

Digital Economy
A digital economy refers to an economy based on digital technologies connected through the internet.
- 1 Components of Digital Economy
- 2 Trends in Emerging Technologies
- 3 SWOT Analysis of the Digital Economy
- 4 Way Forward
Components of Digital Economy
The different technologies and economic aspects of the digital economy can be broken down into three broad components:
1. Core aspects of the digital economy: It comprises of fundamental innovations (semiconductors, processors), core technologies (computers, telecommunication devices) and enabling infrastructures (Internet and telecoms networks).
2. Digital and information technology (IT) sectors: It comprises sectors that produce key digital products or services ( e.g- digital platforms, mobile applications and payment services).
3. Digitizing sectors: These include sectors where digital products and services are being increasingly used (e.g. for e-commerce). It also comprises sectors such as finance, media, tourism and transportation, where digital technologies are transforming the way processes operate. Further, digitally literate workers, consumers and users are crucial for the growth of the digitized economy.
State of Digital Economy in India
- Digital Consumers: India is one of the top three global economies with respect to the number of digital consumers. As per Indian telecom services performance indicators released by TRAI, India had 560 million internet subscribers in 2018.
- Digital Adoption: India has the second-fastest rate of growth of digital adoption among mature and emerging digital economies( which includes Brazil, China, USA, Russia etc), as per TRAI. The adoption of public digital platforms like Aadhar, and UPI have led to faster digital adoption.
- India’s digital divide is narrowing fast as less affluent states are fast catching up with more affluent states.
- Between 2014 and 2018, 7 out of the 10 states with the highest rate of growth in internet subscriptions had per capita GDP lower than India’s average.
- Among the lower-income states, Uttar Pradesh alone added 36 million internet subscriptions.
- Digital economic value: A report released by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, in partnership with McKinsey has pointed out that India can create over $1 trillion of economic value from the digital economy in 2025, with half the opportunity originating in new digital ecosystems that can spring up in diverse sectors.
Global Best Practices
The Swedish Experience :
- Sweden is one of the top five cashless economies in the world. It has adopted effective policies to facilitate transactions using mobile or plastic payments through digital infrastructure.
- As on December 2015, the population of Sweden was estimated at 9.85 million people literacy was almost 100%.
The Kenyan Example
- Kenya has taken adequate measures to facilitate online payments for government services with an aim to reduce fraud and ensure better targeting.
- According to World Bank’s Global Findex report, 58% of the adult population in Kenya had active mobile money accounts in 2014. It was the highest in the world. Kenya is an example where mobile technology and a rise in smartphone ownership have helped in improving online payments despite low Internet penetration.
Trends in Emerging Technologies
1. Blockchain Technologies: Blockchain technologies are a form of distributed ledger technologies that allow multiple parties to engage in secure, trusted transactions without any intermediary. Besides its use as cryptocurrency, it is also in use for digital identification, property rights and aid disbursement.
2. 3D Printing: Three-dimensional (3D) printing, also known as additive manufacturing, can disrupt manufacturing processes by boosting international trade in designs rather than in finished products. For example, in Africa, such ventures exist for medical supplies in Uganda and for filling import gaps in Nigeria. 3. Internet of Things:
- Internet of Things (IOT) refers to the system of internet-connected devices that are embedded in various everyday objects enabling them to communicate with each other by data transfer.
- Its applications vary from energy meters, RFID tagging of goods for manufacturing, logistics management, monitoring weather conditions in agriculture, etc.
- As per a 2018 Ericsson report, there were more “things”(8.6 billion) connected to the Internet than people (5.7 billion mobile broadband subscriptions) in 2018. It has further forecasted that the number of IoT connections would grow by 17 per cent a year.
4. 5G Mobile Broadband : Fifth-generation (5G) wireless technology is critical for IoT due to its greater ability to handle massive volumes of data ( 5G networks can process around 1,000 times more data than today’s systems).
5. Cloud Computing: The cloud is transforming business models. It offers several benefits such as reducing the need of inhouse IT experts and offering flexibility for scaling and maintenance. Some cloud services provide office-like application tools. It is cost-efficient as it reduces the need of purchasing licensed software.
6. Automation and Robotics: Automation and robotics technology are being used widely in manufacturing processes. For instance, robots are mainly used in the automotive, electrical/electronics and metal industries.
7. Artificial Intelligence
- Analysis of large volumes of digital data is propelling the developments in AI, including machine learning. For instance, AI is already in use in areas such as voice recognition and commercial products (such as IBM’s Watson).
- As per ITU, such technologies can generate an additional global economic output of around $13 trillion by 2030, contributing an additional 1.2 per cent to annual GDP growth.
8. Big Data Analytics
- A key technology that runs across all the emerging technologies in the digital economy is big data analytics. This refers to the capacity to analyse and process massive amounts of data.The amount of data generated in the evolving digital economy is constantly and rapidly increasing.
- A white paper by IBM on Marketing Trends for 2017 noted that 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are created every day.
Government Initiatives to spur the digital economy
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Subsidy and benefits disbursements directly to bank accounts.
- Government e-Marketplace: Online marketplace for procurement of goods and services by various government departments.
- e-NAM: Pan-Indian electronic trading portal for agricultural commodities.
- Soil Health Card: Crop-wise recommendations of nutrients and fertilisers required for individual farm.
- BHIM App: Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM) is a mobile payments application based on NPCI’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI). It can be used to send or receive money from other customers and pay utility bills.
SWOT Analysis of the Digital Economy
- Convenient Mode of Payment: Digital economy provides an ease of transaction to the customers. It further offers other benefits, such as reduction in transaction cost of carrying and doing transactions in cash.
- Lower Risk: With proper cybersecurity, online payment is relatively risk-free, whereas there are always safety issues with physical cash
- Reduction in the Cost of Printing Money: Printing of new currency notes and replacement of soiled and mutilated currency notes involves cost. For instance, in 2015, printing currency cost the RBI Rs 27 billion. Thus, the cost can be reduced if the economy moves towards a digital economy.
- Decrease in Crime Rate: Many illegal activities like drug trafficking, prostitution, financing of terrorism and money laundering are carried out only in cash. A digital economy will make it difficult to carry out such operations.
- Good for the Banking Sector: A digital economy will help the banking system. Once people get used to digital payment and transfers, there would be less demand for cash holding. Thus, this would leave more cash in the banking system and thereby enable more savings.
- Economies of Scale: Interconnected networks in the digital economy would allow information flows across and between the networks. This would enable economies of scale due to fixed infrastructure costs of installing the networks.
- Availability of e-services: Digital platforms that enable real-time data updates, would increase accountability and facilitate monitoring, quality checks and timely intervention by the higher administrative authorities.
- Poor quality internet: Internet access is the backbone of a vibrant digital economy. However, it is plagued by issues related to quality and reliability, call drops and weak signals. Existing networks have been strained further by limited spectrum availability and usage, affecting the provision of quality services.
- Digital access and literacy: A vast number of Indian population does not have access to devices such as laptops, computers, smartphones, etc. As per the NITI Aayog Strategy document, digital literacy in India is estimated to be less than 10 percent of the population.
- Skill Gaps: Digital economy would require competent professionals with adequate skills to take the lead. However, India has been lacking in it.For instance, A NASSCOM report has pointed out an employee deficit of around 1.4 lakh jobs in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data Analytics segment across various sectors in India, which is expected to increase to 2.3 lakh by 2021.
- Digital gender gap: According to a study released by LIRNE Asia, an information and communications technology (ICT) policy think tank, India has the highest gender gap in mobile phone and 3rd highest in access to the Internet.
- Access to power: Uninterrupted access to power is essential for a digital economy to function efficiently. For instance, blockchains require a substantial, reliable electricity supply for proper functioning. However, around 22% of rural households across the country still do not have access to electricity.
- Inequality: The influx of frontier technologies of the digital economy may create inequality within the various regions of India. For instance, the deployment of 5G may further increase the urban-rural digital divide, as setting up 5G networks in rural areas with lower demand will be commercially challenging.
Opportunities
- Improve the ease of operations: Transition to a digital economy has the potential to reduce the operational costs of businesses. For instance, adhering to the compliance requirements in a digital form would take minimal time.
- Data as a resource: Data is the driving force behind all technologies of the digital economy. The transformation of data into useful information would aid better decision making.
- Financial Inclusion: Digital economy provides scope to extend banking facilities to unserved and under-served areas through technologies such as mobile banking, common service centres etc.
- Tap the leakages: Use of technologies to transfer subsidies of welfare schemes would help in stopping the leakages by making the process more transparent. For instance, DBT of subsidies under the PAHAL scheme has helped identify and block around 3.34 crore duplicate accounts, helping save thousands of crores.
- Black Money: Digitisation of financial transactions helps in maintaining a digital record and trail of such transactions. Thus, it provides opportunity to the authorities to track and verify transactions in future.
- Tackle Tax Evasion: Digital Economy could help in tackling tax evasion. For instance, the Aadhaar-PAN linkage gives maximum disclosure about the individual to all authorities including the Income Tax Department. It helps the tax authorities to track transaction and check the income tax profile of the individual/entity.
- New job opportunities: As per a report released by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, the value created by the digital economy has the potential to support 60-65 million jobs by 2025. Such job opportunities could include drivers of IoT enabled trucks, delivery agents in e-commerce companies.
- The growth of digital economy has further exacerbated the risks of job loss and unemployment. For instance, the influx of machine learning and artificial intelligence will make a number of low-skilled jobs redundant.
- Emerging technologies, such as 3d printing may also allow developed economies to use robots to “reshore” manufacturing jobs. This would lead to a stream of back-migration and affect the remittance economy
- The quality, speed and price of services are developing at a much faster rate due to better access to global digital platforms for research and development.
- Many critics have raised concerns that it may lead to disruption in the existing industries as new ways of doing business would come up. Any dearth in the adoption of new technologies may hamper the business interests of several firms.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: The regulatory framework for cyber security is inadequate. Hacking and denial-of-service attacks have led to the disruption of services, both in the government and private sector banks.
- Data and Privacy: Digital economy depends on the availability of structured and unstructured datasets. The growth of digital economy will further raise the concerns of data security and privacy of individuals.
Initiatives by the National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI) :
- UPI / UPI 2.0: UPI is a payment system that allows money transfer between any two bank accounts by using a Smartphone. It is based on the immediate payment service (IMPS) platform. UPI 2.0 added new features such as allowing the customers to link the overdraft account to UPI, checking the invoice before making payments to the merchants etc.
- BHIM: Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM) is a mobile payments application based on NPCI’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI). It can be used to send or receive money from other customers and pay utility bills.
- BharatQR: BharatQR (developed by NPCI, Mastercard, and Visa) is an integrated payment system. It facilitates the transfer of money from one bank account to another.
- Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS) : AePS is a bank led model which allows online interoperable financial inclusion transaction at PoS (MicroATM) through the Business correspondent of a bank using the Aadhaar authentication.
- National Automated Clearing House (NACH) : It is a web based solution to facilitate interbank, high volume, electronic transactions which are repetitive and periodic in nature, for instance subsidies, salaries etc.
- Vittiya Saksharta Abhiyan : The main purpose of this campaign is to encourage, create awareness and motivate people to use a digitally enabled cashless economic system for transfer of funds.
Way Forward
- Broadband connectivity: Proper implementation of the new National Digital Communications Policy, 2018 would provide universal broadband coverage at 50 Mbps to every citizen and enable 100 Mbps broadband on demand to all key development institutions (such as: educational institutions, hospitals etc).
- Promoting higher education as centre of innovation: The competitive advantage for a future digital economy lies in developing innovation skills in the workforce. Developing collaborations between higher education institutions and industry, and promoting new innovation clusters and tinkering labs would help in tapping the innovation potential.
- Content in Indian Languages: The state governments can play an important role in providing government e-services in Indian regional languages. The promotion of technologies such as Natural Language Processing in regional languages through machine learning can be explored.
- Government Procurement: The government is a large buyer of services. Thus, it can act as a market maker to create a scale for the country’s best innovations and technology applications. This would require suitable procurement policies by the government that help the startups to scale up their innovations.
Committees on Digital Payments
Ratan Watal Committee on digital payments(2016)
- Payment regulator: It recommended the setting up of an independent payments regulator within the framework of RBI.
- Changes in the Payment and Settlements Act: It suggested amending the Payment and Settlements Act to include provisions regarding consumer protection, data security and privacy.
- Aadhar Usage: It has envisaged a prominent role for Aadhaar, such as promoting Aadhaar as the primary identification for (KYC) purposes and allowing Aadhaar-based e-KYC.
- Cash-handling charge: The committee further suggested that government departments levy a cashhandling charge to discourage cash transactions.
- Interoperability: It suggested facilitating interoperability between banks and the payments service providers based on mobile number and Aadhar.
- It recommended the creation of a fund to promote digital transactions.
- It suggested that all government payments be made digitally .
Nandan Nilekani Panel on Digital Payments (2019)
- Role of government: The government should play an important role in the digitisation of payments.
- G2C Payments: All government-to-citizen payments, such as salaries, transfers in DBT mode etc should be made digitally.
- Payment of bills: All government departments should provide digital payment alternatives for all bills.
- Tax discounts: The government should provide tax discounts to firms that undertake digital transactions for conducting business.
- Interchange rate: The committee has recommended the interchange rate on card transactions to be reduced by 15 basis points.
- Time of transactions: It has recommended RBI to increase the time of transactions for NEFT and RTGS.
- National Common Mobility Card: It has proposed the introduction of a NCMC which is interoperable across different modes of transportation and also acts as an ATM debit card.
Discover more from Free UPSC IAS Preparation For Aspirants
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…

Search Articles
Prelims 2024 current affairs.
- Art and Culture
- Indian Economy
- Science and Technology
- Environment & Ecology
- International Relations
- Polity & Nation
- Important Bills and Acts
- International Organizations
- Index, Reports and Summits
- Government Schemes and Programs
- Miscellaneous
- Species in news
Post-Mains Strategy Session by Mr. Ayush Sinha | ForumIAS
Digital Economy: A Leveller or a Source of Economic Inequality - UPSC PDF Download
Science-technology.
With more and more technological developments, the internet has become a means to make life easier. It has transformed many sectors of the economy and has aided significantly in boosting the country's economic growth. It is no surprise that the digital economy is expanding its reach across the length and breadth of the country and has become an integral part of people’s lives. While going digital has made things simpler in almost all spheres of life (economic, political, social, commercial, etc.), whether it is actually beneficial or not is up for debate. It goes without saying that having a digital economy has made the day to day activities much smoother; it would be incorrect to assume that it hasn’t created problems.
A Leveller or a Cause for Inequality?
The benefits of the digital economy are there for everyone to enjoy. Some of the major advantages offered by the digital economy in India are: -
- An Increase in Online Businesses: Also known as e-commerce, the availability of a well-developed internet network along with facilities such as online banking, trading, video conferencing, etc., makes it so much easier for individuals to carry out their work. Owing to these facilities, marketing, buying and selling, money transactions, etc., have become so much easier, closer to home, and have significantly helped in the empowerment of the underprivileged sections of the Indian society.
- Higher Transparency and More Proof: Once something is on the internet, it stays out there forever, no matter whether you delete it from one domain or another. It never fully disappears. This is a massive advantage, especially when it comes to money transactions and other kinds of agreements entered by the people. For instance, once a person makes a payment online, the transaction record is saved online and is easily accessible as and when required. This has made life simpler for individuals and offers protection in case of instances of fraud, theft, or other forms of cyber-crimes.
- Easy Availability of Services: Not only does the internet provide a means to easily conduct essential activities, but it also allows people to access necessary services conveniently. Information regarding necessary steps, benefits available, documentation required, etc., for different government schemes. Many government agencies have their own apps which allow the users to avail themselves of the essential services within a few minutes.
While the advantages offered by the digital economy are noteworthy, it goes without saying that the digital economy is responsible for creating some inequalities in Indian society as well, such as:
- Unemployment: It goes without saying that an internet driven economy has made life less complicated, but it has also become a cause for concern. With almost everything being done online with the help of software, there is a decrease in the demand for manpower. Fewer and fewer people are required to do a particular work, which has thrown many people into unemployment. For example, when it comes to bank work, the easy availability of banking apps, Paytm, Google Pay, etc., has put many people out of work. Also, for people with a lesser understanding of the internet, it becomes difficult to find a suitable job.
- Increased Cyber Crimes: Even though every activity on the internet can be traced, it does not mean that cybercrime no longer exists. In fact, it is quite the opposite. With almost everyone having access to the internet, some with greater knowledge of its functioning and loopholes, there have been increased cases of cybercrime, including hacking of bank accounts, thefts, illegal transactions, etc., which have eroded the trust of people in the prospects of the digital economy.
- Lack of Security: The ease with which unauthorized entities can access data on the internet can turn out to be quite harmful. Many companies, businesses, and even government agencies store large amounts of data online or on computers. Anyone who knows how to hack into another system, even a secure one, can easily gain access to important and confidential data and can also use it to their advantage.
Steps to Tackle The Issue of Inequality
With constant technological developments, it is good to move along with those changes; it is good to learn new ways of life. However, the problem arises when people get so absorbed in that new life that they do not realize the harm it is causing to themselves and others. In such situations, it becomes important to identify what the problem is and how to find a solution to it. Here are some ways to bridge the gap that was and continues to be created by the digital economy:
- Stricter Cyber Laws: While cybercrime has been on the rise in recent years, thanks to easier access to the internet, the laws for cyber crimes are still not well-defined. There should be improvements in cyber laws so that the victim is provided immediate attention and relief and the culprits are caught in time. There should be increased awareness about such crimes, and efforts should be made to make the internet more secure. Users should be educated about the do’s and don’ts while using the internet to secure their digital space.
- Education: Since almost every sector of the economy uses the internet and its related services to carry out daily functions and run businesses, more and more people should be taught how to use the internet. They should be encouraged to develop skills related to the internet so that they have a better chance of finding employment. This is especially the case with rural areas. While people in small towns and villages do have access to the internet, it is often limited. If they, too, are taught how to perform online banking, purchasing or selling items online, or even promoting a local business online, they would benefit immensely.
- Empowering people: The fact that many business activities are being conducted online and it has become important to have basic knowledge of the functions of the internet for anyone to land a decent job. These trends indirectly contribute to problems such as unemployment. It is the government’s responsibility to create more job opportunities in all sectors and all regions of the country. Efforts must be undertaken by the central government and the state governments to ensure that people, irrespective of their lack of knowledge of the internet, have a way of earning a livelihood.
Over the years, the government has made efforts to transform the traditional economy into a digital economy. It is in no way wrong to hope for an economy that keeps growing steadily while making things easier for the people. But it is also important to be fully aware of the country's situation and its people before giving priority to major changes such as the ones mentioned above. It is necessary to assess both the positive and negative impacts of such a transformation and then develop a balanced approach that satisfies the needs of all stakeholders.
Top Courses for UPSC
Faqs on digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality - upsc, digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality - upsc, viva questions, extra questions, mock tests for examination, objective type questions, important questions, study material, semester notes, practice quizzes, previous year questions with solutions, shortcuts and tricks, past year papers, sample paper, video lectures.

Digital Economy: A Leveller or a Source of Economic Inequality Free PDF Download
Importance of digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality, digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality notes, digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality upsc questions, study digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Change country.
- Our Selections
- About NEXT IAS
- Director’s Desk
- Advisory Panel
- Faculty Panel
- General Studies Courses
- Optional Courses
- Interview Guidance Program
- Postal Courses
- Prelims Test Series
- Mains Test Series (GS & Optional)
- ANUBHAV (All India Open Mock Test)
- Daily Current Affairs
- Current Affairs MCQ
- Monthly Current Affairs Magazine
- Previous Year Papers
- Down to Earth
- Kurukshetra
- Union Budget
- Economic Survey
- Download NCERTs
- NIOS Study Material
- Beyond Classroom
- Toppers’ Copies
- Student Portal
Digital Economy

The Government is working on a comprehensive legal framework for the digital economy.
- The digital economy is the worldwide network of economic activities, commercial transactions and professional interactions that are enabled by information and communications technologies (ICT) .
- It can be succinctly summed up as the economy based on digital technologies.
- The digital economy reflects the move from the third industrial revolution to the fourth industrial revolution.
- The third industrial revolution, sometimes called the digital revolution, refers to the changes that happened in the late 20th century with the transition from analog electronic and mechanical devices to digital technologies.
- The fourth industrial revolution builds on the digital revolution as technologies today continue to bridge the physical and cyberworlds.
Advantages of The Digital Economy
- Increased productivity: The digital economy has increased the productivity of businesses as they can now use technology to automate their operations and processes.
- Increased competitiveness: Businesses can use technology to improve their products and services. This has increased the competitiveness of businesses.
- Reduced costs: Digitisation has helped businesses replace manual tasks with automated processes. This has reduced the costs of businesses and has led to lower prices of products and services for consumers.
- Better & Convenient Products: Today, digitised businesses can offer their customers better products and services at lower prices. New business models like e-commerce and m-commerce have made it possible for customers to shop anytime, anywhere.
- Increased employment opportunities: The digital economy has generated new job opportunities as new businesses are springing up. It has also created new job roles spread all over the world.
- Improved quality of life: The digital economy has made it possible for people to work from anywhere in the world. This has improved the quality of life of people as they can now balance their work and personal life.
- Faster transactions: The digital economy has made it possible for businesses to conduct transactions faster as they can now use online payment methods.
- Improved efficiency: Digitisation of processes has helped businesses become more efficient by removing error-prone manual tasks.
- Innovation: The digitisation of businesses and its processes leads to innovation with respect to not just offerings but also the way businesses operate.
- Increased transparency: The digital economy has increased the transparency of businesses as they can now use technology to share information with their customers.
- Improved communication: Increased connectedness in the digital economy has made it possible for businesses to communicate with their customers more effectively. They now have a number of channels through which they can reach their customers including social media, email, and SMS.
- DigiLocker: It was launched in 2015 to create a cloud-based platform to issue, exchange and verify essential documents or certificates.
- MyGov: It was launched in 2014 to bring the government closer to the people by providing an interface (online forum) for exchange of ideas.
- BharatNet: It was introduced to connect all 250,000 Gram Panchayats (GPs) in the country and provide 100 Mbps internet connectivity.
- Smart Cities: It was initiated in 2015 to transform all Indian cities into smart cities by leveraging various technologies.
- Digitisation of Post Offices
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna
- Digital India
Disadvantages Of Digital Economy
- The digital divide: One of the biggest disadvantages of the digital economy is the digital divide. This is the gap between those who have access to technology and those who don’t. This has created a new form of inequality in the world.
- Cybercrime: The increased use of technology has also led to an increase in cybercrime. This is because criminals can now use technology to commit crimes like identity theft, fraud, and money laundering.
- Data security: With businesses collecting more and more data about their customers, there is a risk of this data being leaked or stolen. This can lead to a loss of trust between businesses and their customers.
- Unemployment: The digitisation of the economy has led to job losses in some sectors as businesses have replaced human workers with technology. This has increased unemployment in these sectors.
- Privacy concerns: As businesses collect more data about their customers, there are concerns about the misuse of this data.
- Heavy investments: The digitisation of businesses requires heavy investments in technology. This is a challenge for small businesses which might not have the resources to invest in technology.
- Monopoly: The digitisation of the economy has led to the rise of a few big companies which have become very powerful. This has created a monopoly in some sectors.
- Addictive nature: The digital economy is very addictive in nature. This is because it is designed to keep people hooked on their devices. This can lead to a number of problems like addiction, anxiety, and depression.
- Potential environmental impact: The increased use of technology in the digital economy has led to an increase in the number of e-waste and heavy carbon footprint.
- There is a need to leverage today’s emerging technologies , such as IoT and prescriptive analytics, to better connect with existing and potential customers and to be more responsive while also being more efficient and effective.
- To compete in the years ahead, organizations — whether they are for-profit businesses, service-oriented entities, such as healthcare systems, or nonprofit and government institutions — will need both leaders and employees who are able to innovate.
- Become better prepared to explore how best to develop or use emerging technologies or risk being left behind as the digital economy moves forward.
Source : TH
Editorial Analysis
- A Community on the Margins :plight of sex workers
- A Bilateral Investment Treaty With a ‘Bit’ of Change
- Declining Health Spending Risks SDG Goals
- India’s Growing Influence in Global Innovation
- GovAI: Reimagining Governance with AI
Headlines of the Day
- Headlines of the Day 23-11-2024
- Headlines of the Day 22-11-2024
- Headlines of the Day 21-11-2024
- Headlines of the Day 20-11-2024
- Headlines of the Day 19-11-2024

Other News of the Day
- Facts In News 23-11-2024
- World Bank’s “Jobs at Your Doorsteps”study
- Telecommunications (Telecom Cyber Security) Rules, 2024
- Reducing Dependence on the Import of the Coking Coal
- China-India State of Play
- At a Glance
Digital economy: Benefits & challenges

• India’s digital economy is poised to constitute one-fifth of the GDP by 2026 from one-tenth at present, according to a Reserve Bank’s ‘Report on Currency and Finance for the year 2023-24’.
• Digitalisation is driving innovation and efficiency, fostering a new model of economic growth, and facilitating quality improvements. Digital transformation is also evident in the financial sector, where adoption of technology solutions by financial institutions, coupled with the advent of new market players like financial technology firms (FinTechs) and large corporations (BigTechs), is reshaping the conventional notions of finance.
• India is leading the global digital revolution, emerging as a frontrunner on the back of its robust digital public infrastructure (DPI), rapidly evolving institutional arrangements, and a growing tech-savvy population.
• Over the past decade, the global digital economy has grown 2.5 times faster than the physical world economy to account for more than 15 per cent of global GDP.
• In a formal sense, the term “digital economy” has been defined as the contribution of any economic transaction involving both digital products and digital industries to GDP — digital products being goods and services with the main function of generating, processing and/or storing digitised data.

Advantages of digital economy
• Digitalisation is set to break the ‘iron laws’ of cross-border trade and bring about a fundamental structural shift in global production processes, trade, and investment flows.
Digitalisation in the financial sector provides enormous benefits in terms of:
i) Fostering innovations
ii) Reducing financial intermediation costs.
iii) Improving customer experiences.
iv) Enhancing competition among the service providers, thereby boosting efficiency and inclusivity of the financial sector.
• Digitalisation offers a unique and dynamic opportunity to expand the reach of financial services to the entire population, especially disadvantaged and voiceless sections, thereby formalising the economy. Globally, there has been an increase in bank account ownership from 61 per cent of the adult population in 2014 to 74 per cent in 2021.
• Digitalisation can play a vital role in increasing the contribution of women to economic activity and effectively targeting delivery of the public schemes for intended beneficiaries.
• Digitalisation is transforming payments for internationally traded goods and services. Technologies like real-time payment systems and blockchain enable instant transfers, reduce delays and improve tracking of funds. Automated processes cut costs, offer better exchange rates and ensure regulatory compliance through data analytics.
• Digitalisation is also rapidly transforming cross-border migrant remittances and global capital flows by lowering costs, increasing transparency and efficiency.
• Digitalisation has diversified the range of players in the financial services industry, with a significant increase in the number of FinTechs across nations.
• The digital revolution is galvanising banking infrastructure and public finance management systems covering both direct benefit transfers and tax collections. Vibrant e-markets are springing up and expanding their reach.

India at the forefront of the digital revolution
• India has one of the largest digitally connected populations worldwide.
The two fundamental drivers of this wave of digitalisation are:
a) Ubiquitous connectivity through mobile, internet-connected devices and communication networks.
b) Low-cost computing and data storage.
• India is home to the second largest telecom subscriber base and internet user base globally. The growth in digital enablers has been powered by competitive offerings by telecom operators, advent of global tech giants and among the cheapest data prices in the world.
• The average time Indian users spend online is 6.45 hours per day, which is close to the global average (6.4 hours).
• Although internet penetration in India was at 55 per cent in 2023, the internet user base has grown by 199 million in the recent three years.
• India’s cost per gigabyte (GB) of data consumed is the lowest globally at an average of Rs 13.32 ($0.16) per GB. India also has one of the highest mobile data consumption in the world, with an average per-user per-month consumption of 24.1 GB in 2023.
• There are about 750 million smartphone users, which is expected to reach about one billion by 2026. India is expected to be the second largest smartphone manufacturer in the next five years.
• India has the world’s third largest startup ecosystem with over 1.4 lakh startups and over 100 unicorns .
• India’s digital trade is projected to increase to $2.4 trillion in 2047, more than 13 times its level in 2020.
• In the digital currency arena, the Reserve Bank of India is at the forefront with pilot runs of the e-rupee, the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
• The digital lending ecosystem is becoming vibrant with initiatives such as Open Credit Enablement Network, Open Network for Digital Commerce and the Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit.
• Digitalisation is empowering India to bridge economic inequalities through a paradigm shift in social welfare schemes via Direct Benefit Transfers (DBTs). Over the last decade and especially since the pandemic, funds disbursed directly to beneficiary accounts through DBT have been ramped up, along with an increase in the number of beneficiaries.
• Digitalisation in finance is paving the way for next-generation banking, improving access to financial services at affordable costs, and enhancing the impact of direct benefit transfers by effective targeting of beneficiaries in a cost-efficient manner.
• Under the payments layer, the development of a real-time, round-the-clock, scalable and interoperable retail payment option is enabled by the Unified Payments Interface (UPI). It powers multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application, merging several banking features, seamless fund routing and merchant payments.
• The payment platform has facilitated secure, convenient and low-cost transactions between individuals, businesses and governments on demand, with settlement in fiat money inside the formal financial system.
• Digital payments have recorded a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 50 per cent and 10 per cent in volume and value terms, respectively, in the last seven years involving 164 billion transactions worth Rs 2,428 lakh crore in 2023-24.
• The UPI has seen a ten-fold increase in volume over the past four years, increasing from 12.5 billion transactions in 2019-20 to 131 billion transactions in 2023-24 — 80 per cent of all digital payment volumes. Currently, the UPI is recording nearly 14 billion transactions a month, buoyed by 424 million unique users in June 2024.

Digitalisation’s Challenges
While digitalisation opens several opportunities across sectors, it also brings in new challenges while accentuating existing ones.
1) Cybersecurity
• Cybersecurity is an important challenge owing to the diverse nature of cyber threats targeting the digital financial infrastructure. In India, security incidents handled by the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) have increased from 53,117 in 2017 to 13,20,106 during the period January-October 2023. Unauthorised network scanning/probing/vulnerable services account for more than 80 per cent of all security incidents in India.
• Globally, cybercrime costs are expected to reach $13.82 trillion by 2028, up from $8.15 trillion in 2023. The average cost of a data breach has also risen to $4.45 million in 2023, a 15 per cent increase over three years. Recognising the significant costs involved, most central banks have increased their cybersecurity investment budgets by 5 per cent since 2020.
• In India, the average cost of data breaches stands at $2.18 million in 2023, a 28 per cent increase since 2020 albeit less than the global average cost of data breach. The most common attacks in India are phishing (22 per cent), followed by stolen or compromised credentials (16 per cent).
2) Consumer Protection
• While digitalisation offers enhanced convenience and accessibility, the growing complexity of financial products also introduces new challenges in ensuring customer protection. With the increasing adoption of digital payments, the share of complaints related to mobile/electronic banking, ATM/debit cards and credit cards received in the offices of the RBI ombudsman accounted for 47 per cent of total complaints in 2022-23.
• India is one of the top ten countries in terms of embedded finance revenue and it is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.4 per cent over 2022-29 to reach $21.1 billion in 2029. While cross-selling and embedded finance models enhance customer convenience, they may raise anti-competition concerns due to bundled services.
• While the digital lending platforms and buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services bolster consumer convenience, they also entail various costs, including exorbitant charges, coercive recovery practices and hidden fees.
• Digitalisation is also giving rise to certain ‘invisible risks’ or ‘dark patterns’, whereby consumers are tricked into making decisions detrimental to their interests.
3) Reshaping of Labour Markets
• Digital technologies are impacting workforce composition, job quality, skill requirements, and labour and regulatory policies. Implementation of AI in financial services is shifting roles to higher-skilled tasks, automating routine functions and aiding decision-making.
• Digitalisation is decentralising financial labour through outsourcing and telework. Automation replacing labour can potentially widen the gap between capital and labour returns, creating a fragmented labour market with low-skill/low-pay and high-skill/high-pay jobs, while middle-tier jobs are displaced by technology.
• Between 2013 and 2019, employees in support roles in the financial sector decreased in many countries, while the number of professionals and technicians rose. This is evident in the Indian banking sector as well.
• Upskilling and reskilling the labour force pose significant challenges, given the growing shift towards digital-intensive roles. The rising importance of AI-related skills in the labour market in India is reflected in the growth in AI talent recruitment relative to overall recruitment in 2023.
• Pre-existing traditional methods of learning and development, however, are inadequate for this transformation, necessitating significant investments to build the required skills at scale, leverage AI in learning and keep pace with the swiftly evolving demands of digital skills.
4) Emerging Regulatory Challenges
• Digitalisation generates regulatory challenges, necessitating that regulators stay ahead of the financial innovation curve while balancing the complex trade-offs related to financial stability, competition and customer protection. This will require enhancing the capacity of regulated entities and oversight authorities, updating legal and regulatory frameworks, engaging stakeholders to identify risks and expanding consumer education.
• Regulations need to set boundaries to contain the irrational exuberance of participants and ensure a sound and robust set of institutions, thereby promoting financial stability. In the context of peer-to-peer lending applications in India, regulations have been found to have a positive impact in building trust, thereby enabling adoption of financial innovations.
• BigTechs, that can quickly become ‘too big to fail’ and dominate markets, may pose significant challenges in assessing risk profiles due to their unique characteristics, extensive group entities, interconnected activities and transnational presence.
• Collection of extensive data by BigTechs can be utilised to favour their own products, obtaining higher margins by making financial institutions’ access to prospective clients via their platforms, engaging in product bundling and cross-subsidising activities. This can give rise to adverse economic and welfare outcomes.
• Unregulated non-bank payment services could disadvantage traditional banks, leading to regulatory arbitrage and deposit disintermediation. Globally, countries have accordingly enacted regulations to strengthen enforcement in FinTech-related activities.
• On the regulatory front, the challenge is to balance financial security through data analytics with the need to protect individual privacy and customer rights.
Manorama Yearbook app is now available on Google Play Store and iOS App Store
Add to Flashcards
- Select a Deck
- Create New Deck
- digital payments
- {{stories.sectionName}} {{stories.title}}

- TRP for UPSC Personality Test
- Interview Mentorship Programme – 2023
- Daily News & Analysis
- Daily Current Affairs Quiz
- Baba’s Explainer
- Dedicated TLP Portal
- 60 Day – Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – 2024
- English Magazines
- Hindi Magazines
- Yojana & Kurukshetra Gist
- Prelims Exclusive Programme (PEP) – 2025
- All India Prelims Test Series – 2025
- Gurukul Foundation
- Gurukul Foundation – Delhi
- Gurukul Advanced
- TLP Connect – 2025
- TLP (+) Plus – 2025
- Integrated Learning Program (S-ILP) – 2025
- MAINS PYQs Mastery
- TLP Plus – 2024
- Sociology Foundation Course – 2025
- Sociology Test Series – 2024 (Coming Soon!)
- Public Administration FC – 2024
- Anthropology Foundation Course
- Anthropology Optional Test Series (Coming Soon!)
- Geography Optional Foundation Course
- Geography Optional Test Series – Coming Soon!
- PSIR Foundation Course
- PSIR Test Series – Coming Soon
- KPSC ಪಶುವೈದ್ಯಾಧಿಕಾರಿ (Veterinary Medical Officer – VMO) Exam 2024
- ‘Mission ಸಂಕಲ್ಪ’ – KPSC Foundation Course
- ‘Mission ಸಂಕಲ್ಪ’ – KPSC Prelims Crash Course
- Daily News & Analysis हिन्दी
- Monthly Magazine
India’s digital economy
- June 24, 2022

In News: Addressing the meeting of the BRICS Business Forum, Prime Minister said the digital transformation unfolding in India has never before been seen on the world stage
- India’s digital economy and the infrastructure sector has a total potential for $2.5 trillion
- There are more than 100 unicorns in over 70,000 start-ups in India , and their number continues to grow.
- The value of the Indian digital economy will reach $1 trillion by 2025
Advantages of a Digital Economy
- Removal of Black Economy: By restricting cash-based transactions and using only digital payments, the government can efficiently expel the black economy.
- Empowerment to People: Direct Benefit Transfer, fight against Corruption
- Creation of new jobs
- Increase in Revenues: Each transaction is recorded, customers will get a bill for their purchase, and the merchants are bound to pay sales tax to the government.
- e-governance: Digital economy will pave a way to e-governance, where delivery of all government services would be done electronically
Measures taken by Government
- Digilockers: it is a “digital locker” service operated by the Government of India that enables Indian citizens to store certain official documents on the cloud.
- Digital Payments: The introduction of Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which introduced the benefits of digital payments in every part of the country.
- BHIM app —It is an app to enable digital payments.
- Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan to make citizen digitally literate.
- BharatNet Project: world’s largest rural broadband connectivity programme using Optical fibre
- Lack of connectivity/infrastructure: Slow roll-out of Wi-Fi hotspots and the slow speed
- Lack of incentives: Most small and medium scale industry is struggling to adapt to modern technology
- Digital illiteracy: Huge digital divide between gender, regions etc
- Lack of skilled manpower: Lack of user education and there are limited facilities to train personnel
Way forward
- India’s technical and management institutes should revamp their curriculum to integrate and promote digital technologies
- Skill development initiatives to train manpower
- Stricter data protection laws that govern such cross border digital flows is needed he digital economy is heavily based on intellectual property, strict protection to patents and copyrighted work, whether produced in India or elsewhere is also need to be implemented.
BRICS summit
- The BRICS summit is being hosted by China as a chair of BRICS this year
- BRICS is an acronym for the grouping of the world’s leading emerging economies , namely Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- The BRICS Leaders’ Summit is convened annually.
- The Chairmanship of the forum is rotated annually among the members, in accordance with the acronym B-R-I-C-S
- Together, BRICS accounts for about 40% of the world’s population and about 30% of the GDP
- The first BRIC Summit took place in 2009 in the Russian Federation
- South Africa was invited to join BRIC in December 2010, after which the group adopted the acronym BRICS.
- South Africa subsequently attended the Third BRICS Summit in Sanya, China, in March 2011.
BRICS initiatives
New Development Bank
- During the Sixth BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (2014) the leaders signed the Agreement establishing the New Development Bank (NDB).
- Fortaleza Declaration stressed that the NDB will strengthen cooperation among BRICS and will supplement the efforts of multilateral and regional financial institutions for global development thus contributing to sustainable and balanced growth.
- NDB is headquartered in Shanghai.
Contingent Reserve Arrangement
- Considering the increasing instances of global financial crisis, BRICS nations signed BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) in 2014 as part of Fortaleza Declaration at Sixth BRICS summit.
- The BRICS CRA aims to provide short-term liquidity support to the members through currency swaps to help mitigating BOP crisis situation and further strengthen financial stability.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to a grouping of countries known as BRICS, consider the following statements: (2014)
- The First Summit of BRICS was held in Rio de Janeiro in 2009.
- South Africa was the last to join the BRICS grouping.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Related Posts :
Daily current affairs ias | upsc prelims and mains exam – 23rd june 2022, four new corals recorded from indian waters.

Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 23rd November 2024
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS हिन्दी | UPSC प्रारंभिक एवं मुख्य परीक्षा – 22nd November 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 23rd November 2024
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 22nd November 2024
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS हिन्दी | UPSC प्रारंभिक एवं मुख्य परीक्षा – 21st November 2024
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 21st November 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 21st November 2024
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS हिन्दी | UPSC प्रारंभिक एवं मुख्य परीक्षा – 20th November 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 20th November 2024
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 20th November 2024
Search now.....
Sign up to receive regular updates.
Sign Up Now !

- Our Centers Delhi Bhubaneswar Lucknow
- UPSC Mains Previous Year Questions
- Digital economy: A leveller or a source of economi
Digital economy: A leveller or a source of economic inequality
- Subject Essay

Verifying, please be patient.
Our Centers
DELHI (Karol Bagh)
GS SCORE, 1B, Second Floor, Pusa Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi - 110005 (Beside Karol Bagh Metro Station Gate No. 8)
Get directions on Google Maps
BHUBANESWAR (Jaydev Vihar)
GS SCORE, Plot No.2298, Jaydev Vihar Square, Near HCG Day Care, BBSR - 751013
LUCKNOW (Aliganj)
GS SCORE, 2nd Floor, B-33, Sangam Chauraha, Sector H, Aliganj, Lucknow, UP - 226024
Delhi (Karol Bagh) Centre
GS SCORE, Second Floor, Metro Tower, 1B, Pusa Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi - 110005 (Beside Karol Bagh Metro Station Gate No. 8)
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +91 8448496262
Classroom / online / Live programs
- Mains Classes
- Mains Advance Classes
- Ethics & Essay Classes
- IAS Foundation
- Aadhar:NCERT Foundation
- Target PT:Prelims Classes
- Current Affairs Mentorship Program
- Optional Classes
- Optional Q&A (TEST SERIES & Mentorship)
- Mains Previous Year Questions
- Offline Test Centers
- All Courses
TOPPER'S CORNER
- Topper's copy
- Topper's profile
- Reports & Magazines
- UPSC Previous Year Papers
- Meet the Mentor
- Interview Guidance
- Privacy Policy
Still Have Questions?
- © 2024 - IAS SCORE
All Rights Reserved.
Welcome to our secure login portal. Access your account with ease.

- Using Password
Not registered yet? register here!
Welcome to our secure register portal. For a brighter future, register now and unlock endless learning opportunities.
User Register
Already have an account? Login
Oops, forgot your password? Don't worry, we've got you covered. Reset it here
Lost your login details? No problem! forgot your password in just a few clicks
Forgot Password
Verify your mobile number, you have successfully logged in.
Join Us on WhatsApp
Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now

DIGITAL ECONOMY

Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
- India’s digital economy and the infrastructure sector has a total potential for $2.5 trillion - Prime Minister Narendra Modi. Addressing a meeting of the BRICS Business Forum, Mr. Modi said the digital transformation unfolding in India had never been seen before on the world stage.
What is the digital economy?
The digital economy refers to economic activity that uses electronic communication and digital technologies to provide goods and services. The main building blocks of the digital economy are
- The internet. This enables firms to offer goods for sale and enables consumers to browse for goods that they need.
- E-mail. Electronic communication enables very cheap, instantaneous communication across the world. It can be used to send information and requests very quickly.
- Digital automation . Firms can use the processing power of computers to make decisions on output, prices and how to reach consumers.
- Digital payments – credit cards, Apple Pay, Google pay, bitcoin, bank transfer. A digital economy is moving us towards a cashless society.
- Increasingly the digital economy relies on AI, mass use of electronic data and automated technology
- Social media . To a lesser extent, social media is an aspect of the digital economy. With individuals using it share recommendations about business.
Essential Elements of Digital Economy
Digital Economy facilitates and executes the buying and selling of products and services through electronic transactions undertaken by means of the internet. Its essential elements are:
- Digitalization and using Information and Communication Technology (ICT), rigorously.
- Knowledge codification
- Conversion of information into commodities
- Organizing work and production in modern ways.
Hyperconnectivity, i.e. emerging interconnectivity of people, firms, systems, etc. as a result of the internet, mobile technology and Internet of Things (IoT).
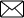
Examples of the digital economy
Airbnb – This enables tourists to book online. It has also made it possible for individual households to let our their house/room to tourists. Before the digital economy it was not practical.
E-commerce site : Amazon market place/Ebay.
Netflix – This enables consumers to purchase tv-series and films over the internet, without need for any physical good.
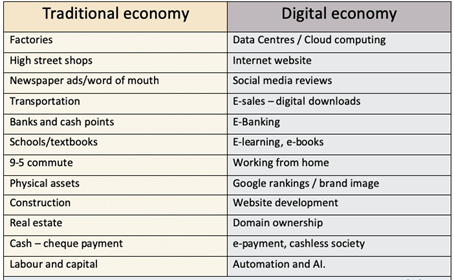
Advantages of the digital economy
Greater information
The internet has enabled consumers to have greater information and choice. For example, it makes it easier to compare prices between firms. It also brings information to a person’s fingertips.
Time saving
For the user, time is a determining factor when making purchases, managing their finances, traveling or even working.
Reduced costs
The digital economy considerably reduces the costs for the merchant and the maintenance of his business.
Increases flexibility
The flexibility that financial technology provides can be seen at all levels of exchange transactions - From the user and the numerous payment methods to the possibility of buying from anywhere in the world.
Provides more information and decision-making power
The power of decision for the user defines many things and the use of the digital economy is exactly that, more information for better decision making.
Process reinvention
The digital economy removes many of the barriers that previously defined the way certain processes are carried out. A clear example is work, which took a 180º turn with technological advances that allow, for example, working from home, making tele-working one of the most widely used alternatives today due to the multiple benefits it combines.
Lower barriers to entry
In some markets, aspects of the digital economy make it easier for new firms to enter. The digital economy has brought many new services which were inconceivable before, such as online home deliveries for grocery to dating apps.
Creates significant data which can give new insights
The mass production of data can help inform governments and charities about what is happening in the economy. For example, in tracking of COVID-19 spread, the use of an app on mobile phones may indicate where local hotspots emerge.
Contributes to Economic Growth:
The widespread digital economy has recorded tremendous growth and innovation as well as it can be broadly applied to other economic sectors.
Creates new jobs
Digital economy has given a boost to jobs too. In the last few years, the development of mobile apps has solely created millions of jobs worldwide.
Improves public services
A set of global access to broadband and a powerful information and communication technology services ecosystem provides a platform to improve service delivery in core sectors.
Rise in e-commerce
A recent growth in e-commerce transactions has been reported in the last few years. And all credit goes to the digitalization of commercial activities, due to which developing, buying, distributing, selling and tracking of products and services, has become much simpler, competitive, and profitable.
Digital delivery of goods and services
From aviation to banking, entertainment to education and insurance to hotel booking, one can easily get the goods and services of their need, online.
Transparency
In the digital economy, major commercial transactions take place online, which eliminates cash transactions, and ultimately increases transparency and reduces corruption.
Expands business opportunities
Digitalization enables small firms and businesses to actively participate in international buying and selling of goods and services.
Limitations of Digital Economy
Cybersecurity
An exponential increase in cyber threats has been reported in recent years due to increasing digitalization in the economy. Except if cybersecurity is countered successfully, it will not be easy to develop a safe and trusted environment, which is conducive to the growing business.
Disruptions in labour markets
Though it is assumed to create new job opportunities, there is also a risk related to the speed of labour market changes and destruction of basic jobs. As everything will be digitized and automated, processes that involve labour and manual work will be avoided and is replaced by technology-oriented work, which will result in loss of jobs and may also widen income inequality.
Strong infrastructure requirement
It requires strong infrastructure concerning internet, telecommunication and mobile industry. For the development of such industries, heavy investment is required, so as to link all the cities, towns and villages.
With the emergence of the digital economy, consumers can get easy and quick access to information, due to the digitization of the content. Moreover, sharing of information with their friends and acquaintances is now just a click away.
Monopoly power
Despite the potential for new start-ups, many aspects of the digital economy have become dominated by firms with monopoly power. For example, Amazon has cornered the market for online sales, meaning many firms have to go through the Amazon market place to reach consumers who go to Amazon out of habit. Similarly, Google and Facebook have all developed very strong brand loyalty and market share in their respective markets. This has made a few tech giants very profitable.
Addictive nature of technology
Whilst, in theory, the internet can save time, e.g. finding bus times is much easier with internet than paper copies, this time saved may be outweighed by the time we waste checking Facebook, twitter, internet searches. Also, the sheer volume of information can cause us to drown in information and lose sight of what we actually need. More choices do not necessarily lead to better outcomes.
Privacy issues
Harvesting and using data has become big business. Facebook collects a large range of data on its users and this has been bought by political interests who can give very targeted political ads to its users.
Bypassing of labour laws
The digital economy has created a trend towards using self-employed freelancers, who are not protected by the same labour laws. For example, delivery drivers for Uber drivers have often been employed on zero-hour contracts. This enables firms to cut labour costs, be more flexible, but it can leave workers without sick pay or employment protections.
Social media has led to more graphic content
The anonymous and distant nature of social media has exacerbated trends to personal attacks and the posting of conspiracy theories or posting of violent/sexual images. The digital economy has enabled the proliferation of content that is damaging to human well-being.
Disruption patterns.
The pace of digitalization can lead to structural unemployment, with some unskilled workers increasingly losing out to skilled workers. Combined with the monopoly power of big tech firms, it is causing an increased inequality in society, which may lead to feelings of alienation and unfairness.
Environmental costs
Digital economy does not always imply a ‘green solution.’ Data centres use electricity and cause CO2 emissions. In the US, data centres account for around two per cent of U.S. electricity use in 2014.
A bigger potential cost is how the digital economy encourages a ‘throw-away’ culture. E.g. the planned obsolescence of mobile phones and computers, encouraging consumers to buy new models, leading to greater use of raw materials.

Some Initiatives taken to digitize India
Infrastructure
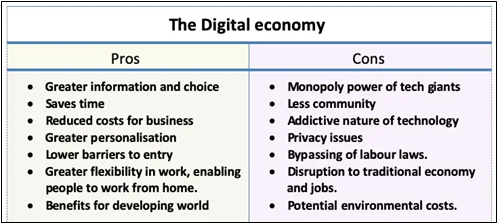
Under this initiative, the Government provides multiple programs that facilitate a reliable digital infrastructure. The following are some of the programs under this:
- AADHAR: One of the key strengths of ‘Digital India’, wherein every resident of the country is given a unique identity number.
- Bharat Broadband Network (BBNL): This is the custodian of Digital India. The creation of the National Optical Fiber Network (NOFN) has been mandated in India.
- Centre for Excellence for Internet of Things (CoE-IT): The main objective of the center is for creating domain capability and innovative applications.
- CERT-IN: This is formed with the intention to secure Indian cyberspace.
- Common Services Centres (CSCS): CSCs are the access points for the delivery of essential public utility services, healthcare, social welfare schemes, financial, education, and agriculture services.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: The purpose of this is to generate secure cyberspace by detecting botnet infections in India and to notify, enable cleaning, and secure systems of end-users so as to prevent further infections.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana : This is one of the flagship programs of the Power Ministry (MoP) and is designed to provide a continuous power supply to the entire rural India.
- DigiLocker : A digital wallet to empower citizens digitally.
- Digital Saksharta Abhiyaan (DISHA): This aims to provide IT training to 52.5. lakh persons.
- Digitize India Platform : This platform provides digitization of scanned document images or physical documents.
Under this initiative, the Government has introduced multiple online services to facilitate greater reach and accessibility:
- Accessible India Campaign and Mobile App : This nation-wide flagship campaign is for achieving universal accessibility for enabling people with disabilities to gain access to equal opportunity.
- Agrimarket App: This mobile application aims to keep farmers abreast with the crop prices and avoid distress sale.
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao: This aims to provide equal opportunity to a girl child, a chance to be born and be educated.
- BHIM (Bharat Interface For Money): This makes payment easy and quick using UPI.
- Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS): This aims for nationwide networking infrastructure for the evolution of an IT-enabled state-of-the-art tracking system around ‘Investigation of crime and detection of criminals.’
- Crop Insurance Mobile App: This app can be used to compute the insurance premium for notified crops based on the area of coverage, amount, and loan amount in the case of loanee farmers.
- Digital AIIMS: A distinctive health identification number for every patient visiting AIIMS was generated on an Aadhar platform.
- E-Granthalaya, E-Panchayat, E-Hospital, E-Pathshala, E- prison: All of these provide digitalization of services like libraries, hospitals, schools, and prisons.
Empowerment

Under this initiative, the Government provides e-governance, skill development, and infrastructure development initiatives:
- Aadhar Enabled Payment System (AEPS)
- Digidhan Abhiyaan
- National Mission on Education using ICT
- North East BPO Promotion Scheme (NEBPS)
- NREGA – Soft
- PayGov India
- Smart Cities
- Pradhan Mantri Jan- Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
- PAHAL (DBTL)
- Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS)
- Visvesvaraya PhD Scheme For Electronics and IT
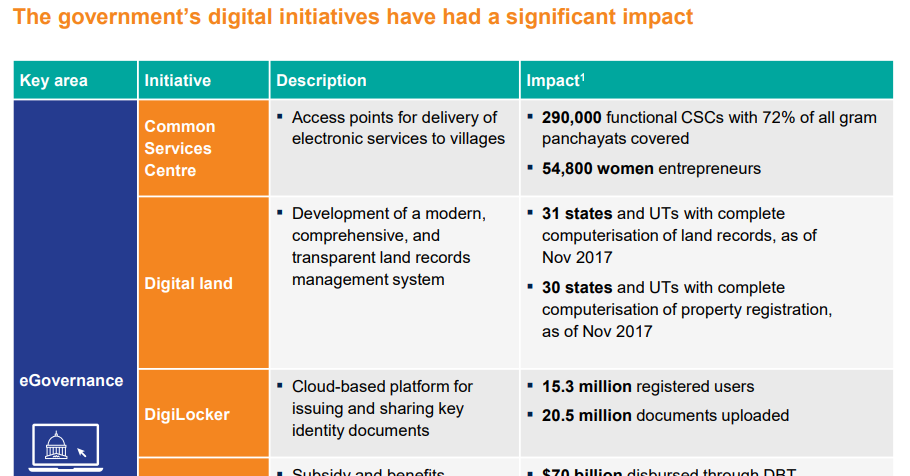
Significant achievements made by India in this field
SWOT Analysis of India in this field
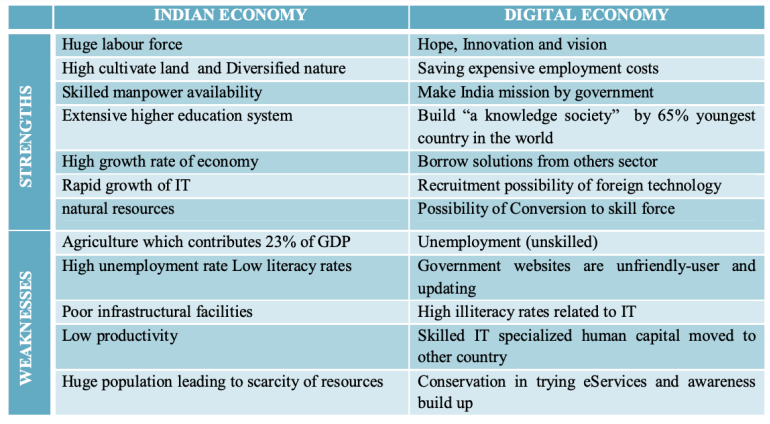
Future Potential

https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GP49V1KRL.1&imageview=0
1.png)
Related Articles

Free access to e-paper and WhatsApp updates

Let's Get In Touch!
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved

COMMENTS
The Significance and Increasing Scope of the Digital Economy: The digital economy is gaining prominence and impacting various aspects of economic activity globally. It emphasizes that the digital economy is no longer limited to a specific sector but is permeating every corner of the economy.
The digital economy, defined by the pervasive use of digital technologies to deliver goods and services, has revolutionised the global economic landscape. It offers transformative potential for innovation, productivity, and inclusivity.
A digital economy refers to an economy based on digital technologies connected through the internet. The different technologies and economic aspects of the digital economy can be broken down into three broad components: 1.
The "Digital Economy: A Leveller or a Source of Economic Inequality UPSC Questions" guide is a valuable resource for all aspiring students preparing for the UPSC exam. It focuses on providing a wide range of practice questions to help students gauge their understanding of the exam topics.
Initiatives such as the Digital India program, Pradhan Mantri Grameen Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDSA), and Unified Payments Interface (UPI), etc. have played a significant role in transforming India into a digitally empowered society and a major player in the digital economy.
The digital economy is the worldwide network of economic activities, commercial transactions and professional interactions that are enabled by information and communications technologies (ICT). It can be succinctly summed up as the economy based on digital technologies.
• India’s digital economy is poised to constitute one-fifth of the GDP by 2026 from one-tenth at present, according to a Reserve Bank’s ‘Report on Currency and Finance for the year 2023-24’. • Digitalisation is driving innovation and efficiency, fostering a new model of economic growth, and facilitating quality improvements.
India’s digital economy and the infrastructure sector has a total potential for $2.5 trillion; There are more than 100 unicorns in over 70,000 start-ups in India, and their number continues to grow. The value of the Indian digital economy will reach $1 trillion by 2025; Advantages of a Digital Economy
UPSC 2025: Mains Mentorship Program (MMP) IAS 2025: Focus - Prelims & Mains Test Series IAS 2025-26: Samarth - Mains Answer Writing
What is the digital economy? The digital economy refers to economic activity that uses electronic communication and digital technologies to provide goods and services. The main building blocks of the digital economy are. The internet. This enables firms to offer goods for sale and enables consumers to browse for goods that they need. E-mail.