- Biology Article
- Mendel Laws Of Inheritance

Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Inheritance can be defined as the process of how a child receives genetic information from the parent. The whole process of heredity is dependent upon inheritance and it is the reason that the offsprings are similar to the parents. This simply means that due to inheritance, the members of the same family possess similar characteristics.
It was only during the mid 19th century that people started to understand inheritance in a proper way. This understanding of inheritance was made possible by a scientist named Gregor Mendel, who formulated certain laws to understand inheritance known as Mendel’s laws of inheritance.
Table of Contents
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
Why was pea plant selected for mendel’s experiments, mendel’s experiments, conclusions from mendel’s experiments, mendel’s laws, key points on mendel’s laws.
Between 1856-1863, Mendel conducted the hybridization experiments on the garden peas. During that period, he chose some distinct characteristics of the peas and conducted some cross-pollination/ artificial pollination on the pea lines that showed stable trait inheritance and underwent continuous self-pollination. Such pea lines are called true-breeding pea lines.
Also Refer: Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance: Mendel’s Contribution
He selected a pea plant for his experiments for the following reasons:
- The pea plant can be easily grown and maintained.
- They are naturally self-pollinating but can also be cross-pollinated.
- It is an annual plant, therefore, many generations can be studied within a short period of time.
- It has several contrasting characters.
Mendel conducted 2 main experiments to determine the laws of inheritance. These experiments were:
Monohybrid Cross
Dihybrid cross.
While experimenting, Mendel found that certain factors were always being transferred down to the offspring in a stable way. Those factors are now called genes i.e. genes can be called the units of inheritance.
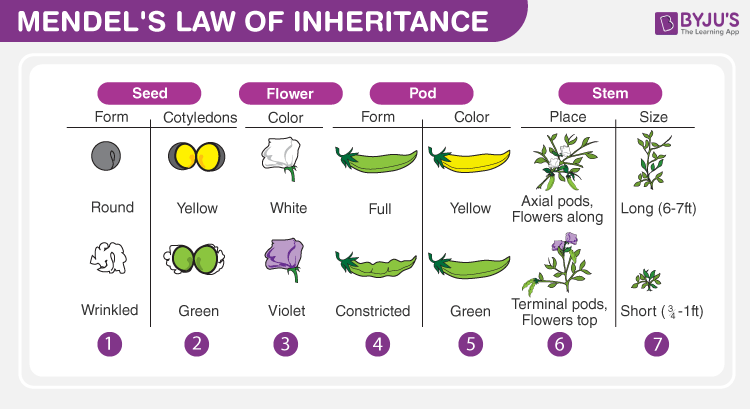
Mendel experimented on a pea plant and considered 7 main contrasting traits in the plants. Then, he conducted both experiments to determine the inheritance laws. A brief explanation of the two experiments is given below.
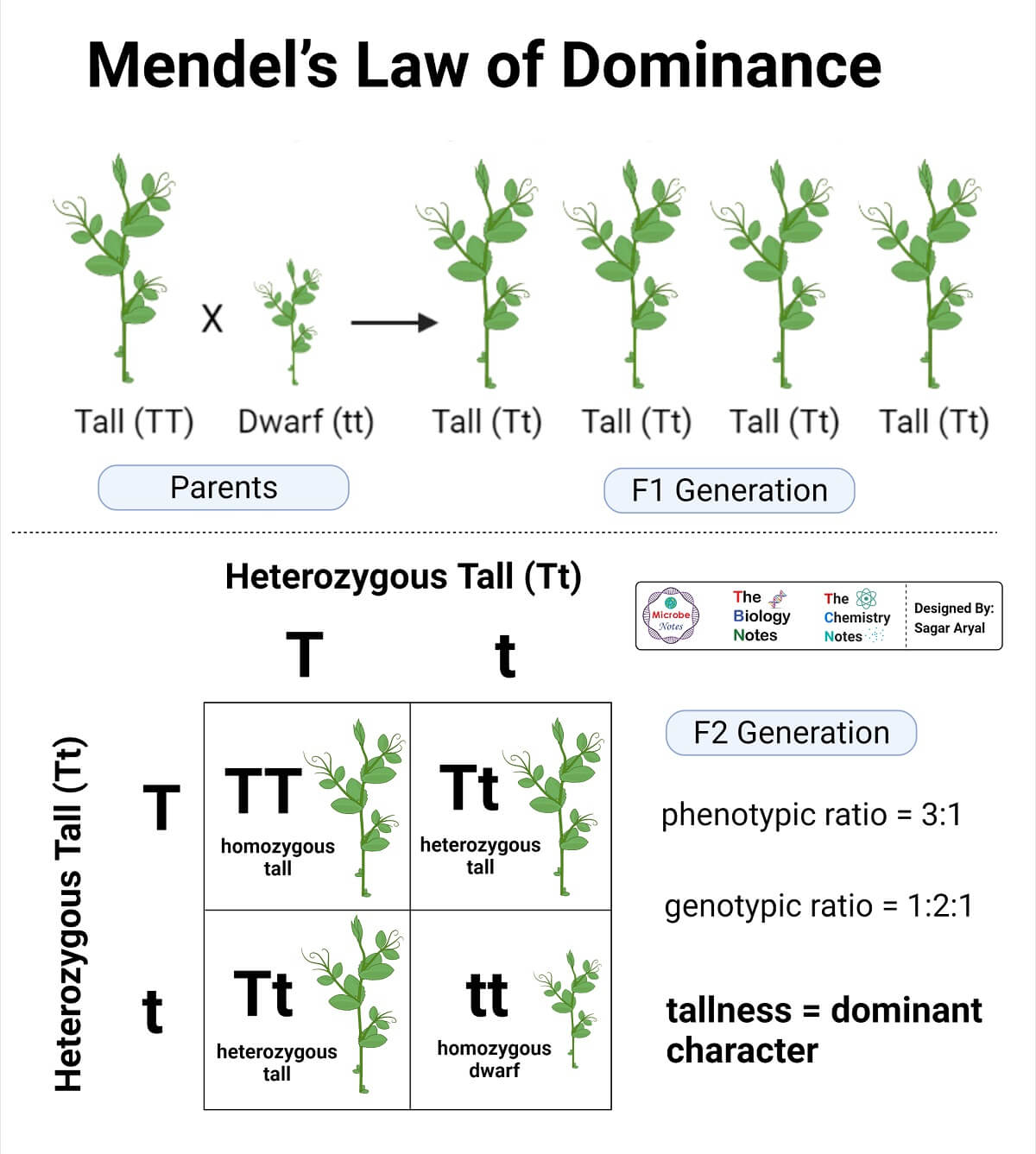
In this experiment, Mendel took two pea plants of opposite traits (one short and one tall) and crossed them. He found the first generation offspring were tall and called it F1 progeny. Then he crossed F1 progeny and obtained both tall and short plants in the ratio 3:1. To know more about this experiment, visit Monohybrid Cross – Inheritance Of One Gene .
Mendel even conducted this experiment with other contrasting traits like green peas vs yellow peas, round vs wrinkled, etc. In all the cases, he found that the results were similar. From this, he formulated the laws of Segregation And Dominance .
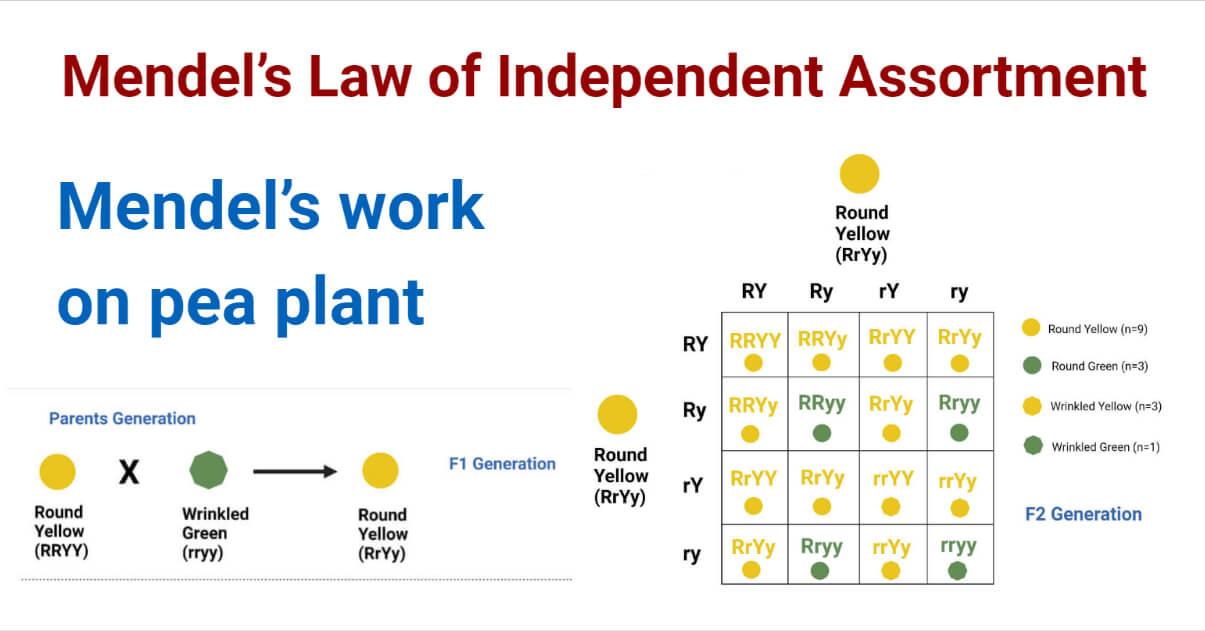
In a dihybrid cross experiment, Mendel considered two traits, each having two alleles. He crossed wrinkled-green seed and round-yellow seeds and observed that all the first generation progeny (F1 progeny) were round-yellow. This meant that dominant traits were the round shape and yellow colour.
He then self-pollinated the F1 progeny and obtained 4 different traits: round-yellow, round-green, wrinkled-yellow, and wrinkled-green seeds in the ratio 9:3:3:1.
Check Dihybrid Cross and Inheritance of Two Genes to know more about this cross.
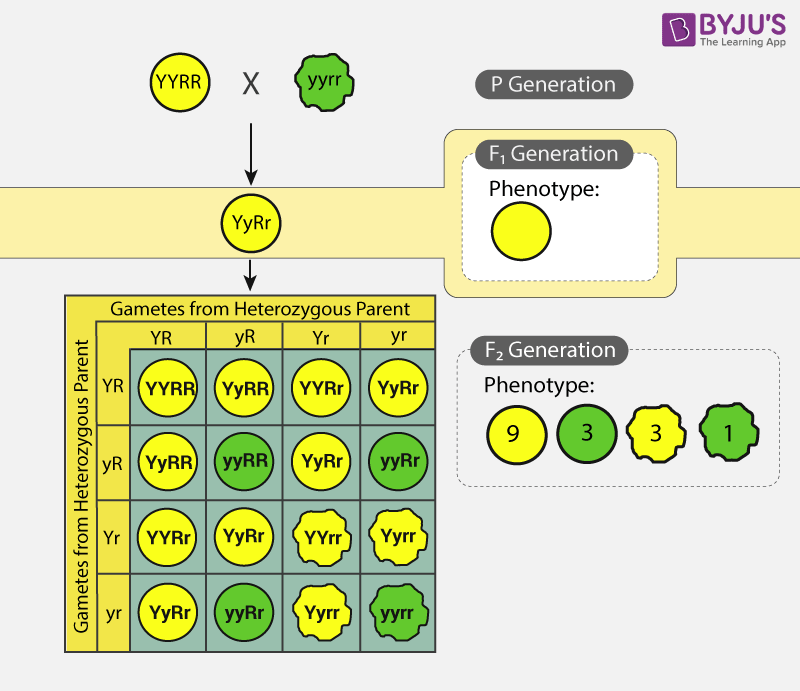
After conducting research for other traits, the results were found to be similar. From this experiment, Mendel formulated his second law of inheritance i.e. law of Independent Assortment.
- The genetic makeup of the plant is known as the genotype. On the contrary, the physical appearance of the plant is known as phenotype.
- The genes are transferred from parents to the offspring in pairs known as alleles.
- During gametogenesis when the chromosomes are halved, there is a 50% chance of one of the two alleles to fuse with the allele of the gamete of the other parent.
- When the alleles are the same, they are known as homozygous alleles and when the alleles are different they are known as heterozygous alleles.
Also Refer: Mendelian Genetics
The two experiments lead to the formulation of Mendel’s laws known as laws of inheritance which are:
- Law of Dominance
- Law of Segregation
- Law of Independent Assortment
This is also called Mendel’s first law of inheritance. According to the law of dominance, hybrid offspring will only inherit the dominant trait in the phenotype. The alleles that are suppressed are called the recessive traits while the alleles that determine the trait are known as the dominant traits.
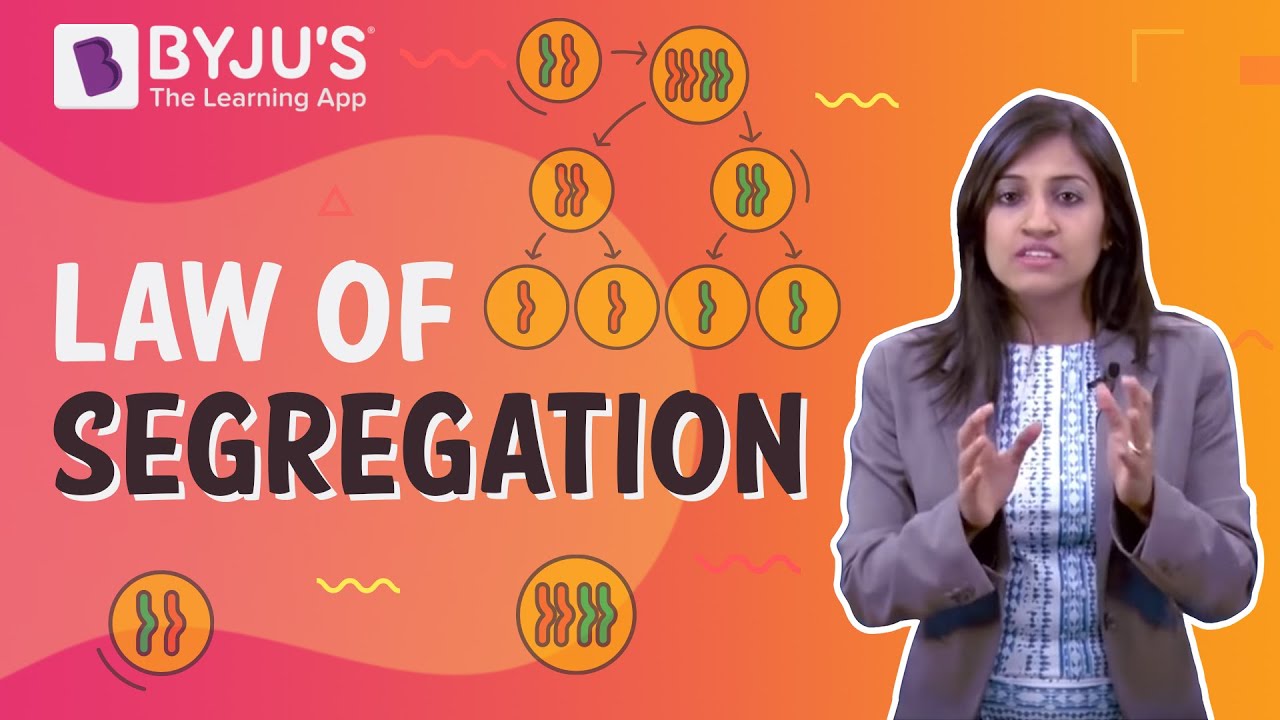
The law of segregation states that during the production of gametes, two copies of each hereditary factor segregate so that offspring acquire one factor from each parent. In other words, allele (alternative form of the gene) pairs segregate during the formation of gamete and re-unite randomly during fertilization. This is also known as Mendel’s third law of inheritance.
Also known as Mendel’s second law of inheritance, the law of independent assortment states that a pair of traits segregates independently of another pair during gamete formation. As the individual heredity factors assort independently, different traits get equal opportunity to occur together.
- The law of inheritance was proposed by Gregor Mendel after conducting experiments on pea plants for seven years.
- Mendel’s laws of inheritance include law of dominance, law of segregation and law of independent assortment.
- The law of segregation states that every individual possesses two alleles and only one allele is passed on to the offspring.
- The law of independent assortment states that the inheritance of one pair of genes is independent of inheritance of another pair.
Also Read: Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance. You can also download the BYJU’S app for further reference on Mendel’s laws.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three laws of inheritance proposed by mendel.
The three laws of inheritance proposed by Mendel include:
Which is the universally accepted law of inheritance?
Law of segregation is the universally accepted law of inheritance. It is the only law without any exceptions. It states that each trait consists of two alleles which segregate during the formation of gametes and one allele from each parent combines during fertilization.
Why is the law of segregation known as the law of purity of gametes?
The law of segregation is known as the law of purity of gametes because a gamete carries only a recessive or a dominant allele but not both the alleles.
Why was the pea plant used in Mendel’s experiments?
Mendel picked pea plants in his experiments because the pea plant has different observable traits. It can be grown easily in large numbers and its reproduction can be manipulated. Also, pea has both male and female reproductive organs, so they can self-pollinate as well as cross-pollinate.
What was the main aim of Mendel’s experiments?
The main aim of Mendel’s experiments was:
- To determine whether the traits would always be recessive.
- Whether traits affect each other as they are inherited.
- Whether traits could be transformed by DNA.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
very nice. it is the best to study about genetics
Genetic inheritance is so interesting
It helped me a lot Thanks
It is so amazing thanks a lot
Superb, it’s interesting.
It is very useful becoz all details explain in simple manner with examples
AWESOME, the above notes are fabulous
well that helped me a lot
Thanks, It helped me a lot!! Impeccable notes !!😍
Nice resource 👍
It helped me alot
If Mendel gave three law the what is the law of unit of characters and who proposed this law . Please clear my doubt a little bit faster , it is little important for me.
The Law of unit characters was proposed by Mendel. He explained that the inheritance of a trait is controlled by unit characters or factors, which are passed from parents to offspring through the gametes. These factors are now known as genes. Each factor exists in pairs, which are known as alleles.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated
Gregor Mendel and the Principles of Inheritance
Traits are passed down in families in different patterns. Pedigrees can illustrate these patterns by following the history of specific characteristics, or phenotypes, as they appear in a family. For example, the pedigree in Figure 1 shows a family in which a grandmother (generation I) has passed down a characteristic (shown in solid red) through the family tree. The inheritance pattern of this characteristic is considered dominant , because it is observable in every generation. Thus, every individual who carries the genetic code for this characteristic will show evidence of the characteristic. In contrast, Figure 2 shows a different pattern of inheritance, in which a characteristic disappears in one generation, only to reappear in a subsequent one. This pattern of inheritance, in which the parents do not show the phenotype but some of the children do, is considered recessive . But where did our knowledge of dominance and recessivity first come from?
Gregor Mendel’s Courage and Persistence
Mendel was curious about how traits were transferred from one generation to the next, so he set out to understand the principles of heredity in the mid-1860s. Peas were a good model system, because he could easily control their fertilization by transferring pollen with a small paintbrush. This pollen could come from the same flower (self-fertilization), or it could come from another plant's flowers (cross-fertilization). First, Mendel observed plant forms and their offspring for two years as they self-fertilized, or "selfed," and ensured that their outward, measurable characteristics remained constant in each generation. During this time, Mendel observed seven different characteristics in the pea plants, and each of these characteristics had two forms (Figure 3). The characteristics included height (tall or short), pod shape (inflated or constricted), seed shape (smooth or winkled), pea color (green or yellow), and so on. In the years Mendel spent letting the plants self, he verified the purity of his plants by confirming, for example, that tall plants had only tall children and grandchildren and so forth. Because the seven pea plant characteristics tracked by Mendel were consistent in generation after generation of self-fertilization, these parental lines of peas could be considered pure-breeders (or, in modern terminology, homozygous for the traits of interest). Mendel and his assistants eventually developed 22 varieties of pea plants with combinations of these consistent characteristics.
Mendel not only crossed pure-breeding parents, but he also crossed hybrid generations and crossed the hybrid progeny back to both parental lines. These crosses (which, in modern terminology, are referred to as F 1 , F 1 reciprocal, F 2 , B 1 , and B 2 ) are the classic crosses to generate genetically hybrid generations.
Understanding Dominant Traits
Understanding recessive traits.
When conducting his experiments, Mendel designated the two pure-breeding parental generations involved in a particular cross as P 1 and P 2 , and he then denoted the progeny resulting from the crossing as the filial, or F 1 , generation. Although the plants of the F 1 generation looked like one parent of the P generation, they were actually hybrids of two different parent plants. Upon observing the uniformity of the F 1 generation, Mendel wondered whether the F 1 generation could still possess the nondominant traits of the other parent in some hidden way.
To understand whether traits were hidden in the F 1 generation, Mendel returned to the method of self-fertilization. Here, he created an F 2 generation by letting an F 1 pea plant self-fertilize (F 1 x F 1 ). This way, he knew he was crossing two plants of the exact same genotype . This technique, which involves looking at a single trait, is today called a monohybrid cross . The resulting F 2 generation had seeds that were either round or wrinkled. Figure 4 shows an example of Mendel's data.
When looking at the figure, notice that for each F 1 plant, the self-fertilization resulted in more round than wrinkled seeds among the F 2 progeny. These results illustrate several important aspects of scientific data:
- Multiple trials are necessary to see patterns in experimental data.
- There is a lot of variation in the measurements of one experiment.
- A large sample size, or "N," is required to make any quantitative comparisons or conclusions.
In Figure 4, the result of Experiment 1 shows that the single characteristic of seed shape was expressed in two different forms in the F 2 generation: either round or wrinkled. Also, when Mendel averaged the relative proportion of round and wrinkled seeds across all F 2 progeny sets, he found that round was consistently three times more frequent than wrinkled. This 3:1 proportion resulting from F 1 x F 1 crosses suggested there was a hidden recessive form of the trait. Mendel recognized that this recessive trait was carried down to the F 2 generation from the earlier P generation .
Mendel and Alleles
As mentioned, Mendel's data did not support the ideas about trait blending that were popular among the biologists of his time. As there were never any semi-wrinkled seeds or greenish-yellow seeds, for example, in the F 2 generation, Mendel concluded that blending should not be the expected outcome of parental trait combinations. Mendel instead hypothesized that each parent contributes some particulate matter to the offspring. He called this heritable substance "elementen." (Remember, in 1865, Mendel did not know about DNA or genes.) Indeed, for each of the traits he examined, Mendel focused on how the elementen that determined that trait was distributed among progeny. We now know that a single gene controls seed form, while another controls color, and so on, and that elementen is actually the assembly of physical genes located on chromosomes. Multiple forms of those genes, known as alleles , represent the different traits. For example, one allele results in round seeds, and another allele specifies wrinkled seeds.
One of the most impressive things about Mendel's thinking lies in the notation that he used to represent his data. Mendel's notation of a capital and a lowercase letter ( Aa ) for the hybrid genotype actually represented what we now know as the two alleles of one gene : A and a . Moreover, as previously mentioned, in all cases, Mendel saw approximately a 3:1 ratio of one phenotype to another. When one parent carried all the dominant traits ( AA ), the F 1 hybrids were "indistinguishable" from that parent. However, even though these F 1 plants had the same phenotype as the dominant P 1 parents, they possessed a hybrid genotype ( Aa ) that carried the potential to look like the recessive P 1 parent ( aa ). After observing this potential to express a trait without showing the phenotype, Mendel put forth his second principle of inheritance: the principle of segregation . According to this principle, the "particles" (or alleles as we now know them) that determine traits are separated into gametes during meiosis , and meiosis produces equal numbers of egg or sperm cells that contain each allele (Figure 5).
Dihybrid Crosses
Mendel had thus determined what happens when two plants that are hybrid for one trait are crossed with each other, but he also wanted to determine what happens when two plants that are each hybrid for two traits are crossed. Mendel therefore decided to examine the inheritance of two characteristics at once. Based on the concept of segregation , he predicted that traits must sort into gametes separately. By extrapolating from his earlier data, Mendel also predicted that the inheritance of one characteristic did not affect the inheritance of a different characteristic.
Mendel tested this idea of trait independence with more complex crosses. First, he generated plants that were purebred for two characteristics, such as seed color (yellow and green) and seed shape (round and wrinkled). These plants would serve as the P 1 generation for the experiment. In this case, Mendel crossed the plants with wrinkled and yellow seeds ( rrYY ) with plants with round, green seeds ( RRyy ). From his earlier monohybrid crosses, Mendel knew which traits were dominant: round and yellow. So, in the F 1 generation, he expected all round, yellow seeds from crossing these purebred varieties, and that is exactly what he observed. Mendel knew that each of the F 1 progeny were dihybrids; in other words, they contained both alleles for each characteristic ( RrYy ). He then crossed individual F 1 plants (with genotypes RrYy ) with one another. This is called a dihybrid cross . Mendel's results from this cross were as follows:
- 315 plants with round, yellow seeds
- 108 plants with round, green seeds
- 101 plants with wrinkled, yellow seeds
- 32 plants with wrinkled, green seeds
Thus, the various phenotypes were present in a 9:3:3:1 ratio (Figure 6).
Next, Mendel went through his data and examined each characteristic separately. He compared the total numbers of round versus wrinkled and yellow versus green peas, as shown in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1: Data Regarding Seed Shape
Table 2: Data Regarding Pea Color
The proportion of each trait was still approximately 3:1 for both seed shape and seed color. In other words, the resulting seed shape and seed color looked as if they had come from two parallel monohybrid crosses; even though two characteristics were involved in one cross, these traits behaved as though they had segregated independently. From these data, Mendel developed the third principle of inheritance: the principle of independent assortment . According to this principle, alleles at one locus segregate into gametes independently of alleles at other loci. Such gametes are formed in equal frequencies.
Mendel’s Legacy
More lasting than the pea data Mendel presented in 1862 has been his methodical hypothesis testing and careful application of mathematical models to the study of biological inheritance. From his first experiments with monohybrid crosses, Mendel formed statistical predictions about trait inheritance that he could test with more complex experiments of dihybrid and even trihybrid crosses. This method of developing statistical expectations about inheritance data is one of the most significant contributions Mendel made to biology.
But do all organisms pass their on genes in the same way as the garden pea plant? The answer to that question is no, but many organisms do indeed show inheritance patterns similar to the seminal ones described by Mendel in the pea. In fact, the three principles of inheritance that Mendel laid out have had far greater impact than his original data from pea plant manipulations. To this day, scientists use Mendel's principles to explain the most basic phenomena of inheritance.
References and Recommended Reading
- Add Content to Group
Article History
Flag inappropriate.


Email your Friend

- | Lead Editor: Terry McGuire

Within this Subject (29)
- Gene Linkage (5)
- Methods for Studying Inheritance Patterns (7)
- The Foundation of Inheritance Studies (11)
- Variation in Gene Expression (6)
Other Topic Rooms
- Gene Inheritance and Transmission
- Gene Expression and Regulation
- Nucleic Acid Structure and Function
- Chromosomes and Cytogenetics
- Evolutionary Genetics
- Population and Quantitative Genetics
- Genes and Disease
- Genetics and Society
- Cell Origins and Metabolism
- Proteins and Gene Expression
- Subcellular Compartments
- Cell Communication
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
© 2014 Nature Education
- Press Room |
- Terms of Use |
- Privacy Notice |

Visual Browse
NOTIFICATIONS
Mendel’s experiments.
- + Create new collection
Mendel is known as the father of genetics because of his ground-breaking work on inheritance in pea plants 150 years ago.
Gregor Johann Mendel was a monk and teacher with interests in astronomy and plant breeding. He was born in 1822, and at 21, he joined a monastery in Brünn (now in the Czech Republic). The monastery had a botanical garden and library and was a centre for science, religion and culture . In 1856, Mendel began a series of experiments at the monastery to find out how traits are passed from generation to generation. At the time, it was thought that parents’ traits were blended together in their progeny .
Studying traits in peas
Mendel studied inheritance in peas ( Pisum sativum ). He chose peas because they had been used for similar studies, are easy to grow and can be sown each year. Pea flowers contain both male and female parts, called stamen and stigma , and usually self-pollinate. Self-pollination happens before the flowers open, so progeny are produced from a single plant.
Peas can also be cross-pollinated by hand, simply by opening the flower buds to remove their pollen-producing stamen (and prevent self-pollination) and dusting pollen from one plant onto the stigma of another.
Traits in pea plants
Mendel followed the inheritance of 7 traits in pea plants, and each trait had 2 forms. He identified pure-breeding pea plants that consistently showed 1 form of a trait after generations of self-pollination.
Mendel then crossed these pure-breeding lines of plants and recorded the traits of the hybrid progeny. He found that all of the first-generation (F1) hybrids looked like 1 of the parent plants. For example, all the progeny of a purple and white flower cross were purple (not pink, as blending would have predicted). However, when he allowed the hybrid plants to self-pollinate, the hidden traits would reappear in the second-generation (F2) hybrid plants.
Dominant and recessive traits
Mendel described each of the trait variants as dominant or recessive Dominant traits, like purple flower colour, appeared in the F1 hybrids, whereas recessive traits, like white flower colour, did not.
Mendel did thousands of cross-breeding experiments. His key finding was that there were 3 times as many dominant as recessive traits in F2 pea plants (3:1 ratio).
Traits are inherited independently
Mendel also experimented to see what would happen if plants with 2 or more pure-bred traits were cross-bred. He found that each trait was inherited independently of the other and produced its own 3:1 ratio. This is the principle of independent assortment.
Find out more about Mendel’s principles of inheritance .
The next generations
Mendel didn’t stop there – he continued to allow the peas to self-pollinate over several years whilst meticulously recording the characteristics of the progeny. He may have grown as many as 30,000 pea plants over 7 years.
Mendel’s findings were ignored
In 1866, Mendel published the paper Experiments in plant hybridisation ( Versuche über plflanzenhybriden ). In it, he proposed that heredity is the result of each parent passing along 1 factor for every trait. If the factor is dominant , it will be expressed in the progeny. If the factor is recessive, it will not show up but will continue to be passed along to the next generation. Each factor works independently from the others, and they do not blend.
The science community ignored the paper, possibly because it was ahead of the ideas of heredity and variation accepted at the time. In the early 1900s, 3 plant biologists finally acknowledged Mendel’s work. Unfortunately, Mendel was not around to receive the recognition as he had died in 1884.
Useful links
Download a translated version of Mendel’s 1866 paper Experiments in plant hybridisation from Electronic Scholarly Publishing.
This apple cross-pollination video shows scientists at Plant & Food Research cross-pollinating apple plants.
See our newsletters here .
Would you like to take a short survey?
This survey will open in a new tab and you can fill it out after your visit to the site.

5.10 Mendel’s Experiments and Laws of Inheritance
Of peas and people.

These purple-flowered plants are not just pretty to look at. Plants like these led to a huge leap forward in biology. They’re common garden peas, and they were studied in the mid-1800s by an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel . Through careful experimentation, Mendel uncovered the secrets of heredity, or how parents pass characteristics to their offspring. You may not care much about heredity in pea plants, but you probably care about your own heredity. Mendel’s discoveries apply to people, as well as to peas — and to all other living things that reproduce sexually. In this concept, you will read about Mendel’s experiments and the secrets of heredity that he discovered.
Mendel and His Pea Plants

Gregor Mendel (Figure 5.10.2) was born in 1822. He grew up on his parents’ farm in Austria. He did well in school and became a friar (and later an abbot) at St. Thomas’ Abbey. Through sponsorship from the monastery, he went on to the University of Vienna, where he studied science and math. His professors encouraged him to learn science through experimentation, and to use math to make sense of his results. Mendel is best known for his experiments with pea plants (like the purple flower pictured in Figure 5.10.1).
Blending Theory of Inheritance

During Mendel’s time, the blending theory of inheritance was popular. According to this theory, offspring have a blend (or mix) of their parents’ characteristics. Mendel, however, noticed plants in his own garden that weren’t a blend of the parents. For example, a tall plant and a short plant had offspring that were either tall or short — not medium in height. Observations such as these led Mendel to question the blending theory. He wondered if there was a different underlying principle that could explain how characteristics are inherited. He decided to experiment with pea plants to find out. In fact, Mendel experimented with almost 30 thousand pea plants over the next several years!
Why Study Pea Plants?
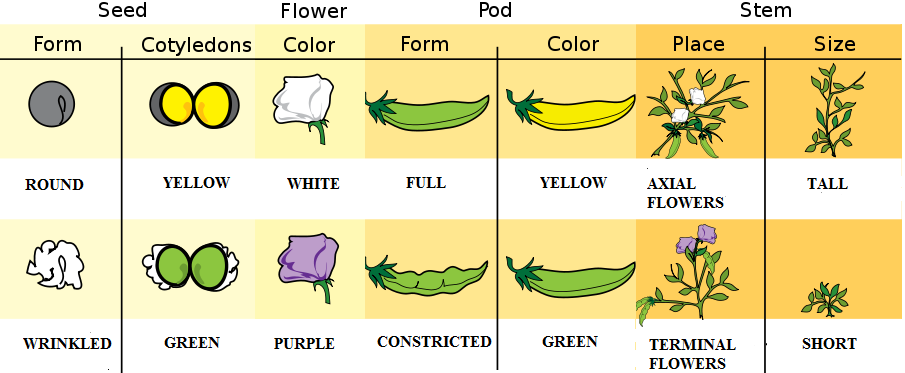
Why did Mendel choose common, garden-variety pea plants for his experiments? Pea plants are a good choice because they are fast-growing and easy to raise. They also have several visible characteristics that can vary. These characteristics — some of which are illustrated in Figure 5.10.4 — include seed form and colour, flower colour, pod form and colour, placement of pods and flowers on stems, and stem length. Each of these characteristics has two common values. For example, seed form may be round or wrinkled, and flower colour may be white or purple (violet).
Controlling Pollination
To research how characteristics are passed from parents to offspring, Mendel needed to control pollination , which is the fertilization step in the sexual reproduction of plants. Pollen consists of tiny grains that are the male sex cells (or gametes) of plants. They are produced by a male flower part called the anther. Pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same or another flower. The stigma is a female part of a flower, and it passes pollen grains to female gametes in the ovary.
Pea plants are naturally self-pollinating. In self-pollination , pollen grains from anthers on one plant are transferred to stigmas of flowers on the same plant. Mendel was interested in the offspring of two different parent plants, so he had to prevent self-pollination. He removed the anthers from the flowers of some of the plants in his experiments. Then he pollinated them by hand using a small paintbrush with pollen from other parent plants of his choice.
When pollen from one plant fertilizes another plant of the same species, it is called cross-pollination . The offspring that result from such a cross are called hybrids . When the term hybrid is used in this context, it refers to any offspring resulting from the breeding of two genetically distinct individuals.
Mendel’s First Set of Experiments
At first, Mendel experimented with just one characteristic at a time. He began with flower colour. As shown in Figure 5.10.5, Mendel cross-pollinated purple- and white-flowered parent plants. The parent plants in the experiments are referred to as the P (for parent) generation.
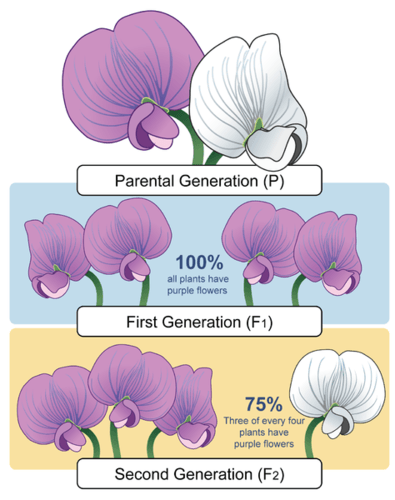
Figure 5.10.5 shows Mendel’s first experiment with pea plants. The F1 generation results from the cross-pollination of two parent (P) plants, and it contains all purple flowers. The F2 generation results from the self-pollination of F1 plants, and contains 75% purple flowers and 25% white flowers.
F1 and F2 Generations
The offspring of the P generation are called the F1 (for filial, or “offspring”) generation. As shown in Figure 5.10.5, all of the plants in the F1 generation had purple flowers — none of them had white flowers. Mendel wondered what had happened to the white-flower characteristic. He assumed that some type of inherited factor produces white flowers and some other inherited factor produces purple flowers. Did the white-flower factor just disappear in the F1 generation? If so, then the offspring of the F1 generation — called the F2 generation — should all have purple flowers like their parents.
To test this prediction, Mendel allowed the F1 generation plants to self-pollinate. He was surprised by the results. Some of the F2 generation plants had white flowers. He studied hundreds of F2 generation plants, and for every three purple-flowered plants, there was an average of one white-flowered plant.
Law of Segregation
Mendel did the same experiment for all seven characteristics. In each case, one value of the characteristic disappeared in the F1 plants, later showing up again in the F2 plants. In each case, 75 per cent of F2 plants had one value of the characteristic, while 25 per cent had the other value. Based on these observations, Mendel formulated his first law of inheritance. This law is called the law of segregation . It states that there are two factors controlling a given characteristic, one of which dominates the other, and these factors separate and go to different gametes when a parent reproduces.
Mendel’s Second Set of Experiments
Mendel wondered whether different characteristics are inherited together. For example, are purple flowers and tall stems always inherited together, or do these two characteristics show up in different combinations in offspring? To answer these questions, Mendel next investigated two characteristics at a time. For example, he crossed plants with yellow round seeds and plants with green wrinkled seeds. The results of this cross are shown in Figure 5.10.6.
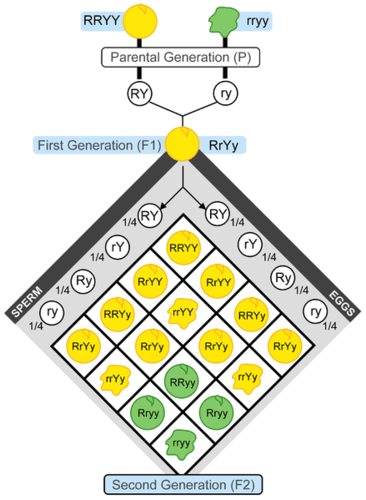
Figure 5.10.6 shows the outcome of a cross between plants that differ in seed colour (yellow or green) and seed form (shown here with a smooth round appearance or wrinkled appearance). The letters R, r, Y, and y represent genes for the characteristics Mendel was studying. Mendel didn’t know about genes, however, because genes would not be discovered until several decades later. This experiment demonstrates that, in the F2 generation, nine out of 16 were round yellow seeds, three out of 16 were wrinkled yellow seeds, three out of 16 were round green seeds, and one out of 16 was wrinkled green seeds.
In this set of experiments, Mendel observed that plants in the F1 generation were all alike. All of them had yellow round seeds like one of the two parents. When the F1 generation plants self-pollinated, however, their offspring — the F2 generation — showed all possible combinations of the two characteristics. Some had green round seeds, for example, and some had yellow wrinkled seeds. These combinations of characteristics were not present in the F1 or P generations.
Law of Independent Assortment
Mendel repeated this experiment with other combinations of characteristics, such as flower colour and stem length. Each time, the results were the same as those shown in Figure 5.10.6. The results of Mendel’s second set of experiments led to his second law. This is the law of independent assortment . It states that factors controlling different characteristics are inherited independently of each other.
Mendel’s Legacy
You might think that Mendel’s discoveries would have made a big impact on science as soon as he made them, but you would be wrong. Why? Because Mendel’s work was largely ignored. Mendel was far ahead of his time, and he was working from a remote monastery. He had no reputation in the scientific community and had only published sparingly in the past. Additionally, he published this research in an obscure scientific journal. As a result, when Charles Darwin published his landmark book on evolution in 1869, although Mendel’s work had been published just a few years earlier, Darwin was unaware of it. Consequently, Darwin knew nothing about Mendel’s laws, and didn’t understand heredity. This made Darwin’s arguments about evolution less convincing to many.
Then, in 1900, three different European scientists — Hugo de DeVries , Carl Correns , and Erich von Tschermak — arrived independently at Mendel’s laws. All three had done experiments similar to Mendel’s and come to the same conclusions that he had drawn several decades earlier. Only then was Mendel’s work rediscovered, so that Mendel himself could be given the credit he was due. Although Mendel knew nothing about genes, which were discovered after his death, he is now considered the father of genetics.
5.10 Cultural Connection
Corn is the world’s most produced crop. Canada produces 13,000-14,000 metric Kilo tonnes of corn annually, mostly in fields in Ontario, Quebec and Manitoba. Approximately 1.5 million hectares are devoted to this crop which is critically important for both humans and livestock as a food source. Despite these high numbers of output, Canada is still only 11th on the list of world corn producers, with USA, China and Brazil claiming the top three places. How did corn become such an important part of modern agriculture?
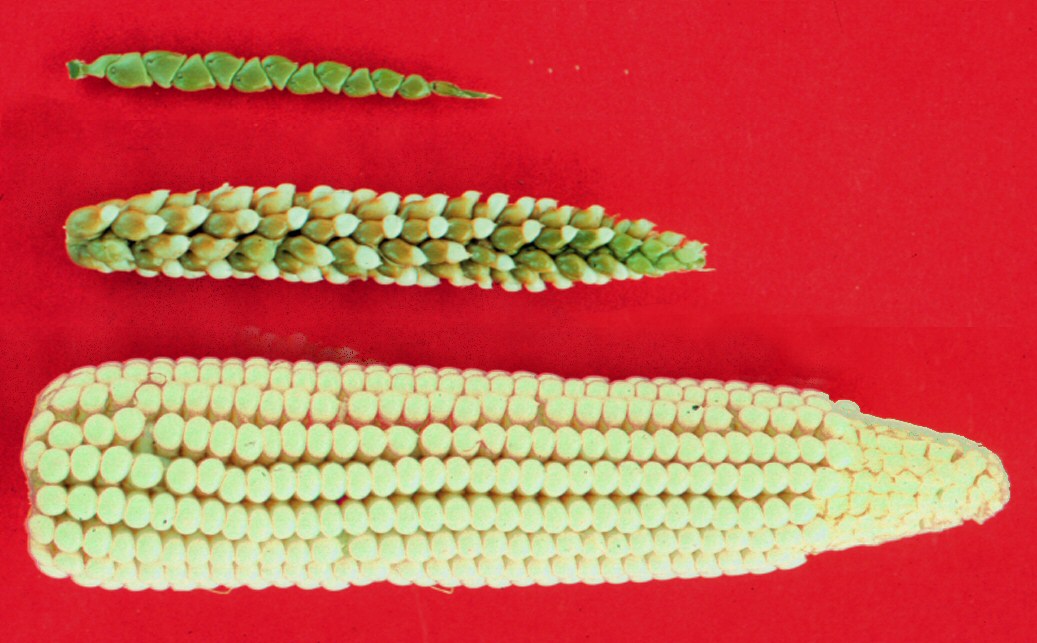

We didn’t always have corn as we know it. Modern corn is descended from a type of grass called teosinte (Figure 5.10.7) native to Mesoamerica (southern part of North America). It is estimated that Indigenous people have been harvesting corn and corn ancestors for over 9000 years. Excavations of the Xihuatoxtla Shelter in southwestern Mexico revealed our earliest evidence of domesticated corn: maize remains on tools dating back 8,700 years.
Ancient Indigenous peoples of southern Mexico developed corn from grass plants using a process we now call selective breeding , also known as artificial selection . Teosinte doesn’t resemble the corn we have today- it had only a few kernels individually encased on very hard shells, and yet today we have multiple varieties of corn with row upon row of bare kernels. This means that ancient agriculturalists among the Indigenous people of Mexico were intentionally cross-breeding strains of teosinte, and later, early maize to create plants which had more kernels, and reduced seed casings. Watch the TED Ed video in the Explore More section to see what other changes agriculturalists have made to modern-day corn.
5.10 Summary
- Mendel experimented with the inheritance of traits in pea plants at a time when the blending theory of inheritance was popular. This is the theory that offspring have a blend of the characteristics of their parents.
- Pea plants were good choices for this research, largely because they have several visible characteristics that exist in two different forms. By controlling pollination, Mendel was able to cross pea plants with different forms of the traits.
- In Mendel’s first set of experiments, he experimented with just one characteristic at a time. The results of this set of experiments led to Mendel’s first law of inheritance, called the law of segregation . This law states that there are two factors controlling a given characteristic, one of which dominates the other, and these factors separate and go to different gametes when a parent reproduces.
- In Mendel’s second set of experiments, he experimented with two characteristics at a time. The results of this set of experiments led to Mendel’s second law of inheritance, called the law of independent assortment . This law states that the factors controlling different characteristics are inherited independently of each other.
- Mendel’s work was largely ignored during his own lifetime. However, when other researchers arrived at the same laws in 1900, Mendel’s work was rediscovered, and he was given the credit he was due. He is now considered the father of genetics.
5.10 Review Questions
- Why were pea plants a good choice for Mendel’s experiments?
- How did the outcome of Mendel’s second set of experiments lead to his second law?
- Discuss the development of Mendel’s legacy.
- If Mendel’s law of independent assortment was not correct, and characteristics were always inherited together, what types of offspring do you think would have been produced by crossing plants with yellow round seeds and green wrinkled seeds? Explain your answer.
5.10 Explore More
How Mendel’s pea plants helped us understand genetics – Hortensia Jiménez Díaz, TED-Ed, 2013.
10 Strange Hybrid Fruits, Junkyboss, 2016.
The history of the world according to corn – Chris A. Kniesly, TED-Ed, 2019.
Attributions
Figure 5.10.1
Purple sweet pea flower by unknown on Yana Ray on publicdomainpictures.net is used under a CC0 1.0 p ublic domain dedication license ( https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en) .
Figure 5.10.2
Gregor_Mendel by unknown from National Institutes of Health , Health & Human Services on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 5.10.3
Gregor Mendel in Lego by Alan on Flickr is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/) license.
Figure 5.10.4
Mendels_peas by Mariana Ruiz [ LadyofHats ] on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC0 1.0 p ublic domain dedication license ( https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en) .
Figure 5.10.5
Mendel’s first experiment with pea plants by CK-12 Foundation is used under a CC BY-NC 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) license.

Figure 5.10.6
Mendel’s Second Experiment by by CK-12 Foundation is used under a CC BY-NC 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) license.
Figure 5.10.7
Maize-teosinte by John Doebley on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en) license.
Brainard, J/ CK-12 Foundation. (2016). Figure 5 Mendel’s first experiment [digital image]. In CK-12 College Human Biology (Section 5.9) [online Flexbook]. CK12.org. https://www.ck12.org/book/ck-12-human-biology/section/5.9/
Brainard, J/ CK-12 Foundation. (2016). Figure 6 Mendel’s second experiment [digital image]. In CK-12 College Human Biology (Section 5.9) [online Flexbook]. CK12.org. https://www.ck12.org/book/ck-12-human-biology/section/5.9/
Junkyboss. (2016, March 31). 10 Strange hybrid fruits. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ogc367xyzfk&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2013, March 12). How Mendel’s pea plants helped us understand genetics – Hortensia Jiménez Díaz. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mehz7tCxjSE&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2019, November 26). The history of the world according to corn – Chris A. Kniesly. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i6teBcfKpik&feature=youtu.be
Wikipedia contributors. (2020, June 1). Carl Correns. In Wikipedia . https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Carl_Correns&oldid=960172546
Wikipedia contributors. (2020, July 8). Charles Darwin. In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Charles_Darwin&oldid=966652322
Wikipedia contributors. (2020, March 9). Erich von Tschermak. In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Erich_von_Tschermak&oldid=944695823
Wikipedia contributors. (2020, July 7). Hugo de Vries. In Wikipedia . https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Hugo_de_Vries&oldid=966513671
The innermost layer of the hair shaft. This nearly invisible layer is the most soft and fragile, and serves as the pith or marrow of the hair.
Located between the hair cuticle and medulla and is the thickest hair layer. It also contains most of the hair's pigment, giving the hair its color. The pigment in the cortex is melanin, which is also found in skin.
When one plant pollinates a plant of another variety. The two plants' genetic material combines and the resulting seeds from that pollination will have characteristics of both varieties and is a new variety.
The outermost part of the hair shaft. It is formed from dead cells, overlapping in layers, which form scales that strengthen and protect the hair shaft.
A part of a hair that is visible above the surface of the skin and consists of dead keratinocytes.
The part of a hair that is located within the hair follicle and consists of living keratinocytes.
The identification by humans of desirable traits in plants and animals, and the steps taken to enhance and perpetuate those traits in future generations.
Biology: A Human Approach by Molly Ostwald is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Microbe Notes
Mendel’s 3 Laws (Segregation, Independent Assortment, Dominance)
- In the 1860s, an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel introduced a new theory of inheritance based on his experimental work with pea plants.
- Mendel believed that heredity is the result of discrete units of inheritance, and every single unit (or gene) was independent in its actions in an individual’s genome.
- According to this Mendelian concept, the inheritance of a trait depended on the passing-on of these units.
- For any given trait, an individual inherits one gene from each parent so that the individual has a pairing of two genes. We now understand the alternate forms of these units as ‘alleles’.
- If the two alleles that form the pair for a trait are identical, then the individual is said to be homozygous and if the two genes are different, then the individual is heterozygous for the trait.
- The breeding experiments of the monk in the mid‐1800s laid the groundwork for the science of genetics.
- He studied peas plant for 7 years and published his results in 1866 which was ignored until 1900 when three separate botanists, who also were theorizing about heredity in plants, independently cited the work.
- In appreciation of his work he was considered as the “Father of Genetics”.
- A new stream of genetics was established after his name as Mendelian genetics which involves the study of heredity of both qualitative (monogenic) and quantitative (polygenic) traits and the influence of environment on their expressions.
- Mendelian inheritance while is a type of biological inheritance that follows the laws originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866 and re-discovered in 1900.
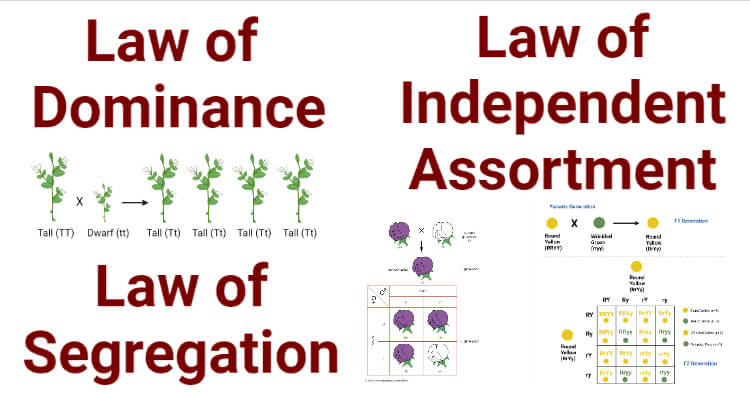
Table of Contents
Interesting Science Videos
Mendel’s Experiment
Mendel carried out breeding experiments in his monastery’s garden to test inheritance patterns. He selectively cross-bred common pea plants ( Pisum sativum ) with selected traits over several generations. After crossing two plants which differed in a single trait (tall stems vs. short stems, round peas vs. wrinkled peas, purple flowers vs. white flowers, etc), Mendel discovered that the next generation, the “F1” (first filial generation), was comprised entirely of individuals exhibiting only one of the traits. However, when this generation was interbred, its offspring, the “F2” (second filial generation), showed a 3:1 ratio- three individuals had the same trait as one parent and one individual had the other parent’s trait.
Mendel’s Laws
I. Mendel’s Law of Segregation of genes (the “First Law”)
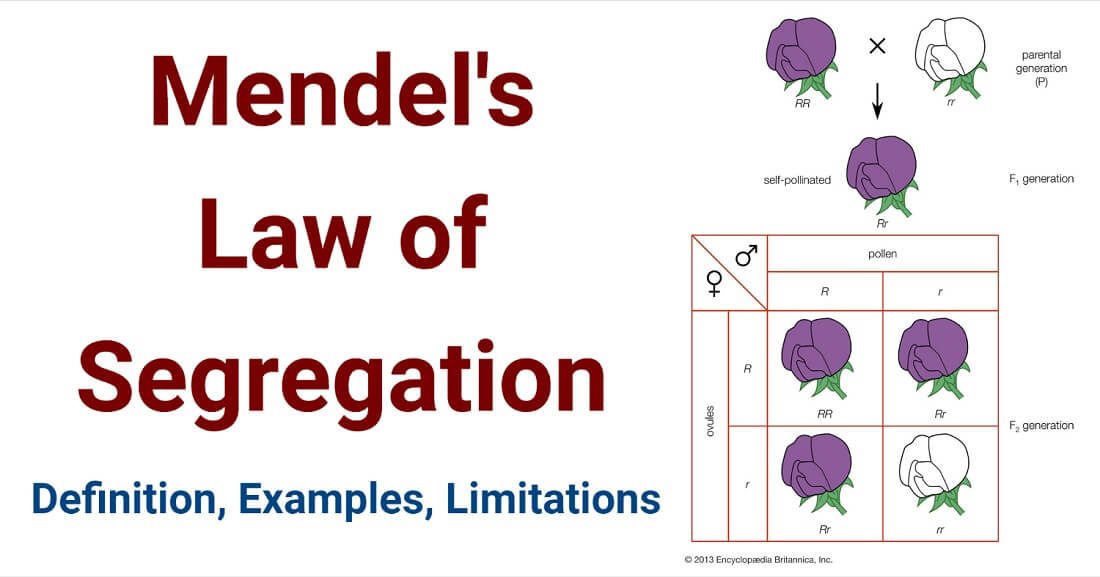
Image Source: Encyclopædia Britannica .
- The Law of Segregation states that every individual organism contains two alleles for each trait, and that these alleles segregate (separate) during meiosis such that each gamete contains only one of the alleles.
- An offspring thus receives a pair of alleles for a trait by inheriting homologous chromosomes from the parent organisms: one allele for each trait from each parent.
- Hence, according to the law, two members of a gene pair segregate from each other during meiosis; each gamete has an equal probability of obtaining either member of the gene.
II. Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment (the “Second Law”)
- Mendel’s second law. The law of independent assortment; unlinked or distantly linked segregating genes pairs behave independently.
- The Law of Independent Assortment states that alleles for separate traits are passed independently of one another.
- That is, the biological selection of an allele for one trait has nothing to do with the selection of an allele for any other trait.
- Mendel found support for this law in his dihybrid cross experiments. In his monohybrid crosses, an idealized 3:1 ratio between dominant and recessive phenotypes resulted. In dihybrid crosses, however, he found a 9:3:3:1 ratios.
- This shows that each of the two alleles is inherited independently from the other, with a 3:1 phenotypic ratio for each.
III. Mendel’s Law of Dominance (the “Third Law”)
- The genotype of an individual is made up of the many alleles it possesses.
- An individual’s physical appearance, or phenotype, is determined by its alleles as well as by its environment.
- The presence of an allele does not mean that the trait will be expressed in the individual that possesses it.
- If the two alleles of an inherited pair differ (the heterozygous condition), then one determines the organism’s appearance and is called the dominant allele; the other has no noticeable effect on the organism’s appearance and is called the recessive allele.
- Thus, the dominant allele will hide the phenotypic effects of the recessive allele.
- This is known as the Law of Dominance but it is not a transmission law: it concerns the expression of the genotype.
- The upper case letters are used to represent dominant alleles whereas the lowercase letters are used to represent recessive alleles.
- Verma, P. S., & Agrawal, V. K. (2006). Cell Biology, Genetics, Molecular Biology, Evolution & Ecology (1 ed.). S .Chand and company Ltd.
- Gardner, E. J., Simmons, M. J., & Snustad, D. P. (1991). Principles of genetics. New York: J. Wiley.
- https://www.cliffsnotes.com/study-guides/biology/plant-biology/genetics/mendelian-genetics
- http://kmbiology.weebly.com/mendel-and-genetics—notes.html
- http://knowgenetics.org/mendelian-genetics/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mendelian_inheritance
- https://www.acpsd.net/site/handlers/filedownload.ashx?moduleinstanceid=40851&dataid=33888&FileName=Mendelian%20Genetics.pdf
About Author
Sagar Aryal

2 thoughts on “Mendel’s 3 Laws (Segregation, Independent Assortment, Dominance)”
Good to know when one works with plants like me.
excellet ohhh
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
21 Mendel’s Experiments
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain the scientific reasons for the success of Mendel’s experimental work
- Describe the expected outcomes of monohybrid crosses involving dominant and recessive alleles

Johann Gregor Mendel (1822–1884) (Figure 1) was a lifelong learner, teacher, scientist, and man of faith. As a young adult, he joined the Augustinian Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno in what is now the Czech Republic. Supported by the monastery, he taught physics, botany, and natural science courses at the secondary and university levels. In 1856, he began a decade-long research pursuit involving inheritance patterns in honeybees and plants, ultimately settling on pea plants as his primary model system (a system with convenient characteristics that is used to study a specific biological phenomenon to gain understanding to be applied to other systems). In 1865, Mendel presented the results of his experiments with nearly 30,000 pea plants to the local natural history society. He demonstrated that traits are transmitted faithfully from parents to offspring in specific patterns. In 1866, he published his work, Experiments in Plant Hybridization, 1 in the proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn.
Mendel’s work went virtually unnoticed by the scientific community, which incorrectly believed that the process of inheritance involved a blending of parental traits that produced an intermediate physical appearance in offspring. This hypothetical process appeared to be correct because of what we know now as continuous variation. Continuous variation is the range of small differences we see among individuals in a characteristic like human height. It does appear that offspring are a “blend” of their parents’ traits when we look at characteristics that exhibit continuous variation. Mendel worked instead with traits that show discontinuous variation . Discontinuous variation is the variation seen among individuals when each individual shows one of two—or a very few—easily distinguishable traits, such as violet or white flowers. Mendel’s choice of these kinds of traits allowed him to see experimentally that the traits were not blended in the offspring as would have been expected at the time, but that they were inherited as distinct traits. In 1868, Mendel became abbot of the monastery and exchanged his scientific pursuits for his pastoral duties. He was not recognized for his extraordinary scientific contributions during his lifetime; in fact, it was not until 1900 that his work was rediscovered, reproduced, and revitalized by scientists on the brink of discovering the chromosomal basis of heredity.
Mendel’s Crosses
Mendel’s seminal work was accomplished using the garden pea, Pisum sativum , to study inheritance. This species naturally self-fertilizes, meaning that pollen encounters ova within the same flower. The flower petals remain sealed tightly until pollination is completed to prevent the pollination of other plants. The result is highly inbred, or “true-breeding,” pea plants. These are plants that always produce offspring that look like the parent. By experimenting with true-breeding pea plants, Mendel avoided the appearance of unexpected traits in offspring that might occur if the plants were not true-breeding. The garden pea also grows to maturity within one season, meaning that several generations could be evaluated over a relatively short time. Finally, large quantities of garden peas could be cultivated simultaneously, allowing Mendel to conclude that his results did not come about simply by chance.
Mendel performed hybridizations , which involve mating two true-breeding individuals that have different traits. In the pea, which is naturally self-pollinating, this is done by manually transferring pollen from the anther of a mature pea plant of one variety to the stigma of a separate mature pea plant of the second variety.
Plants used in first-generation crosses were called P , or parental generation, plants (Figure 2). Mendel collected the seeds produced by the P plants that resulted from each cross and grew them the following season. These offspring were called the F 1 , or the first filial (filial = daughter or son), generation. Once Mendel examined the characteristics in the F 1 generation of plants, he allowed them to self-fertilize naturally. He then collected and grew the seeds from the F 1 plants to produce the F 2 , or second filial, generation. Mendel’s experiments extended beyond the F 2 generation to the F 3 generation, F 4 generation, and so on, but it was the ratio of characteristics in the P, F 1 , and F 2 generations that were the most intriguing and became the basis of Mendel’s postulates.
Garden Pea Characteristics Revealed the Basics of Heredity
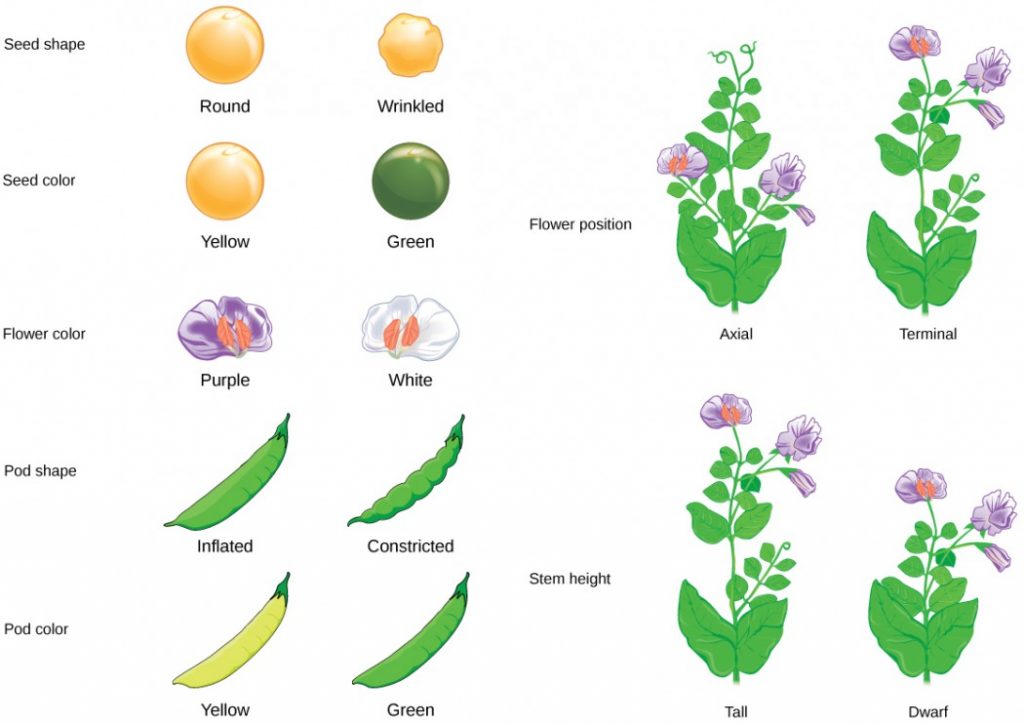
In his 1865 publication, Mendel reported the results of his crosses involving seven different characteristics, each with two contrasting traits. A trait is defined as a variation in the physical appearance of a heritable characteristic. The characteristics included plant height, seed texture, seed color, flower color, pea-pod size, pea-pod color, and flower position. For the characteristic of flower color, for example, the two contrasting traits were white versus violet. To fully examine each characteristic, Mendel generated large numbers of F 1 and F 2 plants and reported results from thousands of F 2 plants.
What results did Mendel find in his crosses for flower color? First, Mendel confirmed that he was using plants that bred true for white or violet flower color. Irrespective of the number of generations that Mendel examined, all self-crossed offspring of parents with white flowers had white flowers, and all self-crossed offspring of parents with violet flowers had violet flowers. In addition, Mendel confirmed that, other than flower color, the pea plants were physically identical. This was an important check to make sure that the two varieties of pea plants only differed with respect to one trait, flower color.
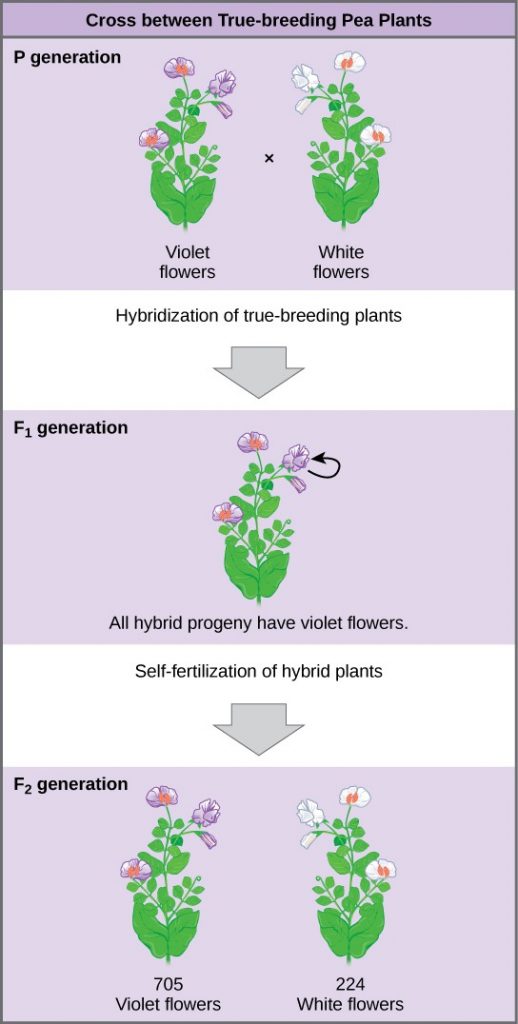
Once these validations were complete, Mendel applied the pollen from a plant with violet flowers to the stigma of a plant with white flowers. After gathering and sowing the seeds that resulted from this cross, Mendel found that 100 percent of the F 1 hybrid generation had violet flowers. Conventional wisdom at that time would have predicted the hybrid flowers to be pale violet or for hybrid plants to have equal numbers of white and violet flowers. In other words, the contrasting parental traits were expected to blend in the offspring. Instead, Mendel’s results demonstrated that the white flower trait had completely disappeared in the F 1 generation.
Importantly, Mendel did not stop his experimentation there. He allowed the F 1 plants to self-fertilize and found that 705 plants in the F 2 generation had violet flowers and 224 had white flowers. This was a ratio of 3.15 violet flowers to one white flower, or approximately 3:1. When Mendel transferred pollen from a plant with violet flowers to the stigma of a plant with white flowers and vice versa, he obtained approximately the same ratio irrespective of which parent—male or female—contributed which trait. This is called a reciprocal cross —a paired cross in which the respective traits of the male and female in one cross become the respective traits of the female and male in the other cross. For the other six characteristics that Mendel examined, the F 1 and F 2 generations behaved in the same way that they behaved for flower color. One of the two traits would disappear completely from the F 1 generation, only to reappear in the F 2 generation at a ratio of roughly 3:1 (Figure 3).
Upon compiling his results for many thousands of plants, Mendel concluded that the characteristics could be divided into expressed and latent traits. He called these dominant and recessive traits, respectively. Dominant traits are those that are inherited unchanged in a hybridization. Recessive traits become latent, or disappear in the offspring of a hybridization. The recessive trait does, however, reappear in the progeny of the hybrid offspring. An example of a dominant trait is the violet-colored flower trait. For this same characteristic (flower color), white-colored flowers are a recessive trait. The fact that the recessive trait reappeared in the F 2 generation meant that the traits remained separate (and were not blended) in the plants of the F 1 generation. Mendel proposed that this was because the plants possessed two copies of the trait for the flower-color characteristic, and that each parent transmitted one of their two copies to their offspring, where they came together. Moreover, the physical observation of a dominant trait could mean that the genetic composition of the organism included two dominant versions of the characteristic, or that it included one dominant and one recessive version. Conversely, the observation of a recessive trait meant that the organism lacked any dominant versions of this characteristic.
CONCEPTS IN ACTION
For an excellent review of Mendel’s experiments and to perform your own crosses and identify patterns of inheritance, visit the Mendel’s Peas web lab .
Also, check out the following video as review
- Johann Gregor Mendel, “Versuche über Pflanzenhybriden.” Verhandlungen des naturforschenden Vereines in Brünn , Bd. IV für das Jahr, 1865 Abhandlungen (1866):3–47. [for English translation, see http://www.mendelweb.org/Mendel.plain.html]
Introductory Biology: Evolutionary and Ecological Perspectives Copyright © by Various Authors - See Each Chapter Attribution is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance – Mendelian Inheritance
What is Mendelian Inheritance/Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance?
Genetics terminology of mendelian inheritance, why mendel chose pea plants, mendel’s key experiments, 1. law of dominance, 2. law of segregation (law of purity of gametes), 3. law of independent assortment, law of segregation vs. law of independent assortment, pedigrees to study inheritance patterns, 1. autosomal dominant inheritance, 2. autosomal recessive inheritance, 3. x-linked inheritance, exceptions and deviation from mendel’s findings, why was the pea plant selected for mendel’s experiments, importance of mendelian inheritance, list of latest research work on mendelian inheritance, practice mcq on mendelian inheritance, what is mendelian inheritance, who was gregor mendel, what are the three laws of mendelian inheritance, how does the law of dominance work, explain the law of segregation., what is the law of independent assortment, what is the difference between genotype and phenotype, what is the significance of dominant and recessive alleles, can traits be influenced by multiple genes, are there exceptions to mendelian inheritance.
- Mendelian inheritance refers to the set of principles that describe how traits are transmitted from parents to their offspring through genes. These principles, formulated by Gregor Mendel, are the cornerstone of classical genetics and provide a systematic way to predict patterns of inheritance.
- Mendel’s work, conducted in the mid-19th century, focused on garden pea plants. He selected specific traits like flower color, seed shape, and plant height, and studied how these traits appeared across generations. His experiments revealed that certain traits follow distinct patterns of inheritance.
- Mendel’s first key principle is the Law of Segregation , which states that each organism carries two alleles for each trait, one from each parent. These alleles separate during the formation of gametes (sperm or egg cells), so each gamete contains only one allele for each trait. This explains why offspring inherit one genetic factor from each parent, ensuring genetic diversity.
- The second principle, the Law of Independent Assortment , explains that genes for different traits segregate independently of one another during gamete formation. This law applies when genes for traits are located on different chromosomes. Therefore, the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of another.
- Additionally, Mendel’s third concept, the Law of Dominance , explains how some alleles can mask the presence of others. For each trait, one allele can be dominant, meaning it will determine the organism’s appearance, while the other allele can be recessive and will only appear if both alleles are recessive.
- Although Mendel’s contributions were initially ignored, his work was rediscovered in the early 20th century, providing a foundation for modern genetics. His laws are still used today to explain inheritance patterns, although we now know that more complex patterns of inheritance, like incomplete dominance and codominance , also exist.
These terms clarify how genes operate, how traits are inherited, and the relationship between genetic information and observable characteristics.
- Gene : A gene is a segment of DNA that holds the instructions for determining specific traits or characteristics in an organism. Each gene occupies a specific location on a chromosome and directs the production of proteins that ultimately influence how an organism looks or functions.
- Allele : Alleles are different versions of the same gene. For example, for the gene controlling flower color, one allele may code for purple flowers, while another may code for white flowers. Each individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent.
- Genotype : The genotype refers to the complete set of alleles an organism possesses. It determines the potential traits an individual can pass to its offspring. For a specific gene, if the two inherited alleles are the same, the organism is homozygous for that gene. If the alleles differ, the organism is heterozygous .
- Phenotype : This is the observable expression of a trait, such as the color of a flower or the shape of a seed. The phenotype results from the interaction between the genotype and the environment, although some traits are largely determined by genetic factors alone.
- Dominant Allele : A dominant allele is an allele that masks the effect of a recessive allele when both are present in the genotype. For instance, if the allele for round seeds is dominant and the allele for wrinkled seeds is recessive, a plant with both alleles will display round seeds.
- Recessive Allele : A recessive allele is one that is only expressed in the phenotype when two copies of it are present. In heterozygous organisms, the recessive trait is not visible, but it can be passed to offspring.
- Locus : The locus is the specific physical location of a gene or allele on a chromosome. Each gene has a defined locus, which remains consistent across individuals of a species.
- Carrier : A carrier is an individual who has one dominant allele and one recessive allele for a trait. While the dominant allele determines the phenotype, the recessive allele can still be passed to offspring, potentially appearing in future generations if the offspring inherit two recessive alleles.

Download the Cheat sheet pdf
Mendel’s Experiment
Gregor Mendel’s experiments between 1856 and 1863 laid the foundation for our understanding of genetic inheritance. Using the pea plant ( Pisum sativum ), he identified patterns of how traits are passed from one generation to the next. Mendel’s work, which focused on breeding experiments, revealed significant insights into inheritance, leading to what we now refer to as Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance.
Mendel selected pea plants for several key reasons:
- Availability of varieties : Pea plants came in distinct forms with clear variations, such as seed color and pod shape.
- Self-pollination capability : Pea plants naturally self-pollinate, ensuring controlled reproduction and reducing the risk of unintended traits mixing.
- Short life cycle : This allowed Mendel to observe multiple generations in a short period.
- Ease of cultivation : Pea plants grow easily, making them ideal for controlled experiments.
- Distinct traits : Mendel focused on seven easily distinguishable traits: seed shape, seed color, flower color, pod shape, pod color, flower position, and stem height.
Mendel carried out two major types of genetic crosses:
1. Monohybrid Cross
- Focus : Inheritance of a single trait.
- Example : Cross between tall plants (TT) and dwarf plants (tt).
- Parental Generation (P) : The initial organisms used in the cross.
- In the F1 generation, all offspring displayed the dominant trait (tallness). The recessive trait (dwarfness) was completely masked.
- In the F2 generation, both dominant and recessive traits appeared in a 3:1 ratio , meaning for every three tall plants, there was one dwarf plant.
Observations from Monohybrid Cross:
- Dominant and Recessive Traits : The dominant trait masks the recessive trait in the F1 generation but reappears in the F2 generation.
- Consistency Across Traits : Mendel’s experiments showed that this 3:1 ratio applied to all seven traits he studied, confirming a predictable inheritance pattern.
2. Dihybrid Cross
- Focus : Inheritance of two traits simultaneously.
- Example : Cross between plants with yellow, round seeds (YYRR) and plants with green, wrinkled seeds (yyrr).
- F1 Generation : All plants exhibited the dominant traits (yellow and round seeds).
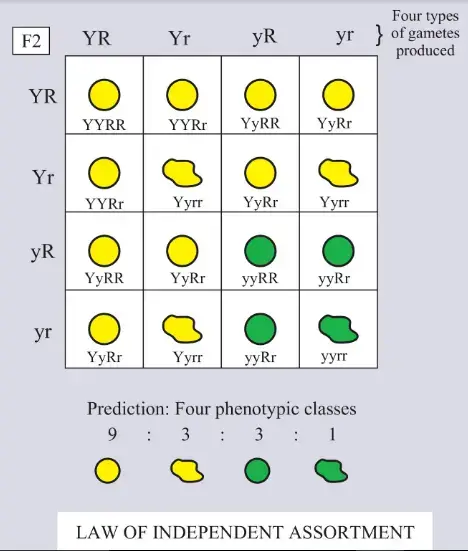
- F2 Generation : Traits reappeared in a phenotypic ratio of approximately 9:3:3:1 , indicating the independent assortment of these traits.
Observations from Dihybrid Cross:
- Independent Assortment : Traits are passed down independently of one another, leading to various combinations in the offspring.
- Phenotypic Ratio : The F2 generation displayed a 9:3:3:1 ratio, meaning nine offspring showed both dominant traits, three showed one dominant and one recessive trait, three showed the reverse combination, and one showed both recessive traits.
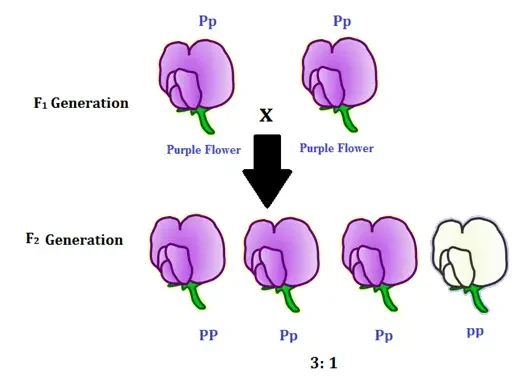
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance or Mendel’s Principles of Inheritance
Gregor Mendel’s pioneering work on pea plants led to the establishment of three fundamental laws of inheritance, which form the foundation of classical genetics. These laws explain how traits are inherited from one generation to the next and describe the predictable patterns of trait transmission. The laws are the Law of Dominance, the Law of Segregation, and the Law of Independent Assortment.
- Definition : The Law of Dominance states that when two different alleles (alternative forms of a gene) are present in an organism, one allele is dominant and the other is recessive. In a heterozygous pairing, the dominant allele is expressed, while the recessive allele remains hidden or unexpressed.
- Example : In Mendel’s monohybrid cross between tall (TT) and dwarf (tt) pea plants, the F1 generation exhibited only tall plants, reflecting the dominance of the tall allele (T) over the recessive dwarf allele (t). Therefore, this law explains how dominant traits override recessive traits in hybrid offspring.
- Function : The Law of Dominance serves to clarify how parental traits are manifested in offspring, particularly in heterozygous organisms.
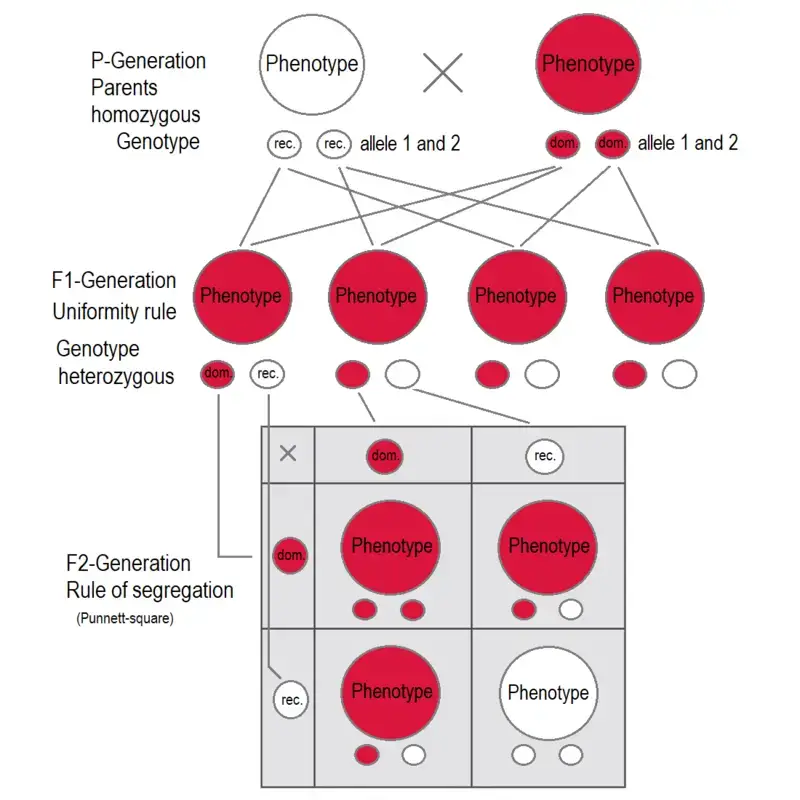
- Definition : The Law of Segregation explains how alleles separate during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells). Each organism carries two alleles for each trait, one inherited from each parent. During gamete formation, these alleles segregate, and each gamete receives only one allele for each trait.
- Example : In Mendel’s F2 generation of the monohybrid cross, the reappearance of the recessive trait (dwarfness) showed that the alleles for tallness and dwarfness separated during gamete formation. Thus, each gamete carried either the tall or dwarf allele, resulting in a 3:1 ratio of tall to dwarf plants in the F2 generation.
- Function : This law highlights the mechanism of allele separation during meiosis , ensuring genetic diversity by allowing different combinations of alleles in the offspring.
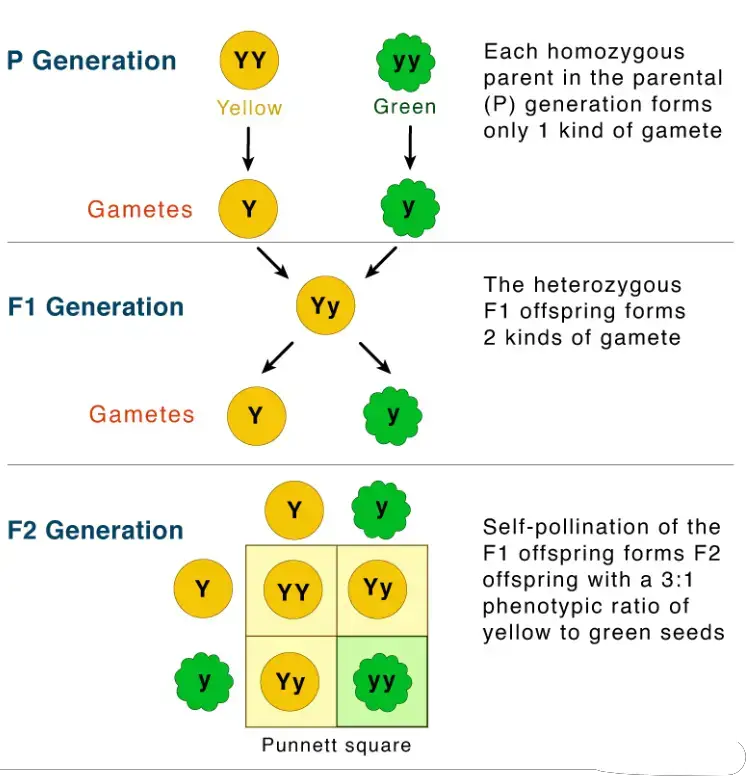
- Definition : The Law of Independent Assortment states that alleles for different traits are distributed to gametes independently of one another. This means that the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of another.
- Example : In Mendel’s dihybrid cross involving two traits—seed color (yellow or green) and seed shape (round or wrinkled)—the F2 generation exhibited a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1. This indicated that the alleles for seed color assorted independently from those for seed shape.
- Function : The Law of Independent Assortment emphasizes the random distribution of alleles for different traits, contributing to the variety of possible genetic combinations in offspring.
The Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment are fundamental principles of Mendelian inheritance that describe the behavior of alleles during the process of gamete formation and the inheritance of multiple traits. Here’s a breakdown of these two laws:
Law of Segregation: The Law of Segregation, also known as the Law of Purity of Gametes, governs how alleles for a particular trait separate during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells). It was discovered by Gregor Mendel through his experiments with pea plants. This law emphasizes that:
- During meiosis, the process of gamete formation, each parent contributes one allele for a specific trait to each offspring.
- The alleles carried by an individual for a particular trait segregate from each other during gamete formation, so that each gamete carries only one allele for that trait.
- This ensures that when fertilization occurs, the offspring inherit one allele from each parent, resulting in the genetic diversity and variability necessary for evolution .
- The segregation of alleles is random and unbiased, meaning that neither allele has an advantage or is favored during the separation process.
Law of Independent Assortment: The Law of Independent Assortment describes how alleles for different traits segregate and assort independently of each other during gamete formation. This principle is closely related to the distribution of alleles from different genes into gametes. Key points of this law include:
- Alleles located on different chromosomes assort independently, meaning that the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of another trait.
- The independent assortment occurs due to the random alignment of homologous chromosomes along the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
- The possible combinations of alleles in gametes are numerous, leading to increased genetic diversity in the offspring.
- This law contributes to the uniqueness of each individual and the variability within populations.
In summary, the Law of Segregation emphasizes the separation of alleles for a single trait during gamete formation, ensuring each offspring inherits one allele from each parent. The Law of Independent Assortment underscores the random and independent distribution of alleles for different traits into gametes, resulting in diverse combinations of traits in offspring. Both laws play a crucial role in shaping the genetic diversity within populations and are essential for understanding inheritance patterns in organisms.
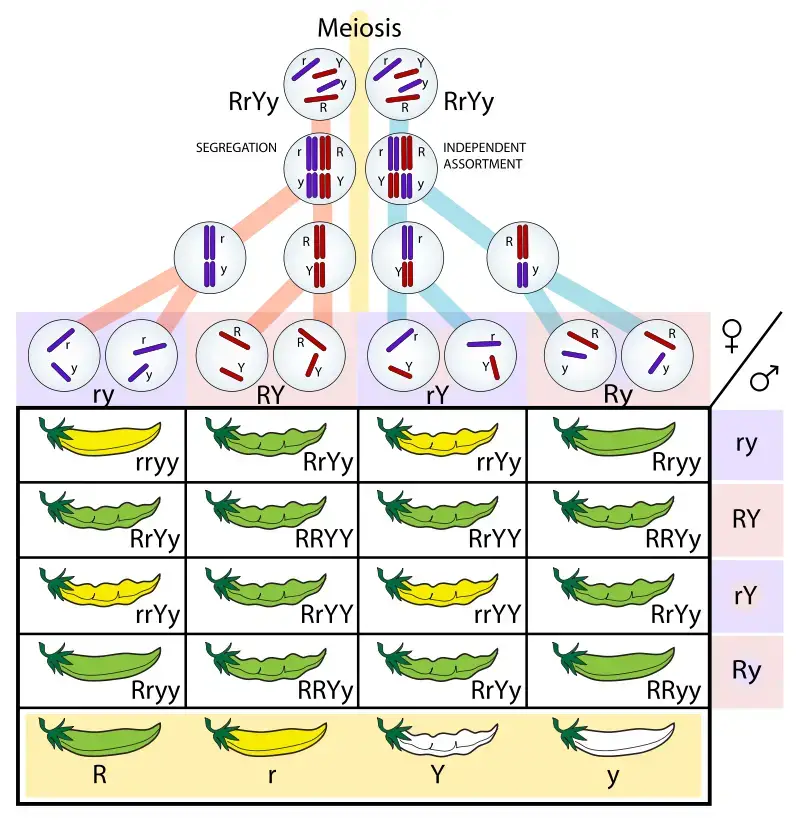
In summary, the Law of Segregation emphasizes the separation of alleles for a single trait during gamete formation, while the Law of Independent Assortment underscores the random and independent distribution of alleles for different traits into gametes. Both laws contribute to genetic diversity and are crucial for understanding inheritance patterns.
Pedigree analysis is a valuable tool used by geneticists to study the inheritance patterns of human genetic diseases. It provides insights into how traits are passed down through generations within families, helping individuals understand their risk of inheriting or passing on specific genetic disorders.
Understanding Genetic Inheritance:
- Many human diseases have a genetic basis, meaning they are caused by specific gene mutations inherited from parents.
- For individuals in families with a history of genetic disorders, it’s important to determine if they carry disease-causing genes and assess the risk of passing the disorder to their children.
- Inherited disorders can follow different patterns of inheritance, including autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, X-linked recessive, and others.
Pedigree Analysis:
- Pedigrees are visual representations of family trees that track the occurrence of specific traits or disorders across generations.
- In pedigrees, each generation is represented by a row, and individuals are depicted using symbols (circles for females, squares for males).
- Relationships between individuals are shown with connecting lines, indicating marriages and parent-offspring relationships.
- Pedigrees allow geneticists to analyze patterns of inheritance, identify carriers of disease-causing alleles, and predict the likelihood of an individual being affected by a genetic disorder.
Pedigree Components:
- Affected Individuals: Those with the genetic disorder are represented by shaded symbols. The presence of the disorder in an individual’s lineage is indicated by a shaded circle or square.
- Carriers: Individuals who carry a disease-causing allele but do not exhibit symptoms are represented by half-shaded symbols (half-filled circles or squares).
- Unaffected Individuals: Those without the genetic disorder are depicted with clear symbols.
- Generations: Rows in the pedigree represent different generations of the family, with the oldest generation at the top.
- Relationships: Horizontal lines connect mating partners, and vertical lines extend downward to connect parents with their offspring.
Interpreting Pedigrees:
- Pedigrees reveal inheritance patterns, helping geneticists determine if a disorder is recessive, dominant, or X-linked.
- Autosomal Recessive: Typically appears in multiple generations, skips generations, and affects males and females equally.
- Autosomal Dominant: Appears in each generation, affects males and females equally, and often has an affected parent.
- X-Linked Recessive: More common in males, can skip generations, and is often passed from carrier females to their sons.
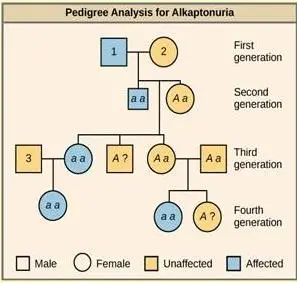
Alkaptonuria is a recessive genetic disorder that impairs the metabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine amino acids . Affected individuals can exhibit darkened skin , brown urine, and may suffer from joint damage and other complications. A pedigree illustrates the inheritance of this disorder, where affected individuals are shown in blue and have the genotype aa, while unaffected individuals are depicted in yellow with the genotypes AA or Aa.
Key Points:
- Alkaptonuria is a recessive genetic disorder causing issues with phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism.
- Affected individuals can display skin darkening, brown urine, joint problems, and other complications.
- Pedigrees visually represent family inheritance patterns, aiding the study of genetic disorders.
- Affected individuals are indicated in blue and have the aa genotype (homozygous recessive).
- Unaffected individuals are depicted in yellow and can have either AA (homozygous dominant) or Aa (heterozygous) genotypes.
- Genotypes of individuals can be inferred from those of their offspring.
- If a child has the disorder but neither parent does, both parents must be heterozygous carriers (Aa).
- Individuals with an unaffected phenotype but unknown genotype are represented as “A?” since they must have at least one normal allele.
This pedigree highlights how analyzing family trees can provide insights into genetic disorders’ inheritance patterns and aid in determining the genotypes of individuals based on the traits they pass down to their offspring.
- A pedigree for a human genetic disease illustrates how the disorder is passed down through generations.
- Affected individuals are shaded, carriers are half-shaded, and unaffected individuals are clear.
- Relationships are depicted through connecting lines, highlighting parent-offspring and marital connections.
Pedigree analysis plays a crucial role in understanding genetic disorders within families and communities. By studying the patterns of inheritance, geneticists can provide valuable information for individuals making informed decisions about their health and family planning.
Non-Mendelian inheritance
- Non-Mendelian inheritance refers to the inheritance patterns of traits that deviate from the expectations set by Mendel’s laws. These laws, proposed by Gregor Mendel, outline how traits associated with single genes on chromosomes within the nucleus segregate during reproduction. In Mendelian inheritance, each parent contributes one of two possible alleles for a trait to their offspring. By knowing the genotypes of the parents in a genetic cross, Mendel’s laws can predict the distribution of phenotypes among their offspring. However, there are instances where the observed proportions of phenotypes in the progeny differ from the predicted values.
- Non-Mendelian inheritance scenarios challenge these straightforward predictions and encompass various mechanisms that influence trait transmission. These mechanisms often involve complex genetic interactions, such as multiple genes affecting a single trait, or genetic traits being influenced by factors beyond nuclear DNA.
- Non-Mendelian inheritance plays a significant role in several genetic diseases and conditions. Some disorders are caused by mutations in genes that don’t adhere to Mendelian inheritance patterns, making the inheritance and expression of these traits more intricate. Additionally, certain diseases are impacted by factors such as mitochondrial DNA , genomic imprinting, or polygenic inheritance , all of which lead to deviations from classical Mendelian ratios.
- In summary, non-Mendelian inheritance encompasses a wide array of genetic scenarios that don’t conform to the simple rules of Mendel’s laws. These complex genetic interactions are vital to understanding the full spectrum of inheritance patterns, especially in cases where diseases and conditions are influenced by a combination of genetic factors beyond the scope of Mendelian genetics.
Non-Mendelian inheritance encompasses various patterns of genetic inheritance that do not adhere to the straightforward principles outlined by Mendel’s laws. These deviations introduce complexity to the understanding of how traits are passed down from one generation to the next. Several types of non-Mendelian inheritance are recognized, each involving unique genetic interactions:
- Incomplete Dominance: Incomplete dominance challenges the principle of dominance proposed by Mendel. Instead of a dominant allele fully masking the recessive allele, both alleles contribute to the phenotype, resulting in an intermediate expression. For example, in Mirabilis jalapa and Antirrhinum majus, flower color demonstrates incomplete dominance.
- Co-dominance : Co-dominance defies the traditional dominance-recessiveness relationship between alleles. Both alleles are equally expressed in the phenotype, allowing both traits to be observed simultaneously. Co-dominance is exemplified by certain chicken varieties with co-dominant alleles for black and white feathers, as well as the ABO blood group system in humans.
- Genetic Linkage : Genetic linkage deviates from Mendel’s principle of independent assortment. When genes are located near each other on the same chromosome, they tend to be inherited together, which contradicts the expected independent segregation of alleles during meiosis.
- Multiple Alleles : Multiple alleles involve genes that possess more than two variations within a population . Unlike Mendel’s experiments that focused on traits regulated by only two alleles, multiple alleles demonstrate the existence of several different forms of a gene. The ABO blood group system in humans, with its three alleles (A, B, and O), illustrates multiple alleles.
- Epistasis : Epistasis involves the interaction of multiple genes, where one gene’s expression influences or masks the expression of another gene. This contrasts with Mendel’s laws, as it showcases the interconnectedness of genetic pathways and how the expression of one gene can modify another gene’s expression.
- Sex-Linked Inheritance : Genetic traits located on sex chromosomes exhibit specific non-Mendelian patterns. Sex-linked inheritance encompasses traits influenced by genes on the X and Y chromosomes, affecting males and females differently. Examples include color blindness and hemophilia.
- Extranuclear Inheritance ( Cytoplasmic Inheritance ): Extranuclear inheritance involves genetic information present in organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts, which is passed down through the cytoplasm of maternal gametes. Disorders like mitochondrial diseases exemplify this mode of inheritance.
- Polygenic Traits: Polygenic traits result from the interaction of multiple genes and exhibit a wide range of phenotypes. Skin color and eye color in humans are examples of polygenic traits influenced by multiple genes.
- Genomic Imprinting: Genomic imprinting involves genes that are marked epigenetically before transmission, altering their expression levels. Imprints are created before gamete formation and can result in the exclusive expression of certain alleles depending on parental origin.
- Trinucleotide Repeat Disorders: Trinucleotide repeat disorders, such as Fragile X syndrome and Huntington’s disease, result from the expansion of microsatellite tandem repeats. These disorders display non-Mendelian inheritance patterns as the number of repeats changes across generations.
These diverse forms of non-Mendelian inheritance underscore the intricate genetic interactions that shape the inheritance of traits and contribute to the complexity of genetic inheritance patterns beyond Mendel’s classical laws.
Modes of Inheritance
In genetics, the term “modes of inheritance” refers to the ways in which genetic traits or disorders are passed from one generation to the next. Mendelian inheritance patterns are categorized primarily into three major types: autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and X-linked inheritance. Each mode of inheritance has distinct characteristics that influence the likelihood of offspring inheriting a specific trait or disease.
- Definition : Autosomal dominant inheritance occurs when a single copy of a dominant allele is sufficient to express a particular trait or disease. The dominant allele is located on one of the autosomes (non-sex chromosomes), meaning it can be passed on from either parent.
- An affected individual only needs to inherit one dominant allele from either parent to exhibit the trait or disease.
- There is a 50% chance that an affected parent will pass the dominant allele to each offspring.
- The trait is expressed in both males and females with equal frequency since it is located on an autosome.
- Examples : Huntington’s disease, which affects the nervous system , and Marfan syndrome, a connective tissue disorder, are classic examples of autosomal dominant conditions.
- Function : This mode of inheritance highlights the role of dominant alleles in determining phenotypes, even when only one allele is altered.
- Definition : Autosomal recessive inheritance requires two copies of an abnormal recessive allele for the trait or disease to be expressed. Individuals who inherit only one copy of the recessive allele are considered carriers but do not show any symptoms.
- Both parents must carry one copy of the abnormal allele for there to be a risk of having an affected child.
- Each child of two carrier parents has a 25% chance of inheriting both copies of the recessive allele, resulting in expression of the trait or disease.
- The trait affects both males and females equally, as it is also located on the autosomes.
- Carriers, with one normal and one abnormal allele, typically do not show any symptoms but can pass the abnormal allele to their offspring.
- Examples : Cystic fibrosis, a disorder that affects the lungs and digestive system, and sickle cell anemia, which impacts red blood cells , are well-known autosomal recessive conditions.
- Function : This inheritance pattern emphasizes the necessity of both alleles being altered for a recessive trait to manifest in an individual.
- Definition : X-linked inheritance involves genes located on the X chromosome. Since males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome, any gene on the X chromosome will be expressed in males, whether it is dominant or recessive. Females, who have two X chromosomes, may carry an abnormal gene on one X chromosome but remain unaffected if the other X chromosome carries a normal version of the gene.
- In males, the presence of a single altered X-linked gene results in expression of the trait or disease, as they do not have a second X chromosome to compensate.
- Females with one altered X-linked gene are typically carriers, meaning they can pass the trait to their offspring without showing symptoms.
- Affected males will pass the X-linked gene to all of their daughters but none of their sons, since sons inherit the Y chromosome from their father.
- Examples : Hemophilia, a disorder that affects blood clotting, and color blindness, which affects color perception, are examples of X-linked recessive conditions.
- Function : This mode of inheritance explains why certain conditions, particularly X-linked recessive traits, are more commonly expressed in males than females.
Gregor Mendel’s pioneering work established foundational principles in the field of genetics, including the laws of segregation and independent assortment. However, subsequent research has identified several deviations from Mendelian inheritance patterns, revealing a more nuanced understanding of genetic processes. These deviations include incomplete dominance, co-dominance, multiple alleles, genetic linkage, and epistasis. Each phenomenon illustrates the complexity of genetic inheritance beyond Mendel’s original framework.
1. Incomplete Dominance
- Definition : Incomplete dominance occurs when the phenotype of the offspring is a blend of the parental phenotypes. This arises when neither allele is completely dominant over the other.
- Mechanism : Unlike Mendel’s principle of dominance, where one allele masks the other, incomplete dominance results in an intermediate expression of traits. For instance, in snapdragon flowers, crossing red-flowered plants with white-flowered plants produces offspring with pink flowers, demonstrating an intermediate phenotype.
- Example : Snapdragon flower color, where the red (R) and white (W) alleles combine to produce pink (RW) flowers.
2. Co-Dominance
- Definition : Co-dominance is a genetic scenario where both alleles are fully expressed, and neither allele is dominant over the other. This results in a phenotype that simultaneously shows traits from both alleles.
- Mechanism : This contrasts with Mendelian dominance, where one allele overrides the expression of the other. In co-dominance, both traits are visible.
- Example : Blood type inheritance in humans. The A and B alleles are co-dominant, leading to the presence of both A and B antigens in individuals with AB blood type.
3. Multiple Alleles
- Definition : Multiple alleles refer to a situation where a gene has more than two allelic forms within a population, expanding the variation beyond Mendel’s two-allele model.
- Mechanism : Mendel’s experiments typically involved genes with only two alleles. However, real-world genes often exhibit more complexity.
- Example : The ABO blood group system involves three alleles—A, B, and O—which interact to determine an individual’s blood type. The combinations of these alleles contribute to the variety in blood types observed in humans.
4. Genetic Linkage
- Definition : Genetic linkage occurs when genes located on the same chromosome are inherited together more frequently than would be expected if they assorted independently.
- Mechanism : This phenomenon contradicts Mendel’s law of independent assortment, which states that genes on different chromosomes segregate independently. Genes that are close together on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together due to reduced likelihood of recombination between them.
- Example : The linkage of genes for eye color and wing size in fruit flies, where these traits are often inherited together rather than independently.
5. Epistasis
- Definition : Epistasis is a form of gene interaction where the expression of one gene influences or masks the expression of another gene. This interaction deviates from Mendelian inheritance by involving multiple genes.
- Mechanism : In epistasis, one gene can suppress or modify the effect of another gene. This is distinct from Mendelian inheritance patterns where genes are considered to have discrete, non-interacting effects.
- Example : In Labrador retrievers, the gene controlling pigment color (B) is influenced by a separate gene that controls pigment deposition (E). An epistatic interaction occurs when the E gene affects the expression of the B gene, leading to variations in coat color.
The following factors explain why the pea plant was particularly suited for Mendel’s research:
1. Availability of Varieties with Observable Traits
- Trait Examples : Observable traits in pea plants include seed color (yellow vs. green), pod color (green vs. yellow), pod shape (inflated vs. constricted), and plant height (tall vs. short).
- Function : These distinct phenotypes allowed Mendel to track and categorize inheritance patterns with high precision.
2. Self-Pollination and Controlled Cross-Pollination
- Mechanism : The corolla of the pea flower fully encloses the reproductive organs, reducing the likelihood of cross-pollination by external agents.
- Function : This ability to both self and cross-pollinate provided Mendel with the flexibility to investigate both inbreeding and hybridization.
3. Accessibility and Ease of Cultivation
- Cultivation : They can be cultivated annually with minimal care, except during the critical pollination phase.
- Function : This ease of cultivation allowed Mendel to maintain large experimental populations and conduct multiple generations of breeding.
4. Distinct Contrasting Characters
- Trait Examples : These include seed shape (round vs. wrinkled), flower position (axial vs. terminal), and plant height (tall vs. dwarf).
- Function : The presence of these distinct characteristics facilitated Mendel’s analysis of how traits are passed from one generation to the next and helped establish the foundational principles of genetic inheritance.
5. Short Life Cycle and High Seed Production
- Seed Production : Pea plants produce a large number of seeds per generation.
- Function : The short life cycle and high seed yield allowed Mendel to accumulate sufficient data quickly and observe genetic patterns over successive generations.
Mendelian inheritance, also known as Mendelism or Mendelian genetics, holds significant importance in the field of biology and genetics for several reasons:
- Foundation of Genetics: Mendel’s experiments with pea plants laid the groundwork for understanding the principles of heredity and how traits are passed from one generation to another. His work marked the beginning of modern genetics.
- Predictive Power: Mendelian inheritance provides a framework for predicting the likelihood of specific traits appearing in offspring based on the genotypes of the parents. This predictability is crucial in agriculture, animal breeding, and even in human genetics for genetic counseling.
- Basis for Genetic Studies: Mendel’s laws serve as a starting point for studying various genetic phenomena, including linkage, recombination, and mutation . These laws help scientists decipher the mechanisms underlying genetic traits and diseases.
- Clinical Relevance: Understanding Mendelian inheritance is essential for diagnosing and treating genetic disorders. It allows for the prediction of inheritance patterns, carrier status, and risk assessment for certain diseases in individuals and families.
- Population Genetics : Mendelian principles play a role in population genetics and evolutionary biology. They contribute to the understanding of how traits can change over time in a population through mechanisms like natural selection .
- Basis for Genetic Research: Mendelian inheritance provided the foundation for subsequent genetic research, including the discovery of DNA as the genetic material and the development of techniques such as polymerase chain reaction ( PCR ) and gene sequencing.
- Genetic Engineering : The understanding of Mendelian genetics has paved the way for genetic engineering and biotechnology. Scientists can manipulate genes and organisms based on these principles, leading to advancements in agriculture, medicine, and other fields.
- Education and Outreach: Mendelian genetics is often introduced in basic biology education. It serves as an accessible way to introduce the concepts of inheritance, genes, and genetic variation to students of various ages.
- Ethical Considerations: The principles of Mendelian inheritance have implications for ethical discussions surrounding genetic testing, gene editing, and issues related to hereditary diseases.
- Building Blocks of Complex Traits: While Mendelian genetics describes simple inheritance patterns, understanding these foundational principles helps researchers unravel the genetics behind more complex traits, including those influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors.
- Abstract : This research delves into the metabolic disorder alkaptonuria (AKU), which is caused by a deficiency of homogentisate dioxygenase (HGD). Sir Archibald Garrod used AKU to illustrate the concept of Mendelian inheritance in man. The study highlights the phase III clinical study SONIA 2, which tested the effectiveness and safety of nitisinone in the treatment of AKU. The results were positive, suggesting that a cure for AKU might be found by 2020. The research also touches upon the potential of enzyme replacement or gene therapy for AKU.
- Authors : A. Zaťková, L. Ranganath, L. Kádasi
- Publication Date : 2020-01-23
- Link to Full Paper
- Abstract : This research aimed to compile a comprehensive panel of genes associated with monogenic causes of stroke. The study systematically searched the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man database and validated the entries against peer-reviewed publications. The resulting gene panel can be used to interpret exome sequencing results regarding monogenic stroke.
- Authors : A. Ilinca, Sofie Samuelsson, P. Piccinelli, M. Soller, U. Kristoffersson, A. Lindgren
- Publication Date : 2018-10-24
- Abstract : The paper discusses the trends in research that aims to increase understanding of overall genomic complexity, complex inheritance patterns of disease, and patient-phenotype-specific genomic associations. It describes the emerging field of translational functional genomics and its role in the future of personalized medicine.
- Authors : S. Chakravorty, M. Hegde
- Publication Date : 2017-08-31
- Abstract : The study verified Mendelian inheritance, genetic linkage, and genotypic disequilibrium for 15 microsatellite loci in Eucalyptus urophylla. The results indicated that the analyzed set of microsatellite loci could be used for various genetic analyses in E. urophylla.
- Authors : S. Pupin, L. Rosse, I. C. Souza, J. Cambuim, C. Marino, M. Moraes, A. Sebbenn
- Publication Date : 2017-08-17
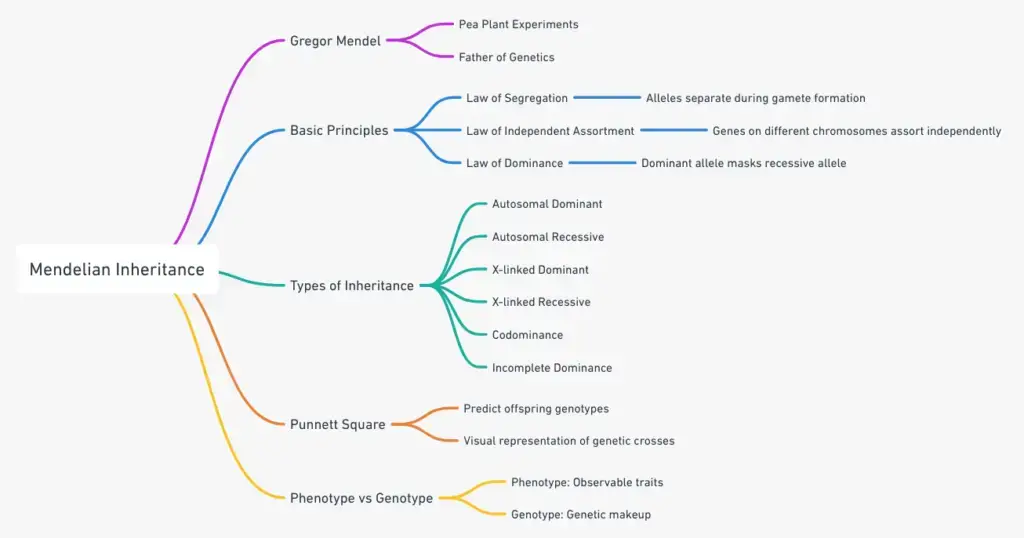
What term is used to describe discrete units of hereditary information that are passed on from parents to offspring? a) Genes b) Alleles c) Chromosomes d) Proteins
Gregor Mendel conducted his groundbreaking experiments using which organism? a) Dogs b) Pea plants c) Bacteria d) Mice
In Mendelian inheritance, what is a gene composed of? a) DNA sequence b) RNA sequence c) Protein sequence d) Carbohydrate sequence
What is the term for a specific variant of a gene? a) Phenotype b) Chromosome c) Allele d) Locus
An organism with two different alleles for a particular gene is known as: a) Homozygous b) Heterozygous c) Dominant d) Recessive
According to the Law of Segregation, what happens during gamete formation? a) Alleles for a gene segregate into separate gametes b) Alleles for a gene blend together c) Genes for different traits segregate together d) Homologous chromosomes stay together
In a heterozygous individual, which allele’s phenotype is expressed? a) Dominant allele b) Recessive allele c) Both alleles’ phenotypes are expressed equally d) Neither allele’s phenotype is expressed
A person with the genotype Aa for a specific gene exhibits the dominant phenotype. What is the genotype of the individual’s parents? a) AA and aa b) Aa and Aa c) Aa and aa d) AA and Aa
What is the term for a gene that masks the expression of another gene? a) Recessive gene b) Dominant gene c) Homozygous gene d) Heterozygous gene
In Mendelian inheritance, when does co-dominance occur? a) When one allele completely masks the expression of another b) When two alleles are equally expressed in the phenotype c) When one allele blends with another in the phenotype d) When multiple alleles interact to produce a single phenotype
a) Genes b) Pea plants a) DNA sequence c) Allele b) Heterozygous a) Alleles for a gene segregate into separate gametes a) Dominant allele b) Aa and Aa b) Dominant gene b) When two alleles are equally expressed in the phenotype
Mendelian inheritance, also known as Mendelism, refers to the set of principles proposed by Gregor Mendel that explains how hereditary traits are passed from parents to their offspring through the transmission of genes.
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk and botanist who conducted pioneering experiments with pea plants in the 19th century, leading to the formulation of the fundamental laws of inheritance now known as Mendel’s principles.
The three laws are the Law of Dominance, the Law of Segregation, and the Law of Independent Assortment. These laws govern how alleles (gene variants) are inherited and determine the expression of traits in offspring.
The Law of Dominance states that one allele (dominant) will mask the expression of another allele (recessive) for a particular trait. Only when an individual is homozygous recessive will the recessive trait be expressed.
The Law of Segregation states that during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), the alleles for a trait segregate or separate from each other. As a result, each gamete carries only one allele for a specific trait.
The Law of Independent Assortment states that alleles for different traits segregate independently during gamete formation. This principle explains how traits are inherited without being influenced by the inheritance of other traits.
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, including the combination of alleles it carries. Phenotype refers to the observable traits or characteristics that result from the interaction between an organism’s genotype and its environment.
Dominant alleles express their phenotype even in heterozygous individuals, while recessive alleles require homozygosity to manifest their phenotype. Dominant alleles mask the expression of recessive alleles in heterozygotes.
Yes, many traits are controlled by multiple genes, a phenomenon known as polygenic inheritance. These traits often display a wide range of phenotypes due to the cumulative effects of multiple gene variants.
Yes, there are instances of non-Mendelian inheritance, such as incomplete dominance, co-dominance, genetic linkage, and epistasis. These cases involve more complex inheritance patterns that deviate from the classical Mendelian principles.
- Harel, T., Pehlivan, D., Caskey, C. T., & Lupski, J. R. (2015). Mendelian, Non-Mendelian, Multigenic Inheritance, and Epigenetics. Rosenberg’s Molecular and Genetic Basis of Neurological and Psychiatric Disease, 3–27. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-410529-4.00001-2
- “Principles of Genetics” by D. Peter Snustad and Michael J. Simmons
- “Introduction to Genetic Analysis” by Anthony J.F. Griffiths, Susan R. Wessler, Sean B. Carroll, and John Doebley
- “Genetics: Analysis and Principles” by Robert J. Brooker
- “Essentials of Genetics” by William S. Klug, Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer, and Michael A. Palladino
- “Molecular Biology of the Cell” by Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, and Peter Walter
- https://knowgenetics.org/mendelian-genetics/
- https://www.biologyonline.com/dictionary/mendelian-inheritance
- https://bioprinciples.biosci.gatech.edu/module-4-genes-and-genomes/4-2-4-mendelian-genetics/
- https://rwu.pressbooks.pub/bio103/chapter/mendelian-genetics/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mendelian_inheritance
Related Biology Study Notes
Various model of replication – theta, rolling circle, and linear dna replication, artificial selection – theory, types, advantages, examples, genetic variation – definition, types, causes, examples, gene expression and cell specialization – ap biology notes, dna helicases – structure, types, mechanism, functions, examples, nondisjunction – types, causes, consequences, examples, transgenic animal – definition, methods, applications, examples, point mutation – definition, causes, types, examples, latest questions.
- All Questions
Start Asking Questions Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Click on your ad blocker icon in your browser's toolbar
- Select "Pause" or "Disable" for this website
- Refresh the page if it doesn't automatically reload

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.13: Introduction to Mendelian Genetics
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 73678

- Marjorie Hanneman, Walter Suza, Donald Lee, & Amy Kohmetscher
- Iowa State University via Iowa State University Digital Press
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Outline the experimental approach Mendel used to propose the idea that genes exist, control traits, and are inherited in predictable ways.
- Compare the methods used by Mendel and Punnett to predict trait inheritance.
Introduction
In plant and animal genetics research, the decisions a scientist will make are based on a high level of confidence in the predictable inheritance of the genes that control the trait being studied. This confidence comes from a past discovery by a biologist named Gregor Mendel, who explained the inheritance of trait variation using the idea of monogenic traits.
Monogenic characters are controlled by the following biological principles:
- Living things have genes in their cells that encode the information to control a single trait. These genes are stable and passed on from cell to cell without changing.
- The genes are in pairs in somatic cells. When these cells divide to form gametes, the pair of genes is divided. One gene from the pair goes into a gamete.
- Male gametes (pollen) combine with female gametes (eggs) in the wheat flower pistil and fuse to form the next generation (zygote). Gamete union is random.
- The zygote, again, has two copies of each gene. As the zygote grows into a multicellular seed and the seed grows into a plant, the same two gene copies are found in every cell.
Let’s take a short genetics history lesson to understand their confidence.

Mendel’s Peas
In the mid 1800’s, an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel (Figure 1) decided he should try to understand how inherited traits are controlled. He needed a model organism he could work with in his research facility, a small garden in the monastery, and a research plan. His plan was designed to test a hypothesis for the inheritance of trait variation.
Since Mendel could obtain different varieties of peas that differed in easy to observe traits such as flower color, seed color and seed shape, and he could grow these peas in his garden, he chose peas as the model organism for conducting his inheritance control study. A model is easy to work with and often what you learn from the model you can apply to other organisms.
The Hypothesis
While many biologists were interested in trait inheritance, at the time Mendel conducted his experiments none of the biologists had published evidence that inheritance could be predicted. Mendel made this bold statement. His hypothesis was that he could observe “mathematical” regularities in the appearance of a trait that was passed on from parents to their offspring. Mendel had the idea that mathematical regularities could be observed and could be used to explain the biology of inheritance!
Mendel’s experimental plan was designed to test the hypothesis. He identified true breeding lines of peas by allowing them to self pollinate (which we will refer to as “selfing”) and examining their offspring. Pea plants have flowers that contain both male and female reproductive parts; if a pea flower is left undisturbed, the male and female gametes from the same flower will combine to produce seeds, the next generation. If the pea always made offspring like itself, Mendel had his true breeding line. He then made planned crosses between lines that differed by just one trait (monohybrid crosses). The controlled monohybrid cross was the first step in his experiment that allowed him to look for mathematical regularities in the data for three generations. Table 1 below shows the data from a series of these monohybrid cross experiments.
The Analysis
By summarizing his data in a single table, Mendel could look for those hypothesized math regularities. A regularity is a repeated observation.
Cross and Phenotypes
Round X Wrinkled
5474 Round 1850 Wrinkled
Cotyledon color
Yellow X Green
6022 Yellow 2001 Green
Seed coat color*
Gray X White
705 Gray 224 White
Inflated X Constricted
All inflated
882 Inflated 299 Constricted
Green X Yellow
428 Green 152 Yellow
Flower position
Axial X Terminal
651 Axial 207 Terminal
Stem length
Tall X Short
787 Tall 277 Short
*Gray seed coat also had purple flowers; White seed coat had white flowers.
Table 1 demonstrates that Mendel was serious about the math. He generated large numbers of offspring that allowed him to observe mathematical ratios. From his table of data, we can see mathematical patterns appear with every monohybrid cross he made.
- F 1 : All the plants had the same phenotype as one of the parents.
- F 2 : Both phenotypes are present, the phenotype that was not expressed in the F 1 appears again in the F 2 but is always the least frequently produced. The average ratio is about 3:1 for the two phenotypes.
What was striking to Mendel was that every character in his study exhibited the same kind of mathematical pattern. This suggested that the same fundamental processes inside the plant’s reproductive cells were at work controlling the inheritance of each trait.
Now Mendel had the task of providing a description of the fundamental biology process controlling each of these traits. He needed to come up with ideas that no one had yet proposed to explain biology.
New Idea #1:
The traits expressed in the pea plant were controlled by some kind of particle. These hereditary particles are stable and passed on intact from parent to offspring through the sex cells. (NOTE: Sex cells or gametes were not a new idea, Mendel was aware that biologists knew sexually reproducing plants and animals needed to make gametes.) We now call these particulate factors genes and will use that term in the rest of this reading.
New Idea #2:
Genes are stable, and genes can have alternative versions (alleles).
New Idea #3:
Genes are in pairs in somatic cells and these paired genes separate during gamete formation. Each gamete will have one gene from the pair of genes. The segregating of the paired genes from the somatic cells of the parent into gametes is random. Because segregation is random, a parent that has two different alleles for a gene pair will make two kinds of gametes and makes these gametes at equal frequencies.
From Mendel’s ideas, we can see that in a situation in which there was a normal version of a gene (we can call it the R gene) and an alternate version (r), the plant could produce gametes with just the R gene or just the r gene.
New Idea #4:
Plant flowers are designed to allow male gametes (pollen) to combine randomly with the female gametes (egg). When the gametes randomly come together, they bring the genes they carry to the same zygote. This means plants could have the genotype RR, Rr , or rr in families that have both the R and r alleles.
New Idea #5:
Mendel proposed that the genes controlling a trait not only paired in somatic cells, they also interacted in controlling the traits of the plants. For the traits in his experiment, he proposed that one allele interacted with the other in a dominant fashion. That means a plant that is the genotype RR would have the same phenotype as an Rr plant. The R allele is dominant to the r allele.
Ideas and Data advance science
Those were Mendel’s new ideas; he used them to make sense of his experiment data and observations. Let’s think like Mendel and apply those ideas.
All the F1 were the same
Mendel’s new ideas could explain this observation. Since his parents were true breeding, he was always making a cross between homozygous parents. Homo means the same, so the parents had two copies of the same version of the gene.
Crossing RR X rr plants to produce Rr
Since the R is dominant to r , then the Rr offspring (named the F 1 ) look the same (have the same phenotype) as the RR parent. Therefore, only one phenotype is observed in the F 1 . But the F 1 genotype is different from either parent. It is heterozygous (two different alleles).

The F 2 : both traits appear in about a 3:1 ratio
Mendel could explain the reappearance of the recessive trait and the ratio by combining the idea of genes with the idea of random segregation. Mendel used simple algebra to explain this result.
First, he wrote out a mathematical expression to account for the gametes made in the male part of the F 1 flower or in the female part.
½ R + ½ r = all the gametes made (Figure 2).
Next, he reasoned that if pollen randomly united with the egg to combine the genes in the gametes, then algebra could be used to predict the result by multiplying the gamete expressions.
(½ R + ½ r) X (½ R + ½ r) = all the F 2 offspring made.
If we do the multiplication above, we get …
¼ RR + ¼ Rr + ¼ Rr + ¼ rr = ¼ RR + ½ Rr + ¼ rr = predicted fractions of F2 genotypes.
If this math is causing your brain to lose focus, you might be experiencing what Mendel’s contemporaries experienced when they read his published research paper. While many biologists were motivated to understand how the variation among animals and plants was controlled and inherited, it took biologists 30 years to recognize that Mendel’s new ideas to explain inheritance of traits in peas could be applied to inheritance of traits in other living organisms.
One possible explanation for this 30-year delay in appreciation is that it was difficult for biologists to understand how math could explain biology. One biologist that did understand what Mendel was describing was Punnett. Punnett decided to convert Mendel’s algebra into a more graphic representation of the process of gamete segregation and random union.
The Punnett Square
Math: (¼ RR + ½ Rr + ¼ rr).
Punnett designated the gametes made in the male and female parents with single letters (Figure 3). The diagram shows that when the gametes combine, the offspring (inside the squares) again have the genes in pairs in their cells. Accounting for the random union of gametes is accomplished with the four squares in the diagram. Two squares give the same Rr result, one the RR genotype and one rr . Both the algebra and diagram approaches provide the same prediction. Crossing an Rr with an Rr will produce three genotypes, RR, Rr and rr . They will be produced in a ratio based on the principle of segregation.

The genes controlling the monogenic traits behaved in predictable ways
Punnett’s diagram clarified for many biologists what Mendel was telling them in his published article. This was a challenging idea to understand because he was asking biologists to use something they could not see (genes) and explain something they could see (traits in peas or some other living organism).
Because Mendel recognized he was proposing a very different idea with the segregation principle, he was likely motivated to share the most convincing evidence possible. Mendel conducted additional experiments. One experiment was to test the hypothesis that there were two different kinds of F 2 which expressed the dominant trait, and these two types were being made by the F 1 in predictable fractions. How would Mendel show that F 2 which had the same phenotype did not always have the same genotype?
Mendel tested the breeding behavior of the F 2 . Mendel harvested all the selfed seed produced by his F 2 and grew progeny rows of F 3 . His segregation principle predicted that of the dominant F 2 , there should be two that are heterozygous for every one homozygote made (on average). The results of this experiment are summarized in Table 2 . Did Mendel’s data support the hypothesis?
Average ratio heterozygote F 2 to homozygote F 2 was 2.06 to 1.
The data show that, if we select a sample of F 2 with the dominant trait (Round seed or Yellow cotyledon), the principle of segregation predicts that there should be 2 heterozygotes for every 1 homozygotes.
Mendel’s data from rows of F 3 that all came from F 2 with the dominant trait supported his hypothesis. There were always two kinds of rows (true breeding and mixed) and the rows were in a 2:1 ratio. This fits with the principle of segregation .
By publishing these results in a scientific journal, Mendel allowed other scientists to learn from his work. This story reveals the real power of publishing research in the “permanent” scientific literature. The power of publication does not mean you were right with your science. The real power is that other scientists can find your paper, read it, think about your ideas, and then test them. In Mendel’s case, he was already dead when his fellow biologists discovered that his new ideas to explain the biology of peas were not only correct, but universal in their application.
Mendel’s Dihybrid Cross Experiments
Proper credit must be given to the idea of independent assortment. Gregor Mendel was the first to put this idea down on paper based on what he observed with his pea experiments. Furthermore, Mendel performed additional experiments to back up his ideas. Let’s examine his experiments with peas from the late 1800’s.
The outline below describes Mendel’s dihybrid cross experiments. The pattern observed in the results should look familiar!
The Experiment
- Parents: round seeds, yellow seeds (RRYY) x wrinkled seeds, green seeds (rryy).
- F 1 : All round and yellow seeds (RrYy).
- Selfing: F 1 (RrYy x RrYy):
Mendel explained his results as follows:
The F 1 plants have the genotype RrYy and can make four kinds of gametes RY, Ry, rY and ry.
Note that with both the Mendel algebra and Punnett square, the RRYY genotype occurs one time and the RrYy genotype occurs four times (Table 4). Mendel’s algebra and Punnett’s squares can be summarized to give the same results.
Selfing the F 2 to produce F 3
The easiest experiment to perform was to let the plants self-pollinate and then keep good records. After scoring his 556 F 2 seeds (Table 5) he took the 315 that were round and yellow and planted them in one part of his garden. The plants that grew were allowed to self-pollinate. Of the 315 round and yellow seeds planted, 301 plants matured and produced seed. The seed produced was the F 3 generation. At harvest, Mendel needed to exercise the utmost care. Each F 2 plant was handled separately. The seeds from the plant were harvested and Mendel then scored the F 3 seeds that came from the same F 2 plant. This can be referred to as F 2:3 data and the table below summarizes his complete experiment using all of the F 2 phenotypes.
Mendel’s F 2 data supported his principle of independent assortment. There were four different types of round yellow F 2 based on the kinds of progeny they could produce or their breeding behaviors. Based on the F 3 progeny produced, the F 2 genotype was deduced. For example, if a round, yellow seed gave all round progeny it must have the genotype RR . If it gave both round and wrinkled it was Rr .
Furthermore, the numbers of F 2 plants with each breeding behavior were in agreement with what was expected with independent assortment. There were four times as many round and yellow F 2 that gave all four phenotypes of F 3 seeds (138) compared to the round and yellow F 2 that were true breeding (38). Overall, there were nine types of breeding behaviors demonstrated in the F 2 demonstrating that there were nine F 2 genotypes. In all cases, the fractions observed in the F 2 agreed to the principle of independent assortment. Mendel’s well-planned experiment provided a convincing demonstration that genes behaved in this predictable manner.
The only thing better than performing an experiment that shows you were right about a new hypothesis is performing two experiments that show that you were right. That is what Gregor Mendel did! In his second experiment he crossed dihybrid F 1 plants with homozygous recessive plants in a test cross. This type of cross is named because the geneticist wants to perform a cross that will test or reveal the genotype of an organism. Therefore, a test cross is usually made between an organism with a dominant trait and a partner with a recessive version of this trait. Mendel performed the RrYy x rryy testcross and the expected progeny are shown in the Punnett square below:
RrYy gametes: RY, Ry, rY, ry
rryy gametes: all ry
The observed result closely matched the expected. The testcross experiment provides additional support for the principle of independent assortment.
Mendel established a rigorous precedent for using carefully planned multi-generation experiments to reveal the principles that governed trait inheritance. The beauty of Mendel’s accomplishments is that both the principles and his experimental approach can be applied to understanding the genetic control and inheritance of traits in many kinds of organisms still today.
Mendel’s principles of segregation and independent assortment are valid explanations for genetic variation observed in many organisms. Alleles of a gene pair may interact in a dominant vs. recessive manner or show a lack of dominance. Even so, these principles can be used to predict the future…at least the potential outcome of specific crosses.
Watch this video about Punnett Squares for more information

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Mendel experimented on a pea plant and considered 7 main contrasting traits in the plants. Then, he conducted both experiments to determine the inheritance laws. A brief explanation of the two experiments is given below. Monohybrid Cross. In this experiment, Mendel took two pea plants of opposite traits (one short and one tall) and crossed them.
Before Mendel's experiments, most people believed that traits in offspring resulted from a blending of the traits of each parent. ... Mendelian Genetics: Patterns of Inheritance and Single-Gene ...
In 1856, Mendel began a series of experiments at the monastery to find out how traits are passed from generation to generation. At the time, it was thought that parents’ traits were blended together in their progeny. Studying traits in peas. Mendel studied inheritance in peas (Pisum sativum). He chose peas because they had been used for ...
Aug 21, 2023 · Mendel conducted pioneering experiments with garden peas (Pisum sativum) in the 19th century and established the fundamental laws of inheritance. Mendelian Inheritance- Mendelism or Mendelian Genetics. Mendel’s contributions to the field of genetics were initially overlooked but were rediscovered and recognized in the early 20th century.
5.10 Mendel’s Experiments and Laws of Inheritance Of Peas and People Figure 5.10.1 Mendel conducted his research in genetics using pea plants. These purple-flowered plants are not just pretty to look at. Plants like these led to a huge leap forward in biology.
Aug 3, 2023 · Mendel’s Experiment. Mendel carried out breeding experiments in his monastery’s garden to test inheritance patterns. He selectively cross-bred common pea plants (Pisum sativum) with selected traits over several generations. After crossing two plants which differed in a single trait (tall stems vs. short stems, round peas vs. wrinkled peas ...
Mendel’s experiments extended beyond the F 2 generation to the F 3 generation, F 4 generation, and so on, but it was the ratio of characteristics in the P, F 1, and F 2 generations that were the most intriguing and became the basis of Mendel’s postulates. Figure 2: Mendel’s process for performing crosses included examining flower color.
Sep 8, 2024 · Mendelian Inheritance: Mendelism or Mendelian Genetics. Download the Cheat sheet pdf. Mendel’s Experiment. Gregor Mendel’s experiments between 1856 and 1863 laid the foundation for our understanding of genetic inheritance. Using the pea plant (Pisum sativum), he identified patterns of how traits are passed from one generation to the next ...
Nov 23, 2024 · Today, the postulates put forth by Mendel form the basis of classical, or Mendelian, genetics. Not all genes are transmitted from parents to offspring according to Mendelian genetics, but Mendel’s experiments serve as an excellent starting point for thinking about inheritance.
Gregor Mendel was the first to put this idea down on paper based on what he observed with his pea experiments. Furthermore, Mendel performed additional experiments to back up his ideas. Let’s examine his experiments with peas from the late 1800’s. The outline below describes Mendel’s dihybrid cross experiments.