject over an extended period, with a focus on providing detailed insights into the subject, which can be an event, person, business, or place.
Data for case studies is collected from diverse sources, including interviews, direct observation, historical records, and documentation.
Case studies find applications across various disciplines, including law, education, medicine, and the sciences. They can serve both descriptive and explanatory purposes, making them a versatile research methodology .
Researchers often turn to the case study method when they want to explore:
- 'How' and 'why' research questions
- Behaviors under observation
- Understanding a specific phenomenon
- The contextual factors influencing the phenomena
Historical Method
The historical method aims to describe and analyze past events, offering insights into present patterns and the potential to predict future scenarios.
Researchers formulate research problems based on a hypothetical idea and then rigorously test this idea using multiple historical resources.
Key steps in the historical method include:
- Developing a research idea
- Identifying appropriate sources such as archives and libraries
- Ensuring the reliability and validity of these sources
- Creating a well-organized research outline
- Systematically collecting research data
The analysis phase involves critically assessing the collected data, accepting or rejecting it based on credibility, and identifying any conflicting evidence.
Ultimately, the outcomes of the historical method are presented in the form of a biography or a scholarly paper that provides a comprehensive account of the research findings.
Action Research
Action research is a dynamic research approach focused on addressing practical challenges in real-world settings while simultaneously conducting research to improve the situation.
It follows a cyclic process, starting with the identification of a specific issue or problem in a particular context.
The key steps in action research include:
- Planning and implementing actions to address the issue
- Collecting data during the action phase to understand its impact
- Reflecting on the data and analyzing it to gain insights
- Adjusting the action plan based on the analysis
This process may be iterative, with multiple cycles of action and reflection.
The outcomes of action research are practical solutions and improved practices that directly benefit the context in which the research is conducted. Additionally, it leads to a deeper and more nuanced understanding of the issue under investigation.
Focus Groups
Focus groups are a qualitative research method used to gather in-depth insights and perspectives on a specific topic or research question.
This approach involves assembling a small group of participants who possess relevant knowledge or experiences related to the research focus.
Key steps in the focus group method include:
- Selecting participants
- Moderating the discussion
- Structuring the conversation around open-ended questions
- Collecting data through audio or video recordings and note-taking
The discussion is dynamic and interactive, encouraging participants to share their thoughts, experiences, and opinions.
The analysis phase involves reviewing the data collected from the focus group discussion to identify common themes, patterns, and valuable insights. Focus groups provide rich qualitative data that offer a deeper and more nuanced understanding of the research topic or question.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research employs different data analysis methods, each suited to specific research goals:
- Thematic Analysis: Identifies recurring themes or concepts within data.
- Content Analysis: Systematically categorizes and quantifies text or media content.
- Narrative Analysis: Focuses on storytelling and narrative elements in data.
- Grounded Theory Analysis: Develops or refines theories based on data.
- Discourse Analysis: Examines language and communication patterns.
- Framework Analysis: Organizes data using predefined categories.
- Visual Analysis: Interprets visual data like photos or videos.
- Cross-case Analysis: Compares patterns across multiple cases.
The choice depends on research questions and data type, enhancing understanding and insights.
Benefits of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers valuable advantages, including:
- Flexibility: Adaptable to various research questions and settings.
- Holistic Approach: Explores multiple dimensions of phenomena.
- Theory Development: Contributes to theory creation or refinement.
- Participant Engagement: Fosters active participant involvement.
- Complements Quantitative Research: Provides a comprehensive understanding.
All in all, different types of qualitative research methodology can assist in understanding the behavior and motivations of people. Similarly, it will also help in generating original ideas and formulating a better research problem.
However, not everyone can write a good research paper. Thus, if you get stuck at any stage, you can get professional help.
MyPerfectWords.com is the best paper writing service, where you can hire a professional writer from our paper writing service .
We assure you that you will receive high-quality paper at the most reasonable rates.
Contact our team with your " pay for my research paper " queries. We are available 24/7!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.
Struggling With Your Paper?
Get a custom paper written at
With a FREE Turnitin report, and a 100% money-back guarantee
LIMITED TIME ONLY!
Keep reading
OFFER EXPIRES SOON!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 16 December 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari

- Request new password
- Create a new account
Introduction to Educational Research
Student resources, chapter summary, chapter 6 • qualitative research methods.
- Qualitative research involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of narrative data.
- The focus of qualitative research is typically on the quality of a particular activity.
- Holistic description of the phenomenon, setting, or topic of interest is a key characteristic of qualitative research.
- Both qualitative and quantitative research methods are valuable in their own rights.
- When deciding on a research methodology, it is best to begin with a topic of interest or specific question and then select the method that will provide you with the best answer to that question.
- Qualitative research is naturalistic.
- Qualitative research is descriptive
- Qualitative researchers are concerned with process as well as product.
- Qualitative researchers analyze their data inductively.
- Qualitative researchers are primarily concerned with how people make sense and meaning of their lives.
- Although the basic steps are fairly consistent, those used in conducting qualitative research may occur out of sequential order, may overlap, and are sometimes conducted concurrently.
- Identification of the phenomenon to be studied
- Review of the related literature
- Identification and selection of participants
- Collection of data
- Analysis of data
- Generation of research questions
- Additional data collection, analysis, and revision of research questions
- Final interpretation of analyses and development of conclusions
- Many different approaches exist for conducting qualitative research.
- Commonly used qualitative approaches include ethnographic research, narrative research, historical research, grounded theory research, phenomenological research, and case study research.
- Ethnographic research involves the in-depth description and interpretation of shared practices and beliefs of a social group or other community.
- Narrative research is an approach used to convey experiences as they are lived and told by individuals.
- Historical research describes events, occurrences, or settings of the past to better understand them.
- Grounded theory research is used to discover an existing theory or generate a new theory resulting directly from data.
- Phenomenological research is used to describe and interpret experiences or reactions of participants to a specific phenomenon from their individual perspectives.
- Case study research is an in-depth analysis of a single entity, known as a case.
- Ethnography is a research approach used to study human interactions in social settings.
- Ethnographic research focuses on social behavior in natural settings.
- It relies on narrative descriptions made by observers or participants in the group being studied.
- Its perspective is holistic.
- In some studies, research questions may emerge after data collection is well under way.
- Procedures of data analysis involve contextualization within the group, setting, or event being observed.
- A privileged observer, also known as a nonparticipant observer, does not engage in the activities of the group.
- A participant observer actively engages in all activities as a regular member of the group being studied.
- Naturalistic observation is a holistic technique where the researcher must record all pertinent information.
- A strength of ethnographic research is its holistic view of education or personal behavior.
- Concerns about ethnographic research involve the reliability of data and the validity of research conclusions, as well as the generalizability of findings.
- Several forms of narrative research exist; all forms tell stories of lived experiences, but they differ according to perspective, amount of life story told, and theoretical lens.
- A biographical study is a type of narrative research where the researcher records the experiences of another person’s life.
- An autobiographical study also involves the experiences of a person’s life but is told by the individual who is the subject of the study.
- A life history tells the story of an individual’s entire life.
- A personal experience story is a study of an individual’s personal experience related to a single or multiple incidents.
- An oral history is conducted by gathering personal reflections of events and their implications from one or more individuals.
- A key technique used in narrative research is restorying, a process of reorganizing personal information and stories into a format that makes sense for the intended audience.
- During the process of restorying, participants as well as the researcher may experience epiphanies.
- A clear strength of narrative research is its ability to tell detailed stories of people’s lives.
- Narrative research, however, is a lengthy process wherein the researcher must uncover a multitude of details in people’s lives.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Qualitative study.
Steven Tenny ; Janelle M. Brannan ; Grace D. Brannan .
Affiliations
Last Update: September 18, 2022 .
- Introduction
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. [1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypothenar to further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a standalone study, purely relying on qualitative data, or part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers to some basic concepts, definitions, terminology, and applications of qualitative research.
Qualitative research, at its core, asks open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers, such as "how" and "why." [2] Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions, qualitative research design is often not linear like quantitative design. [2] One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. [3] Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be complex to capture accurately and quantitatively. In contrast, a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a particular time or during an event of interest. Quantifying qualitative data certainly is possible, but at its core, qualitative data is looking for themes and patterns that can be difficult to quantify, and it is essential to ensure that the context and narrative of qualitative work are not lost by trying to quantify something that is not meant to be quantified.
However, while qualitative research is sometimes placed in opposition to quantitative research, where they are necessarily opposites and therefore "compete" against each other and the philosophical paradigms associated with each other, qualitative and quantitative work are neither necessarily opposites, nor are they incompatible. [4] While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites and certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated.
Qualitative Research Approaches
Ethnography
Ethnography as a research design originates in social and cultural anthropology and involves the researcher being directly immersed in the participant’s environment. [2] Through this immersion, the ethnographer can use a variety of data collection techniques to produce a comprehensive account of the social phenomena that occurred during the research period. [2] That is to say, the researcher’s aim with ethnography is to immerse themselves into the research population and come out of it with accounts of actions, behaviors, events, etc, through the eyes of someone involved in the population. Direct involvement of the researcher with the target population is one benefit of ethnographic research because it can then be possible to find data that is otherwise very difficult to extract and record.
Grounded theory
Grounded Theory is the "generation of a theoretical model through the experience of observing a study population and developing a comparative analysis of their speech and behavior." [5] Unlike quantitative research, which is deductive and tests or verifies an existing theory, grounded theory research is inductive and, therefore, lends itself to research aimed at social interactions or experiences. [3] [2] In essence, Grounded Theory’s goal is to explain how and why an event occurs or how and why people might behave a certain way. Through observing the population, a researcher using the Grounded Theory approach can then develop a theory to explain the phenomena of interest.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is the "study of the meaning of phenomena or the study of the particular.” [5] At first glance, it might seem that Grounded Theory and Phenomenology are pretty similar, but the differences can be seen upon careful examination. At its core, phenomenology looks to investigate experiences from the individual's perspective. [2] Phenomenology is essentially looking into the "lived experiences" of the participants and aims to examine how and why participants behaved a certain way from their perspective. Herein lies one of the main differences between Grounded Theory and Phenomenology. Grounded Theory aims to develop a theory for social phenomena through an examination of various data sources. In contrast, Phenomenology focuses on describing and explaining an event or phenomenon from the perspective of those who have experienced it.
Narrative research
One of qualitative research’s strengths lies in its ability to tell a story, often from the perspective of those directly involved in it. Reporting on qualitative research involves including details and descriptions of the setting involved and quotes from participants. This detail is called a "thick" or "rich" description and is a strength of qualitative research. Narrative research is rife with the possibilities of "thick" description as this approach weaves together a sequence of events, usually from just one or two individuals, hoping to create a cohesive story or narrative. [2] While it might seem like a waste of time to focus on such a specific, individual level, understanding one or two people’s narratives for an event or phenomenon can help to inform researchers about the influences that helped shape that narrative. The tension or conflict of differing narratives can be "opportunities for innovation." [2]
Research Paradigm
Research paradigms are the assumptions, norms, and standards underpinning different research approaches. Essentially, research paradigms are the "worldviews" that inform research. [4] It is valuable for qualitative and quantitative researchers to understand what paradigm they are working within because understanding the theoretical basis of research paradigms allows researchers to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the approach being used and adjust accordingly. Different paradigms have different ontologies and epistemologies. Ontology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of reality,” whereas epistemology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of knowledge" that inform researchers' work. [2] It is essential to understand the ontological and epistemological foundations of the research paradigm researchers are working within to allow for a complete understanding of the approach being used and the assumptions that underpin the approach as a whole. Further, researchers must understand their own ontological and epistemological assumptions about the world in general because their assumptions about the world will necessarily impact how they interact with research. A discussion of the research paradigm is not complete without describing positivist, postpositivist, and constructivist philosophies.
Positivist versus postpositivist
To further understand qualitative research, we must discuss positivist and postpositivist frameworks. Positivism is a philosophy that the scientific method can and should be applied to social and natural sciences. [4] Essentially, positivist thinking insists that the social sciences should use natural science methods in their research. It stems from positivist ontology, that there is an objective reality that exists that is wholly independent of our perception of the world as individuals. Quantitative research is rooted in positivist philosophy, which can be seen in the value it places on concepts such as causality, generalizability, and replicability.
Conversely, postpositivists argue that social reality can never be one hundred percent explained, but could be approximated. [4] Indeed, qualitative researchers have been insisting that there are “fundamental limits to the extent to which the methods and procedures of the natural sciences could be applied to the social world,” and therefore, postpositivist philosophy is often associated with qualitative research. [4] An example of positivist versus postpositivist values in research might be that positivist philosophies value hypothesis-testing, whereas postpositivist philosophies value the ability to formulate a substantive theory.
Constructivist
Constructivism is a subcategory of postpositivism. Most researchers invested in postpositivist research are also constructivist, meaning they think there is no objective external reality that exists but instead that reality is constructed. Constructivism is a theoretical lens that emphasizes the dynamic nature of our world. "Constructivism contends that individuals' views are directly influenced by their experiences, and it is these individual experiences and views that shape their perspective of reality.” [6] constructivist thought focuses on how "reality" is not a fixed certainty and how experiences, interactions, and backgrounds give people a unique view of the world. Constructivism contends, unlike positivist views, that there is not necessarily an "objective"reality we all experience. This is the ‘relativist’ ontological view that reality and our world are dynamic and socially constructed. Therefore, qualitative scientific knowledge can be inductive as well as deductive.” [4]
So why is it important to understand the differences in assumptions that different philosophies and approaches to research have? Fundamentally, the assumptions underpinning the research tools a researcher selects provide an overall base for the assumptions the rest of the research will have. It can even change the role of the researchers. [2] For example, is the researcher an "objective" observer, such as in positivist quantitative work? Or is the researcher an active participant in the research, as in postpositivist qualitative work? Understanding the philosophical base of the study undertaken allows researchers to fully understand the implications of their work and their role within the research and reflect on their positionality and bias as it pertains to the research they are conducting.
Data Sampling
The better the sample represents the intended study population, the more likely the researcher is to encompass the varying factors. The following are examples of participant sampling and selection: [7]
- Purposive sampling- selection based on the researcher’s rationale for being the most informative.
- Criterion sampling selection based on pre-identified factors.
- Convenience sampling- selection based on availability.
- Snowball sampling- the selection is by referral from other participants or people who know potential participants.
- Extreme case sampling- targeted selection of rare cases.
- Typical case sampling selection based on regular or average participants.
Data Collection and Analysis
Qualitative research uses several techniques, including interviews, focus groups, and observation. [1] [2] [3] Interviews may be unstructured, with open-ended questions on a topic, and the interviewer adapts to the responses. Structured interviews have a predetermined number of questions that every participant is asked. It is usually one-on-one and appropriate for sensitive topics or topics needing an in-depth exploration. Focus groups are often held with 8-12 target participants and are used when group dynamics and collective views on a topic are desired. Researchers can be participant-observers to share the experiences of the subject or non-participants or detached observers.
While quantitative research design prescribes a controlled environment for data collection, qualitative data collection may be in a central location or the participants' environment, depending on the study goals and design. Qualitative research could amount to a large amount of data. Data is transcribed, which may then be coded manually or using computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software or CAQDAS such as ATLAS.ti or NVivo. [8] [9] [10]
After the coding process, qualitative research results could be in various formats. It could be a synthesis and interpretation presented with excerpts from the data. [11] Results could also be in the form of themes and theory or model development.
Dissemination
The healthcare team can use two reporting standards to standardize and facilitate the dissemination of qualitative research outcomes. The Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research or COREQ is a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. [12] The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is a checklist covering a more comprehensive range of qualitative research. [13]
Applications
Many times, a research question will start with qualitative research. The qualitative research will help generate the research hypothesis, which can be tested with quantitative methods. After the data is collected and analyzed with quantitative methods, a set of qualitative methods can be used to dive deeper into the data to better understand what the numbers truly mean and their implications. The qualitative techniques can then help clarify the quantitative data and also help refine the hypothesis for future research. Furthermore, with qualitative research, researchers can explore poorly studied subjects with quantitative methods. These include opinions, individual actions, and social science research.
An excellent qualitative study design starts with a goal or objective. This should be clearly defined or stated. The target population needs to be specified. A method for obtaining information from the study population must be carefully detailed to ensure no omissions of part of the target population. A proper collection method should be selected that will help obtain the desired information without overly limiting the collected data because, often, the information sought is not well categorized or obtained. Finally, the design should ensure adequate methods for analyzing the data. An example may help better clarify some of the various aspects of qualitative research.
A researcher wants to decrease the number of teenagers who smoke in their community. The researcher could begin by asking current teen smokers why they started smoking through structured or unstructured interviews (qualitative research). The researcher can also get together a group of current teenage smokers and conduct a focus group to help brainstorm factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke (qualitative research).
In this example, the researcher has used qualitative research methods (interviews and focus groups) to generate a list of ideas of why teens start to smoke and factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke. Next, the researcher compiles this data. The research found that, hypothetically, peer pressure, health issues, cost, being considered "cool," and rebellious behavior all might increase or decrease the likelihood of teens starting to smoke.
The researcher creates a survey asking teen participants to rank how important each of the above factors is in either starting smoking (for current smokers) or not smoking (for current nonsmokers). This survey provides specific numbers (ranked importance of each factor) and is thus a quantitative research tool.
The researcher can use the survey results to focus efforts on the one or two highest-ranked factors. Let us say the researcher found that health was the primary factor that keeps teens from starting to smoke, and peer pressure was the primary factor that contributed to teens starting smoking. The researcher can go back to qualitative research methods to dive deeper into these for more information. The researcher wants to focus on keeping teens from starting to smoke, so they focus on the peer pressure aspect.
The researcher can conduct interviews and focus groups (qualitative research) about what types and forms of peer pressure are commonly encountered, where the peer pressure comes from, and where smoking starts. The researcher hypothetically finds that peer pressure often occurs after school at the local teen hangouts, mostly in the local park. The researcher also hypothetically finds that peer pressure comes from older, current smokers who provide the cigarettes.
The researcher could further explore this observation made at the local teen hangouts (qualitative research) and take notes regarding who is smoking, who is not, and what observable factors are at play for peer pressure to smoke. The researcher finds a local park where many local teenagers hang out and sees that the smokers tend to hang out in a shady, overgrown area of the park. The researcher notes that smoking teenagers buy their cigarettes from a local convenience store adjacent to the park, where the clerk does not check identification before selling cigarettes. These observations fall under qualitative research.
If the researcher returns to the park and counts how many individuals smoke in each region, this numerical data would be quantitative research. Based on the researcher's efforts thus far, they conclude that local teen smoking and teenagers who start to smoke may decrease if there are fewer overgrown areas of the park and the local convenience store does not sell cigarettes to underage individuals.
The researcher could try to have the parks department reassess the shady areas to make them less conducive to smokers or identify how to limit the sales of cigarettes to underage individuals by the convenience store. The researcher would then cycle back to qualitative methods of asking at-risk populations their perceptions of the changes and what factors are still at play, and quantitative research that includes teen smoking rates in the community and the incidence of new teen smokers, among others. [14] [15]
Qualitative research functions as a standalone research design or combined with quantitative research to enhance our understanding of the world. Qualitative research uses techniques including structured and unstructured interviews, focus groups, and participant observation not only to help generate hypotheses that can be more rigorously tested with quantitative research but also to help researchers delve deeper into the quantitative research numbers, understand what they mean, and understand what the implications are. Qualitative research allows researchers to understand what is going on, especially when things are not easily categorized. [16]
- Issues of Concern
As discussed in the sections above, quantitative and qualitative work differ in many ways, including the evaluation criteria. There are four well-established criteria for evaluating quantitative data: internal validity, external validity, reliability, and objectivity. Credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability are the correlating concepts in qualitative research. [4] [11] The corresponding quantitative and qualitative concepts can be seen below, with the quantitative concept on the left and the qualitative concept on the right:
- Internal validity: Credibility
- External validity: Transferability
- Reliability: Dependability
- Objectivity: Confirmability
In conducting qualitative research, ensuring these concepts are satisfied and well thought out can mitigate potential issues from arising. For example, just as a researcher will ensure that their quantitative study is internally valid, qualitative researchers should ensure that their work has credibility.
Indicators such as triangulation and peer examination can help evaluate the credibility of qualitative work.
- Triangulation: Triangulation involves using multiple data collection methods to increase the likelihood of getting a reliable and accurate result. In our above magic example, the result would be more reliable if we interviewed the magician, backstage hand, and the person who "vanished." In qualitative research, triangulation can include telephone surveys, in-person surveys, focus groups, and interviews and surveying an adequate cross-section of the target demographic.
- Peer examination: A peer can review results to ensure the data is consistent with the findings.
A "thick" or "rich" description can be used to evaluate the transferability of qualitative research, whereas an indicator such as an audit trail might help evaluate the dependability and confirmability.
- Thick or rich description: This is a detailed and thorough description of details, the setting, and quotes from participants in the research. [5] Thick descriptions will include a detailed explanation of how the study was conducted. Thick descriptions are detailed enough to allow readers to draw conclusions and interpret the data, which can help with transferability and replicability.
- Audit trail: An audit trail provides a documented set of steps of how the participants were selected and the data was collected. The original information records should also be kept (eg, surveys, notes, recordings).
One issue of concern that qualitative researchers should consider is observation bias. Here are a few examples:
- Hawthorne effect: The effect is the change in participant behavior when they know they are being observed. Suppose a researcher wanted to identify factors that contribute to employee theft and tell the employees they will watch them to see what factors affect employee theft. In that case, one would suspect employee behavior would change when they know they are being protected.
- Observer-expectancy effect: Some participants change their behavior or responses to satisfy the researcher's desired effect. This happens unconsciously for the participant, so it is essential to eliminate or limit the transmission of the researcher's views.
- Artificial scenario effect: Some qualitative research occurs in contrived scenarios with preset goals. In such situations, the information may not be accurate because of the artificial nature of the scenario. The preset goals may limit the qualitative information obtained.
- Clinical Significance
Qualitative or quantitative research helps healthcare providers understand patients and the impact and challenges of the care they deliver. Qualitative research provides an opportunity to generate and refine hypotheses and delve deeper into the data generated by quantitative research. Qualitative research is not an island apart from quantitative research but an integral part of research methods to understand the world around us. [17]
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Qualitative research is essential for all healthcare team members as all are affected by qualitative research. Qualitative research may help develop a theory or a model for health research that can be further explored by quantitative research. Much of the qualitative research data acquisition is completed by numerous team members, including social workers, scientists, nurses, etc. Within each area of the medical field, there is copious ongoing qualitative research, including physician-patient interactions, nursing-patient interactions, patient-environment interactions, healthcare team function, patient information delivery, etc.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Steven Tenny declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Janelle Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Grace Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Tenny S, Brannan JM, Brannan GD. Qualitative Study. [Updated 2022 Sep 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022] Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1; 2(2022). Epub 2022 Feb 1.
- Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). [Phys Biol. 2013] Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). Foffi G, Pastore A, Piazza F, Temussi PA. Phys Biol. 2013 Aug; 10(4):040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2.
- The future of Cochrane Neonatal. [Early Hum Dev. 2020] The future of Cochrane Neonatal. Soll RF, Ovelman C, McGuire W. Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov; 150:105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12.
- Review Invited review: Qualitative research in dairy science-A narrative review. [J Dairy Sci. 2023] Review Invited review: Qualitative research in dairy science-A narrative review. Ritter C, Koralesky KE, Saraceni J, Roche S, Vaarst M, Kelton D. J Dairy Sci. 2023 Sep; 106(9):5880-5895. Epub 2023 Jul 18.
- Review Participation in environmental enhancement and conservation activities for health and well-being in adults: a review of quantitative and qualitative evidence. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016] Review Participation in environmental enhancement and conservation activities for health and well-being in adults: a review of quantitative and qualitative evidence. Husk K, Lovell R, Cooper C, Stahl-Timmins W, Garside R. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 21; 2016(5):CD010351. Epub 2016 May 21.
Recent Activity
- Qualitative Study - StatPearls Qualitative Study - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Qualitative Research Methods: Types, Analysis + Examples
Qualitative research is based on the disciplines of social sciences like psychology, sociology, and anthropology. Therefore, the qualitative research methods allow for in-depth and further probing and questioning of respondents based on their responses. The interviewer/researcher also tries to understand their motivation and feelings. Understanding how your audience makes decisions can help derive conclusions in market research.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is defined as a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication .
This method is about “what” people think and “why” they think so. For example, consider a convenience store looking to improve its patronage. A systematic observation concludes that more men are visiting this store. One good method to determine why women were not visiting the store is conducting an in-depth interview method with potential customers.
For example, after successfully interviewing female customers and visiting nearby stores and malls, the researchers selected participants through random sampling . As a result, it was discovered that the store didn’t have enough items for women.
So fewer women were visiting the store, which was understood only by personally interacting with them and understanding why they didn’t visit the store because there were more male products than female ones.
Gather research insights
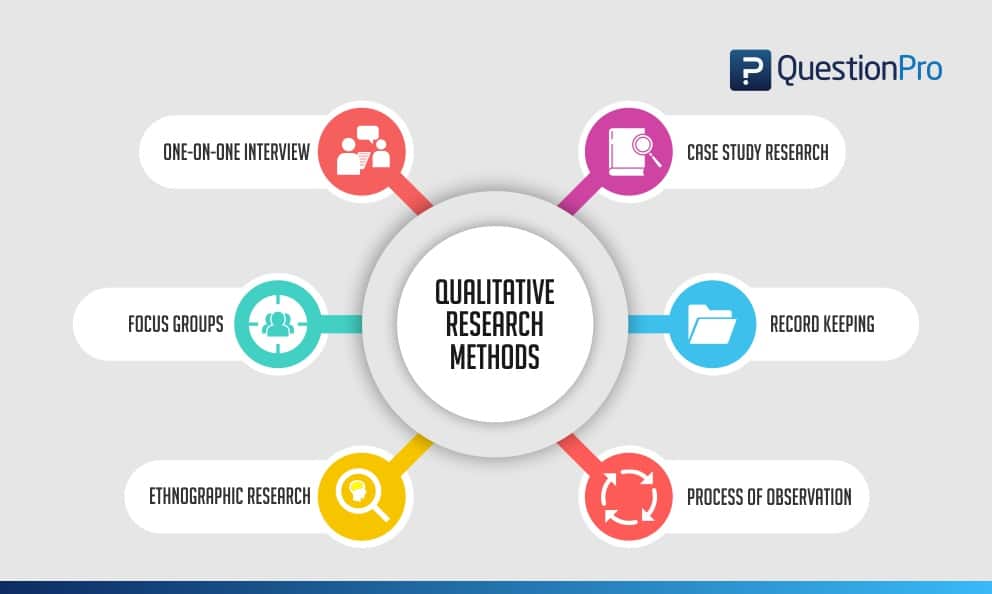
Types of qualitative research methods with examples
Qualitative research methods are designed in a manner that helps reveal the behavior and perception of a target audience with reference to a particular topic. There are different types of qualitative research methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, ethnographic research, content analysis, and case study research that are usually used.
The results of qualitative methods are more descriptive, and the inferences can be drawn quite easily from the obtained data .
Qualitative research methods originated in the social and behavioral research sciences. Today, our world is more complicated, and it is difficult to understand what people think and perceive. Online research methods make it easier to understand that as it is a more communicative and descriptive analysis .
The following are the qualitative research methods that are frequently used. Also, read about qualitative research examples :

1. One-on-one interview
Conducting in-depth interviews is one of the most common qualitative research methods. It is a personal interview that is carried out with one respondent at a time. This is purely a conversational method and invites opportunities to get details in depth from the respondent.
One of the advantages of this method is that it provides a great opportunity to gather precise data about what people believe and their motivations . If the researcher is well experienced, asking the right questions can help him/her collect meaningful data. If they should need more information, the researchers should ask such follow-up questions that will help them collect more information.
These interviews can be performed face-to-face or on the phone and usually can last between half an hour to two hours or even more. When the in-depth interview is conducted face to face, it gives a better opportunity to read the respondents’ body language and match the responses.
2. Focus groups
A focus group is also a commonly used qualitative research method used in data collection. A focus group usually includes a limited number of respondents (6-10) from within your target market.
The main aim of the focus group is to find answers to the “why, ” “what,” and “how” questions. One advantage of focus groups is you don’t necessarily need to interact with the group in person. Nowadays, focus groups can be sent an online survey on various devices, and responses can be collected at the click of a button.
Focus groups are an expensive method as compared to other online qualitative research methods. Typically, they are used to explain complex processes. This method is very useful for market research on new products and testing new concepts.
3. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is the most in-depth observational research method that studies people in their naturally occurring environment.
This method requires the researchers to adapt to the target audiences’ environments, which could be anywhere from an organization to a city or any remote location. Here, geographical constraints can be an issue while collecting data.
This research design aims to understand the cultures, challenges, motivations, and settings that occur. Instead of relying on interviews and discussions, you experience the natural settings firsthand.
This type of research method can last from a few days to a few years, as it involves in-depth observation and collecting data on those grounds. It’s a challenging and time-consuming method and solely depends on the researcher’s expertise to analyze, observe, and infer the data.
4. Case study research
T he case study method has evolved over the past few years and developed into a valuable quality research method. As the name suggests, it is used for explaining an organization or an entity.
This type of research method is used within a number of areas like education, social sciences, and similar. This method may look difficult to operate; however , it is one of the simplest ways of conducting research as it involves a deep dive and thorough understanding of the data collection methods and inferring the data.
5. Record keeping
This method makes use of the already existing reliable documents and similar sources of information as the data source. This data can be used in new research. This is similar to going to a library. There, one can go over books and other reference material to collect relevant data that can likely be used in the research.
6. Process of observation
Qualitative Observation is a process of research that uses subjective methodologies to gather systematic information or data. Since the focus on qualitative observation is the research process of using subjective methodologies to gather information or data. Qualitative observation is primarily used to equate quality differences.
Qualitative observation deals with the 5 major sensory organs and their functioning – sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing. This doesn’t involve measurements or numbers but instead characteristics.
Explore Insightfully Contextual Inquiry in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research: data collection and analysis
A. qualitative data collection.
Qualitative data collection allows collecting data that is non-numeric and helps us to explore how decisions are made and provide us with detailed insight. For reaching such conclusions the data that is collected should be holistic, rich, and nuanced and findings to emerge through careful analysis.
- Whatever method a researcher chooses for collecting qualitative data, one aspect is very clear the process will generate a large amount of data. In addition to the variety of methods available, there are also different methods of collecting and recording the data.
For example, if the qualitative data is collected through a focus group or one-to-one discussion, there will be handwritten notes or video recorded tapes. If there are recording they should be transcribed and before the process of data analysis can begin.
- As a rough guide, it can take a seasoned researcher 8-10 hours to transcribe the recordings of an interview, which can generate roughly 20-30 pages of dialogues. Many researchers also like to maintain separate folders to maintain the recording collected from the different focus group. This helps them compartmentalize the data collected.
- In case there are running notes taken, which are also known as field notes, they are helpful in maintaining comments, environmental contexts, environmental analysis , nonverbal cues etc. These filed notes are helpful and can be compared while transcribing audio recorded data. Such notes are usually informal but should be secured in a similar manner as the video recordings or the audio tapes.
B. Qualitative data analysis
Qualitative data analysis such as notes, videos, audio recordings images, and text documents. One of the most used methods for qualitative data analysis is text analysis.
Text analysis is a data analysis method that is distinctly different from all other qualitative research methods, where researchers analyze the social life of the participants in the research study and decode the words, actions, etc.
There are images also that are used in this research study and the researchers analyze the context in which the images are used and draw inferences from them. In the last decade, text analysis through what is shared on social media platforms has gained supreme popularity.
Choosing the right software can be tough. Whether you’re a researcher, business leader, or marketer, check out the top 10 qualitative data analysis software for analyzing qualitative data.
Characteristics of qualitative research methods

- Qualitative research methods usually collect data at the sight, where the participants are experiencing issues or research problems . These are real-time data and rarely bring the participants out of the geographic locations to collect information.
- Qualitative researchers typically gather multiple forms of data, such as interviews, observations, and documents, rather than rely on a single data source .
- This type of research method works towards solving complex issues by breaking down into meaningful inferences, that is easily readable and understood by all.
- Since it’s a more communicative method, people can build their trust on the researcher and the information thus obtained is raw and unadulterated.
Qualitative research method case study
Let’s take the example of a bookstore owner who is looking for ways to improve their sales and customer outreach. An online community of members who were loyal patrons of the bookstore were interviewed and related questions were asked and the questions were answered by them.
At the end of the interview, it was realized that most of the books in the stores were suitable for adults and there were not enough options for children or teenagers.
By conducting this qualitative research the bookstore owner realized what the shortcomings were and what were the feelings of the readers. Through this research now the bookstore owner can now keep books for different age categories and can improve his sales and customer outreach.
Such qualitative research method examples can serve as the basis to indulge in further quantitative research , which provides remedies.
When to use qualitative research
Researchers make use of qualitative research techniques when they need to capture accurate, in-depth insights. It is very useful to capture “factual data”. Here are some examples of when to use qualitative research.
- Developing a new product or generating an idea.
- Studying your product/brand or service to strengthen your marketing strategy.
- To understand your strengths and weaknesses.
- Understanding purchase behavior.
- To study the reactions of your audience to marketing campaigns and other communications.
- Exploring market demographics, segments, and customer care groups.
- Gathering perception data of a brand, company, or product.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research

Qualitative research methods vs quantitative research methods
The basic differences between qualitative research methods and quantitative research methods are simple and straightforward. They differ in:
- Their analytical objectives
- Types of questions asked
- Types of data collection instruments
- Forms of data they produce
- Degree of flexibility
LEARN MORE ABOUR OUR SOFTWARE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

CultureAmp vs Qualtrics: The Best Employee Experience Platform
Dec 16, 2024

Data Quality Dimensions: What are They & How to Improve
Dec 10, 2024

NPS Analysis: Boosting Customer Retention and Satisfaction
Dec 9, 2024

What Can We Expect Next? — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Dec 3, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
Choosing a Qualitative Research Approach
Arianne teherani , phd, tina martimianakis , phd, terese stenfors-hayes , phd, anupma wadhwa , md, lara varpio , phd.
- Author information
- Copyright and License information
Corresponding author: Arianne Teherani, PhD, University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine, Office of Research and Development in Medical Education, Box 3202, 1855 Folsom Avenue, Suite 200, San Francisco, CA 94143-3202, 415.509.4988, [email protected]
Editor's Note: The online version (29KB, doc) of this article contains a list of further reading resources and the authors' professional information .
The Challenge
Educators often pose questions about qualitative research. For example, a program director might say: “I collect data from my residents about their learning experiences in a new longitudinal clinical rotation. If I want to know about their learning experiences, should I use qualitative methods? I have been told that there are many approaches from which to choose. Someone suggested that I use grounded theory, but how do I know this is the best approach? Are there others?”
What Is Known
Qualitative research is the systematic inquiry into social phenomena in natural settings. These phenomena can include, but are not limited to, how people experience aspects of their lives, how individuals and/or groups behave, how organizations function, and how interactions shape relationships. In qualitative research, the researcher is the main data collection instrument. The researcher examines why events occur, what happens, and what those events mean to the participants studied. 1 , 2
Qualitative research starts from a fundamentally different set of beliefs—or paradigms—than those that underpin quantitative research. Quantitative research is based on positivist beliefs that there is a singular reality that can be discovered with the appropriate experimental methods. Post-positivist researchers agree with the positivist paradigm, but believe that environmental and individual differences, such as the learning culture or the learners' capacity to learn, influence this reality, and that these differences are important. Constructivist researchers believe that there is no single reality, but that the researcher elicits participants' views of reality. 3 Qualitative research generally draws on post-positivist or constructivist beliefs.
Qualitative scholars develop their work from these beliefs—usually post-positivist or constructivist—using different approaches to conduct their research. In this Rip Out, we describe 3 different qualitative research approaches commonly used in medical education: grounded theory, ethnography, and phenomenology. Each acts as a pivotal frame that shapes the research question(s), the method(s) of data collection, and how data are analyzed. 4 , 5
Choosing a Qualitative Approach
Before engaging in any qualitative study, consider how your views about what is possible to study will affect your approach. Then select an appropriate approach within which to work. Alignment between the belief system underpinning the research approach, the research question, and the research approach itself is a prerequisite for rigorous qualitative research. To enhance the understanding of how different approaches frame qualitative research, we use this introductory challenge as an illustrative example.
The clinic rotation in a program director's training program was recently redesigned as a longitudinal clinical experience. Resident satisfaction with this rotation improved significantly following implementation of the new longitudinal experience. The program director wants to understand how the changes made in the clinic rotation translated into changes in learning experiences for the residents.
Qualitative research can support this program director's efforts. Qualitative research focuses on the events that transpire and on outcomes of those events from the perspectives of those involved. In this case, the program director can use qualitative research to understand the impact of the new clinic rotation on the learning experiences of residents. The next step is to decide which approach to use as a frame for the study.
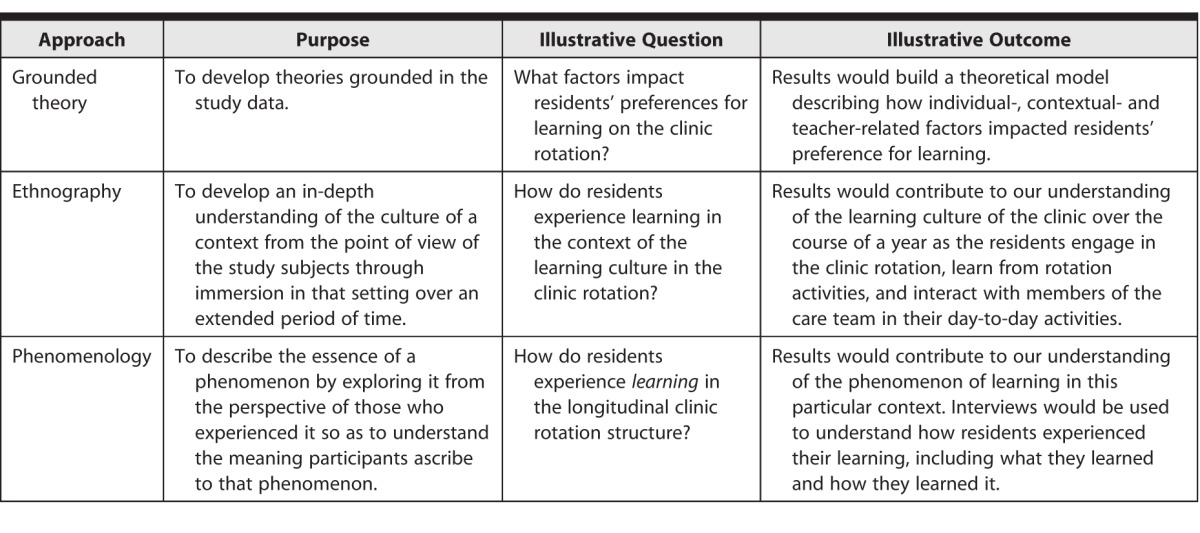
The table lists the purpose of 3 commonly used approaches to frame qualitative research. For each frame, we provide an example of a research question that could direct the study and delineate what outcomes might be gained by using that particular approach.
Methodology Overview
How You Can Start TODAY
Examine the foundations of the existing literature: As part of the literature review, make note of what is known about the topic and which approaches have been used in prior studies. A decision should be made to determine the extent to which the new study is exploratory and the extent to which findings will advance what is already known about the topic.
Find a qualitatively skilled collaborator: If you are interested in doing qualitative research, you should consult with a qualitative expert. Be prepared to talk to the qualitative scholar about what you would like to study and why . Furthermore, be ready to describe the literature to date on the topic (remember, you are asking for this person's expertise regarding qualitative approaches—he or she won't necessarily have content expertise). Qualitative research must be designed and conducted with rigor (rigor will be discussed in Rip Out No. 8 of this series). Input from a qualitative expert will ensure that rigor is employed from the study's inception.
Consider the approach: With a literature review completed and a qualitatively skilled collaborator secured, it is time to decide which approach would be best suited to answering the research question. Questions to consider when weighing approaches might include the following:
Will my findings contribute to the creation of a theoretical model to better understand the area of study? ( grounded theory )
Will I need to spend an extended amount of time trying to understand the culture and process of a particular group of learners in their natural context? ( ethnography )
Is there a particular phenomenon I want to better understand/describe? ( phenomenology )
What You Can Do LONG TERM
Develop your qualitative research knowledge and skills : A basic qualitative research textbook is a valuable investment to learn about qualitative research (further reading is provided as online supplemental material). A novice qualitative researcher will also benefit from participating in a massive online open course or a mini-course (often offered by professional organizations or conferences) that provides an introduction to qualitative research. Most of all, collaborating with a qualitative researcher can provide the support necessary to design, execute, and report on the study.
Undertake a pilot study: After learning about qualitative methodology, the next best way to gain expertise in qualitative research is to try it in a small scale pilot study with the support of a qualitative expert. Such application provides an appreciation for the thought processes that go into designing a study, analyzing the data, and reporting on the findings. Alternatively, if you have the opportunity to work on a study led by a qualitative expert, take it! The experience will provide invaluable opportunities for learning how to engage in qualitative research.
Supplementary Material
The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, the Department of the Navy, the Department of Defense, or the US government.
References and Resources for Further Reading
- 1. Bogdan R, Biklen SK. Qualitative Research for Education: An Introduction to Theories and Methods. 5th ed. London, UK: Pearson;; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Corbin J, Strauss A. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications;; 2008. eds. [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Bergman E, de Feijter J, Frambach J, Godefrooij M, Slootweg I, Stalmeijer R, et al. AM last page: a guide to research paradigms relevant to medical education. Acad Med. 2012;87(4):545. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e31824fbc8a. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Howell KE. An Introduction to the Philosophy of Methodology. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications;; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research. 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications;; 2011. eds. [ Google Scholar ]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
- View on publisher site
- PDF (111.3 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents
A research summary is a concise overview of a study’s purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions. Writing an effective research summary allows you to distill key insights for an audience, enabling them to quickly understand the core message and significance of the study. This guide provides an in-depth look at the structure of a research summary, examples, and tips for writing one that is clear, informative, and engaging.

Research Summary
A research summary condenses the essential parts of a research paper or study into a brief format, usually ranging from a single paragraph to a page. The goal is to give readers a clear understanding of the study’s objectives, methodology, major findings, and implications. Research summaries are often used in academic papers, grant proposals, and professional reports.
Key Characteristics of a Research Summary :
- Conciseness : Communicates the main points without unnecessary detail.
- Clarity : Presents information in a straightforward and easily understandable manner.
- Structure : Follows a logical flow, typically mirroring the structure of the full research report.
Structure of a Research Summary
A well-structured research summary generally includes the following sections:
The title should reflect the main topic or research question, helping readers quickly understand what the study is about. If applicable, the title should also hint at the methodology or scope of the study.
2. Introduction
The introduction provides context for the research question and explains why the study is important. Briefly summarize the problem or gap in knowledge that the study addresses and state the research objectives or hypotheses.
Example : “This study investigates the impact of social media on adolescent mental health, specifically focusing on self-esteem and anxiety. The research aims to understand how social media usage patterns relate to these psychological outcomes.”
3. Methodology
This section briefly outlines the research design, sample size, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. The goal is to give readers an idea of how the study was conducted.
Example : “The study employed a mixed-methods approach, using an online survey of 500 adolescents and in-depth interviews with 20 participants to gather quantitative and qualitative data on social media habits and mental health.”
The results section summarizes the major findings of the study without going into detailed statistics or data. Focus on the key insights that answer the research question or support the hypotheses.
Example : “The analysis revealed a positive correlation between increased social media use and higher levels of anxiety. Participants who spent more than three hours per day on social media reported lower self-esteem scores compared to those with limited usage.”
5. Conclusion
The conclusion provides a brief interpretation of the results, discussing their implications and potential applications. This section may also suggest areas for further research.
Example : “The findings suggest that prolonged social media exposure may negatively impact adolescent mental health. Future research could explore intervention strategies to promote healthier social media habits.”
6. Keywords (Optional)
Some research summaries include keywords to help readers find relevant studies quickly. Keywords should relate to the study’s main concepts or topics, such as “social media,” “mental health,” “adolescents,” and “self-esteem.”
Example of a Research Summary
Title : Effects of Physical Activity on Cognitive Function in Older Adults
Introduction : This study examines the impact of regular physical activity on cognitive function in adults aged 65 and older. With age-related cognitive decline being a major public health concern, understanding the benefits of exercise on brain health could inform preventive strategies.
Methodology : A randomized controlled trial was conducted with 200 participants divided into an exercise group and a control group. The exercise group participated in supervised workouts three times per week, while the control group maintained their usual activities. Cognitive assessments were administered at baseline and after six months.
Results : Participants in the exercise group showed significant improvements in memory and executive function compared to the control group, who exhibited no cognitive gains.
Conclusion : Regular physical activity appears to benefit cognitive function in older adults, potentially delaying age-related cognitive decline. Further research is needed to explore optimal exercise regimens for brain health.
Writing Guide for a Research Summary
Step 1: read the full research report.
To write an accurate summary, read the complete research report or study. Take notes on the main points, including the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
Step 2: Identify the Core Message
Distill the study’s core message by identifying the research objectives, key findings, and implications. This will form the foundation of your summary, ensuring that it remains focused and relevant.
Step 3: Use Clear and Concise Language
A research summary should be concise and free from unnecessary jargon. Use simple language to make the study accessible to a broad audience, especially if the summary is intended for readers outside the research field.
Step 4: Follow the Structure
Adopt a clear structure to organize information logically. Begin with an introduction to the research question, briefly describe the methodology, highlight the main findings, and conclude with the study’s implications.
Step 5: Revise for Brevity and Clarity
Revise your draft to remove redundant information and ensure that each sentence adds value. Aim to keep the summary short, ideally within one or two paragraphs for a single-page summary or slightly longer for comprehensive reviews.
Step 6: Include Keywords if Needed
If the summary will be published in an academic or searchable format, add relevant keywords to help readers find the study easily. Select terms that represent the study’s main themes or topics.
Tips for Writing an Effective Research Summary
- Focus on Key Points : Avoid including minor details and focus on summarizing the main findings.
- Avoid Technical Jargon : Use plain language, especially if the summary is for a general audience.
- Use Active Voice : Active voice makes sentences clearer and more direct.
- Keep it Objective : Avoid adding personal opinions or interpretations beyond what is presented in the study.
- Proofread : Check for clarity, grammar, and adherence to the structure.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Including Too Much Detail : A research summary should only cover the essential points without overwhelming readers.
- Overuse of Technical Terms : Unless intended for a specialist audience, limit technical language to ensure accessibility.
- Neglecting the Structure : Follow the structure to maintain a logical flow of information.
- Personal Interpretations : Stick to summarizing the study’s findings and implications without inserting your own analysis.
- Ignoring the Objective : Keep in mind the purpose of the summary, whether for an academic journal, project proposal, or professional report.
A research summary provides a snapshot of a study’s essential points, helping readers quickly understand the objectives, methods, findings, and implications of the research. By following a structured approach, using clear language, and focusing on the core message, you can write an effective research summary that communicates the study’s contributions. Whether for academic or professional purposes, a well-crafted summary makes research accessible, engaging, and valuable for a wide audience.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., & Williams, J. M. (2016). The Craft of Research . University of Chicago Press.
- Swales, J. M., & Feak, C. B. (2012). Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Tasks and Skills . University of Michigan Press.
- Babbie, E. (2020). The Practice of Social Research . Cengage Learning.
- Neuman, W. L. (2014). Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches . Pearson.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide

Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and...

Thesis – Outline, Structure and Writing Guide

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Research Findings – Types Examples and Writing...

Future Research – Thesis Guide

IMAGES